Yamaha MU100R El manual del propietario
- Categoría
- Sintetizador
- Tipo
- El manual del propietario

92-BP
FCC INFORMATION (U.S.A)
1. IMPORTANT NOTICE : DO NOT MODIFY THIS UNIT!
This product, when installed as indicated in the instructions contained in this manual, meets FCC requirements. Modifications not
expressly approved by Yamaha may void your authority, granted by the FCC, to use the product.
2. IMPORTANT: When connecting this product to accessories and/or another product use only high quality shielded cables. Cable/s
supplied with this product MUST be used. Follow all installation instructions. Failure to follow instructions could void your FCC
authorization to use this product in the USA.
3. NOTE: This product has been tested and found to comply with the requirements listed in FCC Regulations, Part 15 for Class “B”
digital devices. Compliance with these requirements provides a reasonable level of assurance that your use of this product in a
residential environment will not result in harmful interference with other electronic devices. This equipment generates/uses radio
frequencies and, if not installed and used according to the instructions found in the user’s manual, may cause interference harmful to
the operation of other electronic devices. Compliance with FCC regulations does not guarantee that interference will not occur in all
installations. If this product is found to be the source of interference, which can be determined by turning the unit “OFF” and “ON”,
please try to eliminate the problem by using one of the following measures:
Relocate either this product or the device that is being affected by the interference.
Utilize power outlets that are on different branch (circuit breaker or fuse) circuits or install AC line filter/s.
In the case of radio or TV interference, relocate/reorient the antenna. If the antenna lead-in is 300 ohm ribbon lead, change the lead-in
to co-axial type cable.
If these corrective measures do not produce satisfactory results, please contact the your local retailer authorized to distribute this type of
product. If you can not locate the appropriate retailer, please contact Yamaha Corporation of America, Electronic Service Division,
6600 Orangethorpe Ave, Buena Park, CA 90620
*
The above statements apply ONLY to those products distributed by Yamaha Corporation of America or its subsidiaries.
NEDERLAND / NETHERLAND
• Dit apparaat bevat een lithium batterij voor geheugen back-up.
• This apparatus contains a lithium battery for memory back-up.
• Raadpleeg uw leverancier over de verwijdering van de batterij
op het moment dat u het apparaat ann het einde van de
levensduur afdankt of de volgende Yamaha Service Afdeiing:
Yamaha Music Nederland Service Afdeiing
Kanaalweg 18-G, 3526 KL UTRECHT
Tel. 030-2828425
• For the removal of the battery at the moment of the disposal at
the end of the service life please consult your retailer or Yamaha
Service Center as follows:
Yamaha Music Nederland Service Center
Address: Kanaalweg 18-G, 3526 KL UTRECHT
Tel : 030-2828425
• Gooi de batterij niet weg, maar lever hem in als KCA.
• Do not throw away the battery. Instead, hand it in as small
chemical waste.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri—Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering.
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og
type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandoren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma
batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som rekommenderas av
apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens
instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda
paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin.
Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.

