
Installation
and
Maintenance
Manual
with Safety Information
and Parts List
RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS HIGHLIGHTED IN GRAY
IMPORTANT!
DO NOT DESTROY
¡IMPORTANTE!
NO DESTRUIR
Manual
de Instalación
y
Mantenimiento
con Información sobre Seguridad
y Lista de Piezas
REPUESTOS RECOMENDADOS DESTACADOS EN GRIS
Effective June 2018
Bulletin #679
Model DC62, DC63
Model DC82, DC83
HYTROL | Jonesboro, Arkansas
Copyright © 1947- 2018 – Hytrol. All rights reserved.

2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
Receiving and Uncrating ....................2
How to Order Replacement Parts .............2
SAFETY INFORMATION ................3
INSTALLATION
Location .................................4
Conveyor Set-Up..........................4
Racked Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Electrical Equipment .......................5
OPERATION
Conveyor Start-Up.........................5
MAINTENANCE
Lubrication ...............................5
Drive Chain Tension Adjustment............5, 6
Trouble Shooting ..........................6
Maintenance Checklist ............ Back Cover
REPLACEMENT PARTS
DC62 Parts Drawing & List ..................7
DC63 Parts Drawing & List ..................8
DC82 Parts Drawing & List ..................9
DC83 Parts Drawing & List .................10
Spanish Version .........................11
INTRODUCTION
This manual provides guidelines and procedures for installing,
operating, and maintaining your conveyor. A complete parts list
is provided with recommended spare parts highlighted in gray.
Important safety information is also provided throughout the manual.
For safety to personnel and for proper operation of your conveyor, it
is recommended that you read and follow the instructions provided
in this manual.
• Receiving and Uncrating
1. Check the number of items received against the bill of lading.
2. Examine condition of equipment to determine if any damage
occurred during shipment.
3. Move all crates to area of installation.
4. Remove crating and check for optional equipment that may be
fastened to the conveyor. Make sure these parts (or any foreign
pieces) are removed.
• How to Order Replacement Parts
Included in this manual are parts drawings with complete replacement
parts lists. Minor fasteners, such as nuts and bolts, are not
included.
When ordering replacement parts:
1. Contact Dealer from whom conveyor was purchased or nearest
HYTROL Integration Partner.
2. Give Conveyor Model Number and Serial Number or HYTROL
Factory Order Number.
3. Give Part Number and complete description from Parts List.
4. Give type of drive. Example—8” End Drive, 8” Center Drive, etc.
5. If you are in a breakdown situation, tell us.
HYTROL Serial Number
(Located near Drive on Powered Models).
NOTE: If damage has occurred or freight is missing,
Contact your Hytrol Integration Partner.
Jonesboro, Arkansas
Serial # 615415
Model
TA
QR Code
YEAR

3
SAFETY INFORMATION
• Installation
GUARDS AND GUARDING
Interfacing of Equipment. When two or more pieces of equipment are
interfaced, special attention shall be given to the interfaced area to
insure the presence of adequate guarding and safety devices.
Guarding Exceptions. Whenever conditions prevail that would
require guarding under these standards, but such guarding would
render the conveyor unusable, prominent warning means shall be
provided in the area or on the equipment in lieu of guarding.
Guarded by Location or Position. Where necessary for the
protection of employees from hazards, all exposed moving machinery
parts that present a hazard to employees at their work station shall
be mechanically or electrically guarded, or guarded by location or
position.
• Remoteness from frequent presence of public or employed
personnel shall constitute guarding by location.
• When a conveyor passes over a walkway, roadway, or work
station, it is considered guarded solely by location or position if all
moving parts are at least 8 ft. (2.44 m) above the oor or walking
surface or are otherwise located so that the employee cannot
inadvertently come in contact with hazardous moving parts.
• Although overhead conveyors may be guarded by location, spill
guards, pan guards, or equivalent shall be provided if the product
may fall off the conveyor for any reason and if personnel would
be endangered.
HEADROOM
• When conveyors are installed above exit passageways, aisles,
or corridors, there shall be provided a minimum clearance of 6
ft. 8 in. (2.032 m) measured vertically from the oor or walking
surface to the lowest part of the conveyor or guards.
• Where system function will be impaired by providing the minimum
clearance of 6 ft. 8 in. (2.032 m) through an emergency clearance,
alternate passageways shall be provided.
• It is permissible to allow passage under conveyors with less
than 6 ft. 8 in. (2.032 m) clearance from the oor for other than
emergency exits if a suitable warning indicates low headroom.
• Operation
A) Only trained employees shall be permitted to operate conveyors.
Training shall include instruction in operation under normal conditions
and emergency situations.
B) Where employee safety is dependent upon stopping and/or
starting devices, they shall be kept free of obstructions to permit
ready access.
C) The area around loading and unloading points shall be kept clear
of obstructions which could endanger personnel.
D) No person shall ride the load-carrying element of a conveyor
under any circumstances unless that person is specically authorized
by the owner or employer to do so. Under those circumstances, such
employee shall only ride a conveyor which incorporates within its
supporting structure platforms or control stations specically designed
for carrying personnel. Under no circumstances shall any person ride
on any element of a vertical conveyor.
E) Personnel working on or near a conveyor shall be instructed as to
the location and operation of pertinent stopping devices.
F) A conveyor shall be used to transport only material it is capable
of handling safely.
G) Under no circumstances shall the safety characteristics of the
conveyor be altered if such alterations would endanger personnel.
H) Routine inspections and preventive and corrective maintenance
programs shall be conducted to insure that all safety features and
devices are retained and function properly.
I) Personnel should be alerted to the potential hazard of entanglement
in conveyors caused by items such as long hair, loose clothing, and
jewelry.
J) Conveyors shall not be maintained or serviced while in operation
unless proper maintenance or service requires the conveyor to be in
motion. In this case, personnel shall be made aware of the hazards
and how the task may be safely accomplished.
K) Owners of conveyor should insure proper safety labels are afxed
to the conveyor warning of particular hazards involved in operation of
their conveyors.
• Maintenance
• All maintenance, including lubrication and adjustments, shall be
performed only by qualied and trained personnel.
• It is important that a maintenance program be established to
insure that all conveyor components are maintained in a condition
which does not constitute a hazard to personnel.
• When a conveyor is stopped for maintenance purposes, starting
devices or powered accessories shall be locked or tagged out
in accordance with a formalized procedure designed to protect
all persons or groups involved with the conveyor against an
unexpected start.
• Replace all safety devices and guards before starting equipment
for normal operation.
• Whenever practical, DO NOT lubricate conveyors while they are
in motion. Only trained personnel who are aware of the hazard
of the conveyor in motion shall be allowed to lubricate.
Safety Guards
Maintain all guards and safety devices IN POSITION and IN SAFE
REPAIR.
Safety Labels
In an effort to reduce the possibility of injury to personnel working
around HYTROL conveying equipment, safety labels are placed at
various points on the equipment to alert them of potential hazards.
Please check equipment and note all safety labels. Make certain
your personnel are alerted to and obey these warnings. See Safety
Manual for examples of warning labels.
CAUTION! Because of the many moving parts on the conveyor, all personnel
in the area of the conveyor need to be warned that the conveyor is about to
be started.
REMEMBER Do not remove, reuse or modify material handling equipment
for any purpose other than it’s original intended use.