This product utilizes batteries or an external power supply
(adapter). DO NOT connect this product to any power
supply or adapter other than one described in the manual,
on the name plate, or specifically recommended by
Yamaha.
WARNING: Do not place this product in a position
where anyone could walk on, trip over, or roll anything
over power or connecting cords of any kind. The use of
an extension cord is not recommended! If you must use
an extension cord, the minimum wire size for a 25' cord
(or less ) is 18 AWG. NOTE: The smaller the AWG
number, the larger the current handling capacity. For
longer extension cords, consult a local electrician.
This Product should be used only with the components
supplied or; a cart, rack, or stand that is recommended by
Yamaha. If a cart, etc., is used, please observe all safety
markings and instructions that accompany the accessory
product.
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE: The in-
formation contained in this manual is believed to be cor-
rect at the time of printing. However, Yamaha reserves
the right to change or modify any of the specifications
without notice or obligation to update existing units.
This product, either alone or in combination with an ampli-
fier and headphones or speaker/s, may be capable of pro-
ducing sound levels that could cause permanent hearing
loss. DO NOT operate for long periods of time at a high
volume level or at a level that is uncomfortable. If you
experience any hearing loss or ringing in the ears, you
should consult an audiologist. IMPORTANT: The louder
the sound, the shorter the time period before damage oc-
curs.
Some Yamaha products may have benches and/or acces-
sory mounting fixtures that are either supplied with the
product or as optional accessories. Some of these items
are designed to be dealer assembled or installed. Please
make sure that benches are stable and any optional fix-
tures (where applicable) are well secured BEFORE using.
Benches supplied by Yamaha are designed for seating
only. No other uses are recommended.
NOTICE: Service charges incurred due to lack of knowl-
edge relating to how a function or effect works (when the
unit is operating as designed) are not covered by the
manufacturer’s warranty, and are therefore the owners re-
sponsibility. Please study this manual carefully and con-
sult your dealer before requesting service.
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES: Yamaha strives to pro-
duce products that are both user safe and environmentally
friendly. We sincerely believe that our products and the
production methods used to produce them, meet these
goals. In keeping with both the letter and the spirit of the
law, we want you to be aware of the following:
Battery Notice: This product MAY contain a small non-
rechargeable battery which (if applicable) is soldered in
place. The average life span of this type of battery is
approximately five years. When replacement becomes
necessary, contact a qualified service representative to
perform the replacement.
This Product may also use “household” type batteries.
Some of these may be rechargeable. Make sure that the
battery being charged is a rechargeable type and that the
charger is intended for the battery being charged.
When installing batteries, do not mix old batteries with
new, or with batteries of a different type. Batteries MUST
be installed correctly. Mismatches or incorrect installation
may result in overheating and battery case rupture.
Warning: Do not attempt to disassemble, or incinerate
any battery. Keep all batteries away from children. Dis-
pose of used batteries promptly and as regulated by the
laws in your area.
Note: Check with any retailer of household type batteries
in your area for battery disposal information.
Disposal Notice: Should this Product become damaged
beyond repair, or for some reason its useful life is consid-
ered to be at an end, please observe all local, state, and
federal regulations that relate to the disposal of products
that contain lead, batteries, plastics, etc. If your dealer is
unable to assist you, Please contact Yamaha directly.
NAME PLATE LOCATION: The name Plate is located
on the top of the product. The model number, power re-
quirements, etc., are located on this plate. (The serial
number is located on the rear panel.) You should record
the model number, serial number, and the date of pur-
chase in the spaces provided below and retain this manual
as a permanent record of your purchase.
Model
Serial No.
Purchase Date
SPECIAL MESSAGE SECTION
PLEASE KEEP THIS MANUAL
POWER
ON/ OFF

ii
Welcome to the MU100R
Welcome to the MU100R
Welcome to the MU100R
Congratulations and thank you for purchasing the Yamaha MU100R Tone
Generator!
The MU100R is an advanced tone generator providing an amazing total of
1523 high-quality Voices, full General MIDI compatibility — including
Yamaha’s new XG-MIDI (Extended General MIDI) — plus flexible
computer interfacing in a compact, easy-to-use rack mount unit.
Included in the 1523 Voices are 256 extraordinarily realistic and expres-
sive VL Voices — provided by a separate, yet integrated Virtual Acoustic
Synthesis tone generator.
With the convenient built-in host computer interface and MIDI termi-
nals, the MU100R is ideal for any computer music system — from con-
nection to a simple laptop to integration in a complete MIDI studio. With
its large LCD and the intuitive graphic controls on the display, the
MU100R is remarkably easy to use.
The MU100R also features completely independent dual MIDI inputs,
32 Part multi-timbral capacity and full 64-note polyphony for playback
of even the most sophisticated song data. A special Performance mode
gives you flexible four-Voice operation, for live performance applications.
Also built into the system are six digital multi-effects and two EQ sec-
tions (one per-part, and one overall), which give you enormous versatility
in “sweetening” the sound. What’s more, the MU100R provides a host of
comprehensive, yet easy-to-use editing tools for getting just the sound you
need.
The MU100R also has convenient A/D inputs that allow you to connect a
microphone, electric guitar or other instrument, and mix those signals with
the MU100R’s Voices. A separate Hamony effect section lets you auto-
matically apply two-, three- or four-part harmonies to your A/D input vo-
cals, and have them change as you play different chords on a connected
MIDI keyboard.
* Company names and product names in this Owner’s Manual are the trade-
marks or registered trademarks of their respective companies and are
hereby acknowledged.

iv
Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Table of Contents
Welcome to the MU100R....................................................................................................... ii
Unpacking ..............................................................................................................................iii
Table of Contents .................................................................................................................. iv
How to Use This Manual ....................................................................................................viii
PRECAUTIONS.................................................................................................................... ix
The Controls of the MU100R................................................................................................ 1
Front Panel.................................................................................................................... 1
Rear Panel ..................................................................................................................... 3
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do............................................................... 4
What It Is... ....................................................................................................................... 4
About General MIDI .................................................................................................... 4
About XG-MIDI ........................................................................................................... 5
What It Can Do... ............................................................................................................. 5
Using With MIDI Keyboard ......................................................................................... 5
Using With a Computer or Sequencer.......................................................................... 5
About the Modes of the MU100R ................................................................................... 6
Play Modes and the Part Controls ................................................................................ 7
Part Edit Mode.............................................................................................................. 7
Utility Mode ................................................................................................................. 7
Modes and Function Tree...................................................................................................... 8
GUIDED TOUR
Setting Up Your MU100R.............................................................................................. 12
What You'll Need ........................................................................................................ 12
Making the Connections............................................................................................. 12
Powering Up.................................................................................................................... 14
Playing the Demo Song .................................................................................................. 15
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System .......................................................... 17
Connecting to MIDI Devices ..................................................................................... 17
Connecting Directly to a Computer ........................................................................... 19
Macintosh and Compatibles ................................................................................. 19
IBM PC/AT and Compatibles ............................................................................... 21
Selecting and Playing the Performances...................................................................... 23
Calling Up the Performance Play Mode and Playing the Performances ................... 23
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices ...................................................................... 26
Calling Up the XG Mode ........................................................................................... 26
Selecting Voice Banks and Voices From the Panel .................................................... 27
Selecting Voices From a MIDI Keyboard .................................................................. 31
Editing in the Multi Mode ............................................................................................. 32
Single Part Controls.................................................................................................... 33
Changing the Volume and Pan settings of a Part .................................................. 34
On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 35

Table of Contents
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Edit Menu Parameters ................................................................................................ 36
Changing the Filter and EG Settings of a Part ..................................................... 36
On Your Own................................................................................................... 38
Editing Drum Kits — with the Drum Setup Controls ............................................... 39
Making Changes to Individual Drum Sounds — the "Drum" Parameters........... 40
On Your Own................................................................................................... 42
Editing in the Performance Mode ................................................................................ 43
All Part Controls ......................................................................................................... 44
Transposing the Overall Key of a Performance ......................................................... 45
Single Part Controls — Selecting Different Voices for the Performance .................. 46
On Your Own................................................................................................... 47
Edit Menu Parameters — Creating a Two-Voice Layer............................................. 48
Setting Up a Keyboard Split....................................................................................... 50
On Your Own................................................................................................... 51
Using the Assignable Controller in a Performance.................................................... 51
Saving Your Original Performance............................................................................. 52
Assignable Controller (AC1) ......................................................................................... 53
Controllers and Control Numbers .............................................................................. 53
Control Numbers and the Actual Sound..................................................................... 54
Assigning the Assignable Controller.......................................................................... 55
Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up ......................................................... 56
Using the Assignable Controller — Some Applications............................................ 57
Changing the Brightness on a Piano Voice........................................................... 57
Experssive Volume Control of a Part .................................................................... 59
Expressive Control of Individual Drum Sounds .................................................. 59
On Your Own................................................................................................... 61
Playing and Editing VL Voices...................................................................................... 62
About the VL Voice Section ....................................................................................... 62
Virtual Acoustic Synthesis .................................................................................... 63
VA Advantages ................................................................................................ 63
VL Tone Generator Model .............................................................................. 63
Voice Organization................................................................................................ 67
Selecting VL Voice banks and VL Voices .................................................................. 69
Editing a VL Voice...................................................................................................... 71
Effects .............................................................................................................................. 73
Using Reverb and Chorus........................................................................................... 73
Applying Distortion to a Part — Using the Variation Effects.................................... 75
Harmony Effect .............................................................................................................. 77
Using the Harmony Effect.......................................................................................... 77
On Your Own................................................................................................... 79
Equalizer (EQ)................................................................................................................ 80
Adjusting the Tone of a Specific Part — Part EQ...................................................... 80
Adjusting the Overall Tone — Main EQ.................................................................... 82
Individual Outputs ......................................................................................................... 83
Using the Individual Outputs ..................................................................................... 83