4
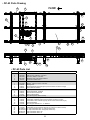
SIDE CHANNEL
(CANAL LATERAL)
A1
A2
B2
B1
PREFERRED FLOW
(FLUJO PREFERIDO)
12" OPEN TAIL
(EXTREMO ABIERTO 12")
INTERMEDIATE MODULE
(MODULO INTERMEDIO)
DRIVE MODULE
(MODULO MOTRIZ)
INTERMEDIATE MODULE
(MODULO INTERMEDIO)
12" OPEN TAIL
(EXTREMO ABIERTO 12")
FIGURE 4A
“MATCH-MARK” NUMBERS
(NÚMEROS DE “MARCA DE REFERENCIA”)
FO:
MARK:
TOOL BOX
QR
CODE
H
Y
T
R
O
L
C
O
D
E
MODEL
A
FO:
MARK:
TOOL BOX
QR
CODE
H
Y
T
R
O
L
C
O
D
E
MODEL
A
WEARSTRIP
CHAIN
1/2
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
SUPPORT
WELDMENT
5/8-11 HEX JAM NUT
FOOT PAD
(GUIAS DE CADENA)
(CADENA)
(CONTRATUERCA HEX 5/8-11)
(PIE DE SOPORTE)
(SOPORTE)
DCDS–04 THRU –10
DCDS–03
DCDS–02
17" - 31"
12"
5" - 19"
4" - 16"
2 5/8"
1" MIN
3" MAX
1" MIN
3" MAX
1" MIN
3" MAX
15" - 17"
12"
12"
3" - 5"
2"
13" - 15"
1" - 3"
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
FIGURE 4B
FIGURE 4C
• Location
1. Refer to building layout for
obstructions such as machines,
columns, walls, openings, etc.
Check to see that conveyor layout
drawings correspond with building
layout.
2. Determine direction of product
flow. Figure 4A indicates the flow
as related to the drive.
3. Refer to “Match-Mark” numbers
on ends of conveyor sections
(Figure 4A). Position them in this
sequence near area of installation.
• Conveyor Set- Up
1. Mark a chalk line on floor to
locate centerline of the conveyor.
2. Attach open tail to infeed and
discharge sections, if not already
attached, and place in position.
3. Place remaining sections on
extended support of previous
section. (see Fig. 4B for
Intermediate supports and Fig. 4C
for drive support.)
4. Fasten sections together at coupling channels and support frames (Fig.
4B). Hand tighten bolts at this time.
5. Check to see that conveyor is level across width and length of unit.
Adjust foot pads as necessary.
6. Tighten all coupling channels and support frame bolts as necessary.
7. Check for proper alignment of chain guide wearstrips. Install drag
chains using connector links provided. NOTE: Drag chain tension has
been pre-determined at the factory. Refer to “Maintenance” section for
periodic chain tension adjustment procedures.
INSTALLATION
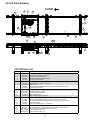
• Racked Sections
It is important that each bed section be checked for an out-of-square condition. If
conveyor is not square, tracking problems will result. Figure 4D indicates a racked
section.
TO CORRECT AN OUT-OF-SQUARE SECTION
1. Locate points on corners of section and measure distance “A” & “B”. If the
dimensions are not equal, the section will need to be squared. (Figure 4D).
2. After all bed sections have been checked and corrected for “racked condition”,
tighten all coupling channels and support frame bolts.
3. Make final check to see that all conveyor sections are level across width and
length. If entire conveyor is level, supports can be lagged to floor.
“Racked” conveyor sections will cause product to travel toward side of conveyor.
IMPORTANT! Being out of level across this width of
conveyor can cause product drift on long conveyor lines.
FIGURE 4D