vi
Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Mute/Solo ........................................................................................................................ 85
Using Mute/Solo......................................................................................................... 85
A/D Inputs....................................................................................................................... 87
Using the A/D Inputs .................................................................................................. 87
Data Flow Block Diagram ............................................................................................. 91
MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables ............................................................................ 92
REFERENCE
Multi Mode...................................................................................................................... 95
Part Controls ............................................................................................................... 95
Single Part Control................................................................................................ 96
All Part Control..................................................................................................... 98
Multi Edit Mode ....................................................................................................... 100
Filter (FIL) .......................................................................................................... 100
Envelope Generator (EG) ................................................................................... 102
Equalizer (EQ) .................................................................................................... 105
Vibrato................................................................................................................. 106
Others .................................................................................................................. 107
Drum Setup Controls .......................................................................................... 114
VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin)..................................................................... 119
Performance Mode ....................................................................................................... 127
Performance Part Control ......................................................................................... 128
All Part ................................................................................................................ 128
Single Part ........................................................................................................... 129
Performance Edit Mode............................................................................................ 131
Common.............................................................................................................. 131
Part ...................................................................................................................... 134
Copy and Store Operations....................................................................................... 137
Copy .................................................................................................................... 137
Store .................................................................................................................... 138
Recall Function ................................................................................................... 140
Effect Edit Mode .......................................................................................................... 141
Reverb (REV) ........................................................................................................... 142
Chorus (CHO)........................................................................................................... 143
Variation (VAR) ........................................................................................................ 144
Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2)............................................................................................ 146
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters .................................................................... 147
About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion .......................................... 152
Equalizer (EQ) Edit ..................................................................................................... 155

Table of Contents
vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Utility Mode .................................................................................................................. 156
System Functions (SYS) .......................................................................................... 157
Dump Out Functions (DUMP) ................................................................................. 161
Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI ................................................................. 161
Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST.......................................................... 161
Initialize Functions (INIT) ....................................................................................... 165
Demo Song Play (DEMO) ....................................................................................... 168
VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN).......................................... 169
VL Voice System Parameters.............................................................................. 169
Harmony System Parameters.............................................................................. 171
Sound Module Mode (MODE).................................................................................... 172
Miscellaneous Functions.............................................................................................. 173
Show Control Change............................................................................................... 173
Show Exclusive......................................................................................................... 175
APPENDIX
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 178
Error Messages ............................................................................................................. 180
Specifications ................................................................................................................ 181
Glossary......................................................................................................................... 183
Index .............................................................................................................................. 185