5
Ambient Temperature
Degrees F
SAE ISO
20-40
40-100
100-120
20
30
40
46 or 68
100
150
CAUTION! Because of the many moving parts on the conveyor, all personnel in the
area of the conveyor need to be warned that the conveyor is about to be started.
WARNING! Electrical controls shall be installed and wired by a qualied electrician. Wiring
information for the motor and controls are furnished by the equipment manufacturer.
• Electrical Equipment
CONTROLS
Electrical Code: All motor controls and wiring shall conform to the National
Electrical Code (Article 670 or other applicable articles) as published by the
National Fire Protection Association and as approved by the American Standards
Institute, Inc.
CONTROL STATIONS
A) Control stations should be so arranged and located that the operation of the
equipment is visible from them, and shall be clearly marked or labeled to indicate
the function controlled.
B) A conveyor which would cause injury when started shall not be started until
employees in the area are alerted by a signal or by a designated person that the
conveyor is about to start.
When a conveyor would cause injury when started and is automatically
controlled or must be controlled from a remote location, an audible device shall
be provided which can be clearly heard at all points along the conveyor where
personnel may be present. The warning device shall be actuated by the controller
device starting the conveyor and shall continue for a required period of time
before the conveyor starts. A flashing light or similar visual warning may be used
in conjunction with or in place of the audible device if more effective in particular
circumstances.
Where system function would be seriously hindered or adversely affected by
the required time delay or where the intent of the warning may be misinterpreted
(i.e., a work area with many different conveyors and allied devices), clear, concise,
and legible warning shall be provided. The warning shall indicate that conveyors
and allied equipment may be started at any time, that danger exists, and that
personnel must keep clear. The warnings shall be provided along the conveyor at
areas not guarded by position or location.
C) Remotely and automatically controlled conveyors, and conveyors where
operator stations are not manned or are beyond voice and visual contact from drive
areas, loading areas, transfer points, and other potentially hazardous locations on
the conveyor path not guarded by location, position, or guards, shall be furnished
with emergency stop buttons, pull cords, limit switches, or similar emergency stop
devices.
All such emergency stop devices shall be easily identifiable in the immediate
vicinity of such locations unless guarded by location, position, or guards. Where
the design, function, and operation of such conveyor clearly is not hazardous to
personnel, an emergency stop device is not required.
The emergency stop device shall act directly on the control of the conveyor
concerned and shall not depend on the stopping of any other equipment. The
emergency stop devices shall be installed so that they cannot be overridden from
other locations.
D) Inactive and unused actuators, controllers, and wiring should be removed from
control stations and panel boards, together with obsolete diagrams, indicators,
control labels, and other material which serve to confuse the operator.
SAFETY DEVICES
A) All safety devices, including wiring of electrical safety devices, shall be
arranged to operate in a “Fail-Safe” manner, that is, if power failure or failure of the
device itself would occur, a hazardous condition must not result.
B) Emergency Stops and Restarts. Conveyor controls shall be so arranged
that, in case of emergency stop, manual reset or start at the location where the
emergency stop was initiated, shall be required of the conveyor(s) and associated
equipment to resume operation.
C) Before restarting a conveyor which has been stopped because of an
emergency, an inspection of the conveyor shall be made and the cause of the
stoppage determined. The starting device shall be locked out before any attempt
is made to remove the cause of stoppage, unless operation is necessary to
determine the cause or to safely remove the stoppage.
Refer to ANSI Z244.1-1982, American National Standard for Personnel Protection
– Lockout/Tagout of Energy Sources – Minimum Safety Requirements and OSHA
Standard Number 29 CFR 1910.147 “The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/
Tagout).”
OPERATION
• Conveyor Start-Up
Before conveyor is turned on, check for foreign objects that may have been left
inside the conveyor during installation. These objects could cause serious damage
during start-up.
After conveyor has been turned on and is operating, check motors, reducers, and
moving parts to make sure they are working freely.
MAINTENANCE
• Lubrication
The drive chain is pre-lubricated from the manufacturer by a hot dipping process that
ensures total lubrication of all components. However, continued proper lubrication will
greatly extend the useful life of every drive chain.
Drive Chain lubrication serves several purposes including:
• Protecting against wear of the pin-bushing joint
• Lubricating chain-sprocket contact surfaces
• Preventing rust or corrosion
For normal operating
environments, lubricate every
2080 hours of operation or
every 6 months, whichever
comes first. Lubricate with a
good grade of non-detergent
petroleum or synthetic lubricant (i.e., Mobile 1 Synthetic). For best results, always
use a brush to generously lubricate the chain. The proper viscosity of lubricant greatly
affects its ability to flow into the internal areas of the chain. Refer to the table above
for the proper viscosity of lubricant for your application.
The drive chain’s lubrication requirement is greatly affected by the operating
conditions. For harsh conditions such as damp environments, dusty environments,
excessive speeds, or elevated temperatures, it is best to lubricate more frequently. It
may be best, under these conditions, to develop a custom lubrication schedule for your
specific application. A custom lubrication schedule may be developed by inspecting the
drive chain on regular time intervals for sufficient lubrication. Once the time interval is
determined at which the chain is not sufficiently lubricated, lubricate it and schedule the
future lubrication intervals accordingly.
• Trouble Shooting
The following chart list possible problems that may occur in the operation of a powered conveyor.
TROUBLE SHOOTING DRIVES
TROUBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Conveyor will not start or
motor quits frequently.
1) Motor is overloaded or is drawing too much current. 1) Check for overloading of conveyor.
2) Check heater or circuit breaker and change if necessary.
Drag chain and sprockets
wear excessively.
1) Lack of lubrication on chain may have caused chain to
stretch and create an improper chain to sprocket mesh.
2) Sprockets are out of alignment.
3) Loose chain.
1) Replace chain and sprockets. NOTE: If problem reoccurs, a chain take-up may be
required.
2) Align drive sprockets with fixed idlers.
3) Tighten chain.
Loud popping or grinding
noise.
1) Defective bearing.
2) Loose set screws in bearing.
3) Loose drive chain.
1) Replace bearing.
2) Tighten set screw.
3) Tighten chain.
Motor or reducer
overheating.
1) Conveyor is overloaded.
2) Low voltage to motor.
3) Low lubricant level in reducer.
1) Check capacity of conveyor and reduce load to recommended level.
2) Have electrician check and correct as necessary.
3) Relubricate per manufacturer’s recommendations. For HYTROL reducer, refer to
separate manual.

6
A
A
SECTION A-A
DRIVE SPROCKET
(CATRINA MOTRIZ)
TAKE UP SPROCKET
(CATARINA DEL TENSOR)
TAKE UP PLATE
(PLACA DEL TENSOR)
TAKE UP JACKBOLT
(TORNILLO TENSOR)
FIXED IDLER
(RODILLOS DE ALINEACION FIJOS)
A
A
SECTION A-A
CAUTION! NEVER remove chain guards while the conveyor is running.
Always replace guards after adjustments are made.
DISTANCE BETWEEN SPROCKETS
(DISTANCIA ENTRE PINONES)
HALFWAY
(A LA MITAD)
SLACK 2% OF DISTANCE
BETWEEN SPROCKETS
(FLOJAR 2% DISTANCIA
ENTRE PINONES)
FIGURE 6A
• Drag Chain Tension Adjustment
NOTE: Chain tension should be pre-set at factory. However, during normal
operation, chain may stretch enough to require adjustment.
1. Remove chain guard.
2. To adjust chain tension, loosen four (4) bolts that fasten take-up plate to
drive frame. Tighten take-up bolts until desired tension is reached. (Fig.
6A.) Lift the chain half way between tail sprockets and measure the gap.
It should be 2% of the distance between tail sprockets. (Figure 6B). Make
sure both sides are adjusted the same amount. Re-tighten mounting bolts.
3. Lubricate chain per lubrication instructions.
4. Replace chain guard.
FIGURE 6B

7
• DC-62 Parts List
REF NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
055.09745
028.6385
028.2003
029.1025
029.213
Eurodrive Gearmotor - 1-1/2 HP, 230/460/3/60
Idler Sprocket - 60B15H x .515" Bore
Sprocket - 60B15 x 1-3/8" Bore
#60 Roller Chain with Straight Sidebars
Connector Link #60 Chain
6
7
8
9
10
090.2037
010.2028
B-23697
B-22817
B-22516
Shaft Key - 5/16" SQ. x 1" LG.
Bearing - Cast Iron, 4-Bolt, 1-3/8" Bore
Bearing Plate
Drive/Tail Module Tread Plate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Spacer Plate for Gearbox
11
12
13
14
15
099.456
B-22513
B-22512
B-22511
B-22510
Wearstrip - #60 Chain Guide
Strand Guard Weld - Outboard
Sprocket Tension Plate Weld
Take-Up Bracket Weld
Drive Shaft (Specify Strand Centers)
16
17
18
19
20
B-22509
B-22818
B-22562
B-12672
B-19000
Drive Frame Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Intermediate Treadplate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Intermediate Frame Weldment (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Foot Pad Assembly
Drive Support Weldment 15" - 17" Elevation
21
22
23
24
25
B-22819
B-22820
B-22522
B-22532-R
B-22532-L
Drive Support Weldment 17" - 31" Elevation (Specify Elevation and Outside Strand Centers)
Intermediate Support Weldment (Specify Top of Chain and Strand Centers)
12" Open Tail Module Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - RH
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - LH
9
8
10
1
7
15
3
6
12
11
24
23
25
18
17
13
2
16
14
20
21
19
22
2
4
5
FLOW
• DC-62 Parts Drawing

8
• DC-63 Parts List
REF NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
055.09745
028.6385
028.2003
029.1025
029.213
Eurodrive Gearmotor - 1-1/2 HP, 230/460/3/60
Idler Sprocket - 60B15H x .515" Bore
Sprocket - 60B15 x 1-3/8" Bore
#60 Roller Chain with Straight Sidebars
Connector Link #60 Chain
6
7
8
9
10
090.2037
010.2028
B-23697
B-22817
B-22516
Shaft Key - 5/16" SQ. x 1" LG.
Bearing - Cast Iron, 4-Bolt, 1-3/8" Bore
Bearing Plate
Drive/Tail Module Tread Plate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Spacer Plate for Gearbox
11
12
13
14
15
099.456
B-22513
B-22512
B-22511
PT-014051
Wearstrip - #60 Chain Guide
Strand Guard Weld - Outboard
Sprocket Tension Plate Weld
Take-Up Bracket Weld
Drive Shaft (Specify Strand Centers)
16
17
18
19
20
WA-006255
B-22818
B-25644
B-12672
B-19000
Drive Frame Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Intermediate Treadplate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Intermediate Frame Weldment (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Foot Pad Assembly
Drive Support Weldment 15" - 17" Elevation
21
22
23
24
25
26
B-22819
W-02028
WA-008500-L
WA-008500-R
B-22532-R
B-22532-L
Drive Support Weldment 17" - 31" Elevation (Specify Elevation and Outside Strand Centers)
Intermediate Support Weldment (Specify Top of Chain and Strand Centers)
12" Open Tail Module Weld - LH (Specify Strand Ctrs)
12" Open Tail Module Weld - RH (Specify Strand Ctrs)
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - RH
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - LH
9
8
15
24
7
10
3 6
1
12
11
17
18
11
26
23
26
25
13
2
16
14
20
21
19
22
4
5
2
FLOW
• DC-63 Parts Drawing

9
9
8
10
1
7
15
3
6
12
11
24
23
25
18
17
13
2
16
14
20
21
19
22
2
4
5
FLOW
• DC-82 Parts Drawing
• DC-82 Parts List
REF NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
911.0205
028.6365
028.3043
029.1035
029.214
Eurodrive Gearmotor - 2 HP, 230/460/3/60
Idler Sprocket - 80B15H x .750" Bore
Sprocket - 80B15 x 1-1/2" Bore
#80 Roller Chain with Straight Sidebars
Connector Link #80 Chain
6
7
8
9
10
090.204
010.2041
PT-031822
B-25631
PT-043649
Shaft Key - 3/8" SQ. x 1" LG.
Bearing - Cast Iron, 4-Bolt, 1-1/2" Bore
Bearing Plate
Drive/Tail Module Tread Plate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Spacer Plate for Gearbox
11
12
13
14
15
099.457
WA-011860
WA-011833
WA-000478
PT-063273
Wearstrip - #80 Chain Guide
Strand Guard Weld - Outboard
Sprocket Tension Plate Weld
Take-Up Bracket Weld
Drive Shaft (Specify Strand Centers)
16
17
18
19
20
WA-011816
PT-110884
B-22562
B-12672
B-19000
Drive Frame Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Intermediate Treadplate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Intermediate Frame Weldment (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Foot Pad Assembly
Drive Support Weldment 15" - 17" Elevation
21
22
23
24
25
B-22819
W-02821
WA-032892
WA-011366-R
WA-011366-L
Drive Support Weldment 17" - 31" Elevation (Specify Elevation and Outside Strand Centers)
Intermediate Support Weldment (Specify Top of Chain and Strand Centers)
12" Open Tail Module Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - RH
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - LH

10
REF NO. PART NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
911.0205
028.6365
028.3043
029.1035
029.214
Eurodrive Gearmotor - 2 HP, 230/460/3/60
Idler Sprocket - 80B15H x .750" Bore
Sprocket - 80B15 x 1-1/2" Bore
#80 Roller Chain with Straight Sidebars
Connector Link #80 Chain
6
7
8
9
10
090.204
010.2041
B-031822
B-25631
PT-043649
Shaft Key - 3/8" SQ. x 1" LG.
Bearing - Cast Iron, 4-Bolt, 1-1/2" Bore
Bearing Plate
Drive/Tail Module Tread Plate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Spacer Plate for Gearbox
11
12
13
14
15
099.457
B-011860
WA-011833
WA-000478
PT-101876
Wearstrip - #80 Chain Guide
Strand Guard Weld - Outboard
Sprocket Tension Plate Weld
Take-Up Bracket Weld
Drive Shaft (Specify Strand Centers)
16
17
18
19
20
WA-032889
PT-110884
W-02818
B-12672
B-19000
Drive Frame Weld (Specify Strand Centers)
Intermediate Treadplate (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Intermediate Frame Weldment (Specify Strand Centers and Section Length)
Foot Pad Assembly
Drive Support Weldment 15" - 17" Elevation
21
22
23
24
25
26
B-22819
W-02824
WA-032894-L
WA-032894-R
WA-011366-R
WA-011366-L
Drive Support Weldment 17" - 31" Elevation (Specify Elevation and Outside Strand Centers)
Intermediate Support Weldment (Specify Top of Chain and Strand Centers)
12" Open Tail Module Weld - LH (Specify Strand Ctrs)
12" Open Tail Module Weld - RH (Specify Strand Ctrs)
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - RH
Open Tail Stiffener Weld - LH
• DC-83 Parts List
9
8
15
24
7
10
3 6
1
12
11
17
18
11
26
23
26
25
13
2
16
14
20
21
19
22
4
5
2
FLOW
• DC-83 Parts Drawing