viii
How to Use This Manual
How to Use This Manual
How to Use This Manual
You are probably eager to try out your new MU100R Tone Generator right
away and hear what it can do, rather than have to read through a lot of in-
structions before you can even get a sound out of it.
The structure of the manual is very straightforward. You can approach it in
a linear manner, reading through from beginning to end, or on an “on-de-
mand” basis, going directly to the information you need as you need it.
However, to get the most out of your MU100R, we strongly suggest that you
read the following sections in the order given:
1) Precautions
This gives you important information on how to care for your new
MU100R, how to avoid damaging it, and how to ensure long-term, re-
liable operation.
2) The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
This briefly provides an overview of the functions and features of the
MU100R and offers some important hints on how you can use it effec-
tively. It also provides convenient page references so that you can eas-
ily find out about features and functions of interest.
3) The Controls of the MU100R
This section introduces you to the panel controls and connectors.
4) Guided Tour
This is perhaps the most important and valuable section of the manual.
It gets you started using your new MU100R, helping you set up the in-
strument and play it — and it introduces you to virtually all of the im-
portant functions and features. The hands-on experience you gain in
this section will help you quickly master the instrument and aid you in
navigating the more detailed sections of the manual.
5) Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System;
Using the MU100R with a Computer or Sequencer
These sections (within the Tutorial) provide all you need to know to effec-
tively integrate the MU100R into your present computer music system.
6) Reference
Once you’re familiar with everything above, lightly go over this com-
prehensive guide to all editing functions. You won’t need (or want) to
read everything at once, but it is there for you to refer to when you
need information about a certain feature or function.
7) Appendix
Use the sections in the Appendix as necessary. For example, the Index
will come in handy when you need to quickly find information on a
specific topic. Other sections, such as the Glossary, Troubleshooting
and Error Messages provide additional useful information.
8) Sound List & MIDI Data booklet
This separate booklet features lists of the Performances, Voices, drum
sounds, effect types and parameters, as well as details on all relevant
MIDI messages and data.

PRECAUTIONS
ix
• Do not operate the instrument for a long period of time at a high or
uncomfortable volume level, since this can cause permanent hearing
loss. If you experience any hearing loss or ringing in the ears, consult a
physician.
■REPLACING THE BACKUP BATTERY
• This instrument contains a non rechargeable internal backup battery
which permits internal data to remain stored even when the power is off.
When the backup battery needs replacing, the message “Battery Low!”
will display in the display. When this happens, immediately back up
your data (using an external device such as the floppy disk-based
Yamaha MIDI Data Filer MDF2), then have qualified Yamaha service
personnel replace the backup battery.
• Do not attempt to replace the backup battery yourself, in order to prevent
the possible serious hazards. Always have qualified Yamaha service
personnel replace the backup battery.
• Never place the backup battery in a location that a child can reach, since
a child might accidentally swallow the battery. If this should happen,
consult a physician immediately.
■SAVING USER DATA
• Save all data to an external device such as the Yamaha MIDI Data Filer
MDF2, in order to help prevent the loss of important data due to a
malfunction or user operating error.
Yamaha cannot be held responsible for damage caused by improper
use or modifications to the instrument, or data that is lost or destroyed.
Always turn the power off when the instrument is not in use.
PRECAUTIONS
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE PROCEEDING
* Please keep these precautions in a safe place for future reference.
WARNING
Always follow the basic precautions listed below to avoid the possibility of serious injury or even death from electrical
shock, short-circuiting, damages, fire or other hazards. These precautions include, but are not limited to, the following:
• Do not open the instrument or attempt to disassemble the internal parts
or modify them in any way. The instrument contains no user-serviceable
parts. If it should appear to be malfunctioning, discontinue use
immediately and have it inspected by qualified Yamaha service
personnel.
• Do not expose the instrument to rain, use it near water or in damp or wet
conditions, or place containers on it containing liquids which might
spill into any openings.
• If the AC adaptor cord or plug becomes frayed or damaged, or if there is
a sudden loss of sound during use of the instrument, or if any unusual
smells or smoke should appear to be caused by it, immediately turn off
the power switch, disconnect the adaptor plug from the outlet, and have
the instrument inspected by qualified Yamaha service personnel.
• Use the specified adaptor (PA-5B or an equivalent recommended by
Yamaha) only. Using the wrong adaptor can result in damage to the
instrument or overheating.
• Before cleaning the instrument, always remove the electric plug from
the outlet. Never insert or remove an electric plug with wet hands.
• Check the electric plug periodically and remove any dirt or dust which
may have accumulated on it.
CAUTION
Always follow the basic precautions listed below to avoid the possibility of physical injury to you or others, or damage
to the instrument or other property. These precautions include, but are not limited to, the following:
• Do not place the AC adaptor cord near heat sources such as heaters or
radiators, and do not excessively bend or otherwise damage the cord,
place heavy objects on it, or place it in a position where anyone could
walk on, trip over, or roll anything over it.
• When removing the electric plug from the instrument or an outlet, always
hold the plug itself and not the cord.
• Do not connect the instrument to an electrical outlet using a multiple-
connector. Doing so can result in lower sound quality, or possibly cause
overheating in the outlet.
• Unplug the AC power adaptor when not using the instrument, or during
electrical storms.
• Before connecting the instrument to other electronic components, turn
off the power for all components. Before turning the power on or off for
all components, set all volume levels to minimum.
• Do not expose the instrument to excessive dust or vibrations, or extreme
cold or heat (such as in direct sunlight, near a heater, or in a car during
the day) to prevent the possibility of panel disfiguration or damage to
the internal components.
• Do not use the instrument near other electrical products such as
televisions, radios, or speakers, since this might cause interference which
can affect proper operation of the other products.
• Do not place the instrument in an unstable position where it might
accidentally fall over.
• Before moving the instrument, remove all connected adaptor and other
cables.
• When cleaning the instrument, use a soft, dry cloth. Do not use paint
thinners, solvents, cleaning fluids, or chemical-impregnated wiping
cloths. Also, do not place vinyl or plastic objects on the instrument,
since this might discolor the panel or keyboard.
• Do not rest your weight on, or place heavy objects on the instrument,
and do not use excessive force on the buttons, switches or connectors.