11
ÍNDICE
INTRODUCCIÓN
Recepción y Desembalaje...................................11
Cómo Ordenar Refaccionamiento ............................11
INFORMACIÓN DE SEGURIDAD ...................................11
INSTALACIÓN
Instalación de los Soportes. .................................12
Montaje del Transportador ..................................12
Secciones Descuadradas ...................................12
Equipo Eléctrico........................................12, 13
OPERACIÓN
Arranque del Transportador .................................13
MANTENIMIENTO
Lubricación ..............................................13
Resolviendo Problemas.....................................13
Ajuste de la tensión de la cadena Motorizada ...................14
Lista del Plan de Mantenimiento ............... Cubierta Posterior
PARTES DE REPUESTO
Dibujo y Lista de Partes del DC-62 ...........................7
Dibujo y Lista de Partes del DC-63 ...........................8
Dibujo y Lista de Partes del DC-82 ...........................9
Dibujo y Lista de Partes del DC-83 ..........................10
INTRODUCCIÓN
Este manual proporciona información para instalar, operar y dar mantenimiento a su
transportador. Se proporciona una lista completa de partes, con el refaccionamiento
recomendado resaltado en gris. También se proporciona información importante de
seguridad a lo largo de este manual. Para seguridad del personal y para un mejor
funcionamiento del transportador, se recomienda que se lean y se sigan cada una de las
instrucciones proporcionadas en este manual.
• Recepción y Desembalaje
1. Verique el número de partes recibidas con respecto al conocimiento del embarque.
2. Examine las condiciones del equipo para determinar si algún daño ha ocurrido durante
el transporte.
3. Traslade todo el equipo al área de instalación.
4. Remueva todos los empaques y verique si hay partes adicionales que puedan estar
sujetas al equipo. Asegúrese de que estas partes (u otras partes ajenas al equipo) sean
removidas.
• Cómo Ordenar Refaccionamiento
En este manual encontrará dibujos de las partes con listas completas de las
refacciones. Partes pequeñas, como tornillos y tuercas no están incluidos. Para ordenar
refaccionamiento:
1. Contacte al representante que le vendió el transportador o el distribuidor de Hytrol
más cercano.
2. Proporcione el Modelo del Transportador y el Número de Serie o Número
de la Orden de Fabricación.
3. Proporcione el Número de las partes y descripción completa que aparece
en la Lista de Partes.
4. Proporcione el tipo de motor. Ejemplo- Unidad Motriz en Extremo Final de 8”, Unidad
Motriz Central de 8”, etc.
5. Si su equipo se encuentra en una situación crítica, comuníquese con nosotros
inmediatamente.
NOTA: Si algún daño ha ocurrido o faltan partes, contacte a su integrador Hytrol
INFORMACIÓN DE SEGURIDAD
• Instalación
PROTECCIÓN Y SEGURIDAD
Interfaz de los equipos. Cuando dos o más piezas de equipo son interconectadas, se
deberá prestar especial atención a la zona de la interfaz para asegurar la presencia de
guardas y dispositivos de seguridad adecuados.
Localización o posición. Para procurar la protección de los trabajadores ante los riesgos,
todas las partes móviles expuestas de la maquinaria deberán ser aseguradas mecánica
o eléctricamente, o protegidas mediante el cambio de localización o posición.
La presencia alejada del público o empleado constituirá una medida de seguridad por
ubicación.
Cuando el transportador esté instalado sobre pasillos, corredores o estaciones de
trabajo; se considera protegido únicamente por localización o posición si todas las partes
en movimiento están mínimo a 8 pies (2,44 m) por encima del piso o área de tránsito. De
otra manera se pueden ubicar de tal manera que los empleados no entren en contacto
con partes móviles peligrosas sin querer.
Aunque los transportadores aéreos pueden estar protegidos por su ubicación, deben
proporcionarse guardas para evitar derrames: guardas laterales e inferiores; Esto si el
producto pued e caerse del transportador y así mantener al personal fuera de peligro.
ESPACIO LIBRE SUPERIOR
Cuando los transportadores son instalados sobre pasillos, salidas o corredores; se
deberá disponer de un espacio libre mínimo de 6 pies 8 pulgadas (2,032 m), medido
verticalmente desde el suelo o mezanine a la parte más baja del transportador o de las
guardas
Cuando el funcionamiento del sistema sea afectado al guardar la distancia mínima de 6
pies 8 pulgadas (2,032 m), deberán autorizarse pasillos alternos de emergencia.
Es posible permitir el paso bajo transportadores con menos de 6 pies 8 pulgadas (2.032
m) desde el piso, con excepción de las salidas de emergencia. Para esto se requiere una
señalización apropiada que indique altura baja.
• Operación
A) Sólo los empleados capacitados están autorizados a operar los transportadores. El
entrenamiento debe incluir: operación bajo condiciones normales y en situaciones de
emergencia.
B) Cuando la seguridad de los trabajadores dependa de dispositivos de paro y/o
arranque, tales dispositivos deben mantenerse libres de obstrucciones para permitir un
acceso rápido.
C) El área alrededor de los puntos de carga y descarga deberá mantenerse libre de
obstrucciones que puedan poner en peligro al personal.
D) Ninguna persona podrá viajar en el elemento de carga de un transportador sin
excepción; al menos que esta persona esté especícamente autorizado por el propietario
o el empleador. En esas circunstancias, el empleado deberá montarse solamente en
un transportador que tenga incorporado en sus plataformas de estructura de soporte o
estaciones de control especialmente diseñadas para el transporte de personal. Esto no
es permisible en un transportador vertical.
E) El personal que trabaja con un transportador, o cerca de uno; debe ser noticado de
la ubicación y operación de los dispositivos de paro pertinentes.
F) Un transportador debe ser usado únicamente para transportar el material que es
capaz de cargar.
G) Las indicaciones de seguridad del transportador no deben ser alteradas bajo ninguna
circunstancia, especialmente si esto pone en peligro al personal.
H) Las Inspecciones de rutina, así como el mantenimiento correctivo y preventivo deben
ser llevados a cabo de modo que todos los dispositivos e indicaciones de seguridad sean
respetados y funcionen adecuadamente.
I) El personal debe ser noticado del peligro potencial que puede ser causado en los
transportadores debido al uso de cabello largo, ropa holgada y joyería.
J) Nunca se debe dar mantenimiento o servicio a un transportador mientras se encuentre
en operación, a menos que el mantenimiento o servicio apropiado lo requiera. En este
caso, el personal debe ser noticado del peligro que esto representa y de cómo se puede
llevar a cabo el procedimiento de la manera más segura.
K) Los dueños de los transportadores deben asegurarse de que las etiquetas de
seguridad se encuentren colocadas sobre el transportador, indicando los peligros que
implica la operación de sus equipos.
• Mantenimiento
Todo mantenimiento, incluyendo lubricación y ajustes, debe ser llevado a cabo
únicamente por personal entrenado y calicado.
Es importante que el programa de mantenimiento establecido asegure que todos los
componentes del transportador reciban el mantenimiento en condiciones que no
constituyan un peligro para el personal.
Cuando un transportador es detenido para propósitos de mantenimiento, los dispositivos
de arranque y de potencia deben ser asegurados o etiquetados de acuerdo a un
procedimiento formalizado diseñado para proteger a todas las personas o grupos que
trabajan con el transportador en caso de que ocurra algún arranque inesperado.
Verique todos los dispositivos y guardas de seguridad antes de arrancar el equipo para
una operación normal.
Aunque parezca práctico, nunca lubrique los transportadores mientras se encuentren en
movimiento. Sólo el personal capacitado que conoce de los peligros de un transportador
en movimiento puede realizar la lubricación.
Guardas de seguridad
Mantenga todas las guardas y dispositivos de seguridad en su posición y en buenas
condiciones.
Etiquetas de seguridad
Etiquetas de seguridad han sido ubicadas en diferentes puntos del equipo para alertar
de los peligros potenciales existentes; esto en un esfuerzo por reducir la posibilidad de
lesiones en el personal que trabaja alrededor de un transportador HYTROL. Por favor,
revise el equipo e identique todas las etiquetas de seguridad. Asegúrese de que el
personal conozca y obedezca estas advertencias. Reérase al manual de seguridad
para ver ejemplos de etiquetas de advertencias.
Jonesboro, Arkansas
Serial # 615415
Model
TA
QR Code
YEAR
¡RECUERDE! No remueva, reúse o modique el material que incluye el equipo
para ningún propósito que no sea para el que fueron diseñados originalmente.
¡PRECAUCIÓN! Debido a que el transportador contiene muchas partes en
movimiento, todo el personal que se encuentra en el área debe ser noticado
cuando el equipo esté a punto de arrancar.

12
SIDE CHANNEL
(CANAL LATERAL)
A1
A2
B2
B1
PREFERRED FLOW
(FLUJO PREFERIDO)
12" OPEN TAIL
(EXTREMO ABIERTO 12")
INTERMEDIATE MODULE
(MODULO INTERMEDIO)
DRIVE MODULE
(MODULO MOTRIZ)
INTERMEDIATE MODULE
(MODULO INTERMEDIO)
12" OPEN TAIL
(EXTREMO ABIERTO 12")
FIGURE 4A
“MATCH-MARK” NUMBERS
(NÚMEROS DE “MARCA DE REFERENCIA”)
FO:
MARK:
TOOL BOX
QR
CODE
H
Y
T
R
O
L
C
O
D
E
MODEL
A
FO:
MARK:
TOOL BOX
QR
CODE
H
Y
T
R
O
L
C
O
D
E
MODEL
A
WEARSTRIP
CHAIN
1/2
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
SUPPORT
WELDMENT
5/8-11 HEX JAM NUT
FOOT PAD
(GUIAS DE CADENA)
(CADENA)
(CONTRATUERCA HEX 5/8-11)
(PIE DE SOPORTE)
(SOPORTE)
DCDS–04 THRU –10
DCDS–03
DCDS–02
17" - 31"
12"
5" - 19"
4" - 16"
2 5/8"
1" MIN
3" MAX
1" MIN
3" MAX
1" MIN
3" MAX
15" - 17"
12"
12"
3" - 5"
2"
13" - 15"
1" - 3"
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
TOP OF CHAIN
(TOPE DE CADENA)
FIGURE 12B
FIGURE 12C
• Localización
1. Refiérase a la disposición del
edificio para evitar obstrucciones
tales como maquinaria, columnas,
paredes, etc. Revise que el diseño
del sistema de transportación
corresponda con el plano del
edificio.
2. Determine la dirección o flujo del
producto. La Figura 6A indica el flujo
con respecto a la unidad motriz.
3. Refiérase a los números de
Secuencia de Armado en los
extremos de las secciones del
transportador (Figura 12A).
Colóquelas en esta secuencia cerca
al área de instalación.
INSTALACION
• Secciones Descuadradas
Es importante revisar que las secciones estén encuadradas. Si el transportador no está
encuadrado, pueden presentarse problemas de alineación. La Figura 12D muestra una
sección descuadrada.
PARA CORREGIR UNA SECCION DESCUADRADA
1. Localice puntos en las esquinas de la sección y mida la distancia “A” y “B”. Si las
dimensiones no son iguales, la sección necesitará ser ajustada (Figura 12D).
2. Después de que todas las secciones hayan sido verificadas y corregidas, apriete
todos los tornillos de las placas de unión y de la base superior del soporte.
3. Haga un chequeo final para verificar que todas las secciones del transportador estén
niveladas a lo ancho y a lo largo. Si todo el transportador está nivelado, los soportes
pueden ser anclados al suelo.
• Equipo Eléctrico
CONTROLES
Código Eléctrico: Todos los controles del motor y las conexiones deben ajustarse al
Código Nacional de Electricidad, (Artículo 670 u otros artículos aplicables) como fue
¡IMPORTANTE! El transportador desnivelado a lo ancho puede causar
el amontonamiento de las cajas en líneas largas de transportadores.
FIGURE 12D
¡PRECAUCIÓN! Debido a la cantidad de partes en movimiento del transportador,
todo el personal en el área debe ser notificado cuando el transportador sea puesto
en marcha.
• Montaje
1. Marque con tiza una línea en
el suelo para ubicar el centro del
transportador.
2. Conecte el extremo abierto a las
secciones de carga y descarga si es
que no se encuentran ya conectadas,
y coloque en posición.
3. Coloque las secciones restantes
en el soporte extendido de la sección
anterior. (Ver Fig. 12B para soportes intermedios y Fig. 12C para soporte de
sección motriz).
4. Asegure las secciones en canales de empalme con marcos de soporte (Fig.
12B). Apriete los tornillos manualmente.
5. Revise si el transportador está nivelado a lo ancho y largo de la unidad.
Ajuste los pies de soporte como sea necesario.
6. Apriete los tornillos en canales de empalme con marcos de soporte como
sea necesario.
7. Revise la alineación apropiada de las guías de cadena. Instale las cadenas
usando los conectores proporcionados. NOTE: La tensión de la cadena ha sido
predeterminada en la fábrica. Refiérase a la sección de “Mantenimiento” para
determinar el procedimiento periódico de ajuste de tensión de la cadena.
FIGURE 12A