The Controls of the MU90R
1
The Controls of the MU100R
The Controls of the MU100R
Front Panel
1 PHONES jack
For connection to a set of stereo headphones (1/4” plug).
2 VOLUME control
For adjusting the overall volume of the MU100R.
3 A/D INPUT 1, 2 jacks
For connection of a microphone, electric guitar or other electronic instruments
(mono 1/4” plugs).
4 A/D INPUT VOLUME control
For control of the level of the A/D inputs.
5 PLAY button
For entering the Play mode and switching among the different Play displays.
(See page 24.)
6 UTIL (UTILITY) button
For entering the Utility mode. (See page 15.)
7 MODE button
For entering the Sound Module mode. (See page 23.)
8 EDIT button
For entering the Edit mode. (See page 36.)
9 EFFECT button
For entering the Effect Edit mode. (See page 74.)
: EQ button
For entering the EQ Edit mode. (See page 82.)
1324 58
7
9
6
0

2
The Controls of the MU90R
The Controls of the MU100R
A MUTE/SOLO button
Pressing this alternately mutes or solos the selected Part. (See page 85.)
B ENTER button
For calling up menu items in the display and for executing certain functions
and operations. Double-clicking this (pressing it twice quickly) calls up the
Show Exclusive function (see page 175).
C EXIT button
For leaving various display pages and returning to previous displays. Also for
canceling certain functions and operations.
D PART -/+ buttons
For selecting different Parts. In the Effect Edit mode, these can be used to
switch among the different effects. Pressing these together alternately switches
between All Part and Single Part control. (See page 48.)
E SELECT </> buttons
For selecting the various menu items, parameters and controls on the display.
F VALUE -/+ buttons
For changing the value of a selected parameter or control.
Hint
You can rapidly move through the values by holding down one of the [VALUE
-
/
+
]
buttons. You can move even more rapidly by holding down one button and then press-
ing and holding down the other. For example, to rapidly advance (increase) the value,
hold down the [VALUE
+
] button and simultaneously press and hold down the [VALUE
-
] button.
G Data dial
For rapidly adjusting/changing values of the selected function or parameter.
Rotate this clockwise to increase the value.
H POWER switch
Pressing this turns the power on and off.
POWER
ON/ OFF
GHA
C
E
B
F
D

The Controls of the MU90R
3
The Controls of the MU100R
Rear Panel
1 MIDI THRU, MIDI OUT and MIDI IN A/B terminals
For connection to other MIDI devices, such as a MIDI keyboard, tone genera-
tor, sequencer, or to a computer that has a MIDI interface. MIDI IN A and B
are independent MIDI ports, allowing full 32-channel MIDI input. MIDI OUT
is for data dumps to another MIDI device, while MIDI THRU is for “daisy-
chain” connection of additional MU100Rs or other MIDI instruments. (See
page 17 for more information on MIDI connections.)
2 HOST SELECT switch
For selecting the type of host computer. (See page 19.)
3 TO HOST terminal
For connection to a host computer that does not have a MIDI interface. (See
page 19.)
4 DC IN jack
For connection to the PA-5B AC power adaptor.
5 OUTPUT R, L/MONO jacks (Right, Left/Mono)
For connection to a stereo amplifier/speaker system. When using a mono sys-
tem, connect it to the L/MONO jack.
6 INDIV. (Individual) OUTPUT 1, 2 jacks
For independent output of selected Parts (1/4” jack). Parts selected for output
through these jacks are not output through the main OUTPUT or PHONES
jacks. (See pages 113 and 118.)
543216