13
Temperatura Ambiente
(Grados F°) (Grados C°)
SAE ISO
20 - 40
40 - 100
100 - 120
-07 - 04
04 - 38
38 - 49
20
30
40
46 or 68
100
150
¡PRECAUCION! Debido a la cantidad de partes en movimiento en el transportador,
todo el personal en el área del transportador necesita ser advertido de que este
está a punto de ponerse en marcha.
publicado por la Asociación Nacional de Protección Contra Incendios, y aprobado por el
Instituto de Estándares Americanos.
ESTACIONES DE CONTROL
A) Las estaciones de control deberán estar ordenadas y ubicadas en lugares donde
el funcionamiento del equipo sea visible y deberán estar claramente marcadas o
señalizadas para indicar la función controlada.
B) Un transportador que pueda causar lesiones cuando sea puesto en marcha, no
deberá ponerse en funcionamiento hasta que los trabajadores en el área sean alertados
por una señal o por una persona designada.
Cuando un transportador pueda causar lesiones al momento de arranque y
es controlado automáticamente, o es controlado desde una ubicación lejana; se deberá
proporcionar un dispositivo sonoro el cual pueda ser escuchado claramente en todos los
puntos a lo largo del transportador donde el personal pueda estar presente. El dispositivo
de advertencia deberá ser activado por el dispositivo de arranque del transportador y
deberá continuar sonando por un determinado periodo de tiempo previo al arranque del
transportador. Si es más efectivo y de acuerdo a las circunstancias se puede utilizar una
luz intermitente o una advertencia visual similar, en lugar del dispositivo sonoro.
Cuando el funcionamiento del sistema pueda ser seriamente obstruido
o adversamente afectado por el tiempo de retardo requerido, o cuando el intento de
advertencia pueda ser mal interpretado (ej., un área de trabajo con diversas líneas de
transportadores y los dispositivos de advertencia relacionados), advertencias claras,
concisas y legibles deben ser proporcionadas. Las advertencias deben indicar que los
transportadores y los equipos relacionados pueden ser puestos en marcha en cualquier
momento, que existe un peligro y que el personal debe mantenerse alejado. Estas
advertencias deben ser proporcionadas a lo largo del transportador en áreas que no
sean protegidas por la posición o la ubicación.
C) Los transportadores controlados automáticamente, desde estaciones
lejanas y los transportadores donde las estaciones de funcionamiento no estén
controladas por una persona o estén más allá del alcance de la voz y del contacto
visual de las áreas de conducción, áreas de carga, puntos de transferencia y otros sitios
potencialmente peligrosos localizados en la trayectoria del transportador que no tenga
protección por posición, ubicación o guardas, deberán ser equipados con interruptores
de parada de emergencia, cordones de parada de emergencia, interruptores de límite o
dispositivos similares para paradas de emergencia.
Todos estos dispositivos de parada de emergencia deberán ser fácilmente
identificables en las cercanías inmediatas a estos puntos potencialmente peligrosos, a
no ser que estén protegidos dada su ubicación, posición o protegidos con guardas. No se
requieren los dispositivos de parada de emergencia donde el diseño, el funcionamiento y
la operación de tales transportadores no represente un claro peligro para el personal.
El dispositivo de parada de emergencia debe actuar directamente en el
control del transportador concerniente y no debe depender de la parada de cualquier
otro equipo. Los dispositivos de parada de emergencia deben ser instalados de tal forma
que no puedan ser anulados desde otras localidades.
D) Los controles, los actuadores inactivos o no usados y los cables, deberán ser
removidos de las estaciones de control y de los tableros de mando, junto con los
diagramas, indicadores, etiquetas de control y otros materiales obsoletos, los cuales
pueden confundir al operador.
DISPOSITIVOS DE SEGURIDAD
A) Todos los dispositivos de seguridad, incluyendo la conexión de dispositivos eléctricos,
deben estar dispuestos para operar en una manera de “Fallo - Seguro”; es decir, si se
presenta una pérdida de corriente o una falla en el mismo dispositivo, esto no debe
representar ningún peligro.
B) Paros de Emergencia y Reinicio. Los controles del transportador deberán estar
dispuestos de tal manera que, en caso de un paro de emergencia se requiera un inicio o
arranque manual en la ubicación donde el paro de emergencia se presentó para poder
reanudar la operación del transportador o transportadores y equipo asociado.
C) Antes de volver a poner en marcha un transportador que haya sido detenido por una
emergencia, debe revisarse y determinar la causa del paro. El dispositivo de arranque
deberá ser bloqueado antes de intentar corregir o remover la causa que originó el paro,
a no ser que la operación del transportador sea necesaria para determinar la causa o
para solucionar el problema.
Refiérase a: ANS I Z244.1-1982, “American National Standard for Personnel Protection” -
Lockout/Tagout of Energy Sources - Minimum Safety Requirements and OSHA Standard
Number 29 CFR 1910.147 “The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout).”
OPERACION
• Arranque del Transport
Antes de poner en marcha el transportador, revise si hay objetos ajenos que puedan
haber sido dejados dentro del transportador durante la instalación. Estos objetos pueden
causar serios daños en el arranque.
Después de poner en marcha el transportador y esté operando, verique los motores,
reductores y partes en movimiento para estar seguro de que están trabajando
libremente.
MAINTENIMIENTO
• Lubricación
La cadena motriz ha sido pre-lubricada por el fabricante mediante un proceso de sumersión
caliente que asegura una lubricación total de todos sus componentes. Sin embargo, una
lubricación apropiada y continua extenderá su vida útil enormemente.
La lubricación de la cadena motriz cumple varios propósitos:
• Proteger contra el desgaste de la unión de pines de la cadena
• Lubricar las superficies de contacto entre la cadena y el sprocket
• Prevenir la oxidación o corrosión.
En operaciones bajo condiciones
ambientales normales, lubrique cada
2080 horas de operación o cada 6
meses, lo que ocurra primero. Lubrique
con un lubricante sintético (ej. Mobile
1 sintético) o basado en petroleo
no-detergente de buen grado. Para
mejores resultados, siempre utilice una brocha para lubricar la cadena generosamente.
La viscosidad apropiada del lubricante afecta enormemente el fluido del mismo hacia las
áreas internas de la cadena. Refiérase a la tabla para consultar la viscosidad de lubricante
adecuada para su aplicación.
El requerimiento de lubricación de la cadena motriz se vé afectado por las condiciones de
operación. En condiciones difíciles tales como: ambientes húmedos, ambientes con polvo,
velocidades excesivas, o temperaturas elevadas, se recomienda lubricar la
cadena con más frecuencia. Lo apropiado sería que bajo estas condiciones se establezca
un programa de lubricación específico para su aplicación. Este programa podrá llevarse a
cabo inspeccionando la lubricacion suficiente de la cadena motriz en intervalos regulares
de tiempo. Una vez se ha determinado el intervalo en el cual la cadena no se encuentra
suficientemente lubricada, lubríquela y programe los siguientes intervalos de acuerdo al
intervalo anterior.
• Resolviendo Problemas
Los siguientes cuadros describen posibles problemas que pueden ocurrir en la operación de un transportador motorizado.
RESOLVIENDO PROBLEMAS DE TRANSMISION
PROBLEMA CAUSA SOLUCION
El transportador no
arranca o el motor se
detiene frecuentemente.
1) El motor está sobrecargado.
2) El motor pasa demasiada corriente.
1) Revise si hay sobrecarga del transportador.
2) Revise los circuitos e interruptores de protección y sobrecarga, y cámbielos si es
necesario.
Desgaste excesivo de
la cadena motriz y las
catarinas.
1) Falta de lubricación en la cadena causando su
extensión lo cual crea una cadena inapropiada.
2) Los catarinas están desalineadas.
3) La cadena está floja.
1) Reemplace la cadena y las catarinas. Proporcione una adecuada lubricación. NOTA:
Si el problema repite, posiblemente se requiere tensionar la cadena.
2) Alinee catarinas motrices con rodillos de alineación fijos.
3) Tensione la cadena.
Funcionamiento muy
ruidoso.
1) Rodamientos defectuosos.
2) El tornillo candado está ojo.
3) La cadena motriz está oja.
1) Reemplace los rodamientos.
2) Apriete el tornillo candado.
3) Apriete la cadena.
Motor o reductor
recalentado.
1) Transportador está sobrecargado.
2) Bajo voltaje al motor.
3) Bajo nivel de lubricante en reductor.
1) Revise la capacidad del transportador y reduzca la carga al nivel recomendado.
2) Que un electricista revise y corrija si es necesario.
3) Vuelva a lubricar de acuerdo a las recomendaciones del fabricante. Para el reductor
Hytrol, refiérase al manual adjunto.

14
A
A
SECTION A-A
DRIVE SPROCKET
(CATRINA MOTRIZ)
TAKE UP SPROCKET
(CATARINA DEL TENSOR)
TAKE UP PLATE
(PLACA DEL TENSOR)
TAKE UP JACKBOLT
(TORNILLO TENSOR)
FIXED IDLER
(RODILLOS DE ALINEACION FIJOS)
A
A
SECTION A-A
PRECAUCIÓN! NUNCA quite los guardias
de la cadena mientras el transportador esté
en marcha. Siempre reemplace los guardias
después de realizar ajustes.
DISTANCE BETWEEN SPROCKETS
(DISTANCIA ENTRE PINONES)
HALFWAY
(A LA MITAD)
SLACK 2% OF DISTANCE
BETWEEN SPROCKETS
(FLOJAR 2% DISTANCIA
ENTRE PINONES)
FIGURE 14A
NOTA: La tensión de la cadena va ser pre-ajustada en la fábrica. Sin embargo,
durante el funcionamiento normal, la cadena puede estirarse lo suficiente como para
requerir un ajuste.
1. Retire la guarda de la cadena .
2. Para ajustar la tensión de la cadena, afloje los cuatro (4) tornillos que sujetan la
placa de tensora al marco de la unidad motriz. Apretar los tornillos tensores hasta
alcanzar la tensión deseada. (Fig. 14A.) Levante la mitad del camino de la cadena
entre los piñones al extremo y mida la distancia. Debe ser 2% de la distancia entre
los piñones. (Figure 14B). Asegúrese de que ambos lados se ajustan la misma
cantidad. Vuelva a apretar los tornillos de montaje.
3. Lubrique la cadena de acuerdo a las instrucciones de lubricación.
4. Vuelva a colocar la guarda de cadena.
FIGURE 14B
• Ajuste de Tensión de la Cadena Motorizada

15

16
We know conveyor.
SYSTEMS • SOLUTIONS • SERVICE
(870) 935.3700
(870) 931.1877
WWW.HYTROL.COM
2020 HYTROL STREET
JONESBORO, ARKANSAS 72401
A:
T:
F:
W:
• Preventive Maintenance Checklist
(Lista de Mantenimiento Preventivo)
The following is a general maintenance checklist which covers the major components of your conveyor. This will be helpful in establishing a standard
maintenance schedule.
COMPONENT
(Componente)
SUGGESTED ACTION
(Acción Sugerida)
SCHEDULE
W M Q
Motor
Check Noise (Revisar el Ruido)
Check Temperature (Revisar la Temperatura)
Check Mounting Bolts (Revisar los Tornillos de Montaje)
Reducer
(Reductor)
Check Noise (Revisar el Ruido)
Check Temperature (Revisar la Temperatura)
Check Oil Level (Revisar el Nivel de Aceite)
Bearings
(Rodamientos)
Check Noise (Revisar el Ruido)
Check Mounting Bolts (Revisar los Tornillos de Montaje)
Drive Chain
(Cadena Motriz)
Check Tension (Revisar la Tension)
Check Lubrication (Revisar la Lubricación)
Check for Wear (Revisar el Desgaste)
Sprockets
(Catarinas)
Check for Wear (Revisar el Desgaste)
Check Set Screws (Revisar los Tornillos Candado)
Structural (Estructura)
General Check: Check All Loose Bolts, etc. tightened (Revisar Gen-
eral: Tornillos sueltos, etc.)
W = WEEKLY (Semanal) M = MONTHLY (Mensual) Q = QUARTERLY (Trimestral)
Note: Check Set Screw for proper torque value after the rst 24 hours of operation.
NOTA: REVISAR LOS TORNILLOS DE FIJACIÓN PARA OBTENER EL TORQUE
ADECUADO DESPUÉS DE LAS PRIMERAS 24 HORAS DE OPERACIÓN.
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
HYTROL DC82 Installation and Maintenance Manual
- Tipo
- Installation and Maintenance Manual
en otros idiomas
- English: HYTROL DC82
Otros documentos
-
 Hytrol Conveyor ProSort 100 Manual de usuario
Hytrol Conveyor ProSort 100 Manual de usuario
-
 Hytrol Conveyor 199-CREZD Manual de usuario
Hytrol Conveyor 199-CREZD Manual de usuario
-
Middleby Marshall PS360WB SERIES Manual de usuario
-
Middleby Marshall PS500 Manual de usuario
-
Middleby Marshall Model PS536 Guía de instalación
-
Middleby Marshall PS570 series Guía de instalación
-
Hobart FT1000 Series Installation Instructions Manual
-
Middleby Marshall PS314SBI Manual de usuario
-
Servis-Rhino AGM62 Manual de usuario
-
Bush Hog Disc Hay Mower El manual del propietario

