4
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
What It Is...
The MU100R is a full-featured and easy-to-use tone generator, that provides an
unprecedented wealth of Voices and expressive sonic control. It features full
General MIDI Level 1 compatibility with 128 General MIDI Voices and 9 drum
kits. It also provides new XG-MIDI (Extended General MIDI) compatibility,
with an huge total of 1074 Voices and 36 drum kits. Moreover, it has an inte-
grated VL tone generator that provides 256 stunning monophonic Voices utiliz-
ing Yamaha’s sophisticated Virtual Acoustic Synthesis system.
The MU100R has 64-note polyphony and is 32-Part multi-timbral. In other
words, the MU100R has 32 different Parts, each with its own Voice, so that up to
32 different Voices can be sounded simultaneously. Since the MU100R features
dual MIDI input ports (A and B), 16 Parts can be played from one MIDI port and
the remaining 16 from the other port.
Additional A/D Parts let you connect up to two external signals — such as a
microphone, electric guitar or CD player — and mix them with the MU100R’s
Voices.
The MU100R also has a TO HOST terminal for easy interfacing with a com-
puter, allowing you to play the Voices using your favorite music software. This
is where the advanced multi-timbral capabilities come in, letting you playing
sophisticated arrangements using up to 32 different Voices at the same time.
Although Voices cannot be directly edited, the various Part controls and Edit
mode give you tools for transforming or customizing the sound of the Voices.
What’s more, the MU100R has a built-in multi-effect processor, with seven in-
dependent digital effect “units” for enhancing the sound. Included in these is a
powerful Harmony section that allows you to generate realistic vocal harmonies
with your actual voice (using one of the A/D Parts).
The MU100R also features a special Performance mode, in which four Parts
are played simultaneously over a single MIDI channel. Connected to a MIDI
keyboard, this effectively gives you four tone generators in one. The MU100R
gives you 100 factory-programmed Preset Performances plus 100 Internal Per-
formance locations for storing your own original Performances.
About General MIDI
General MIDI is a new addition to the worldwide MIDI standard. MIDI, as
you know, stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, and makes it
possible for various electronic musical instruments and other devices to “com-
municate” with each other. For example, by connecting a sequencer to the
MU100R’s MIDI IN terminal, you could play back a song on the sequencer
using the Voices of the MU100R.

The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
5
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
So, where does General MIDI fit in all of this? One of the most important
features of General MIDI is in the standardization of Voices. This means that a
song recorded in the General MIDI format can be played back on any General
MIDI compatible tone generator and sound just as the composer intended. For
example, if there is an alto sax solo in the song, it will be played by an alto sax
Voice on the General MIDI tone generator (and not by a tuba or harpsichord!).
Since the MU100R is fully compatible with General MIDI, you can take advan-
tage of the vast wealth of musical material recorded in that format.
About XG-MIDI
The new XG format is an extension of General MIDI, and provides a number of
significant improvements and enhancements. XG-compatible song data takes
advantage of the extensive MIDI control and built-in effects of the MU100R
(and other MU-series instruments).
To take greatest advantage of the powerful capabilities of XG-MIDI, we rec-
ommend using XG-compatible instruments and software. For example, XG-
compatible keyboards such as the Yamaha CBX-K1 keyboard and software give
you direct controls for accessing the full expressive potential of the MU100R’s
XG Voices and the XG-related parameters.
What It Can Do...
Here are a few ideas on how you can use the MU100R. The list below is not
comprehensive, but is meant to be a general guide to the possibilities and pro-
vide a starting point or springboard for your own creative ideas and explorations.
Using With MIDI Keyboard
Use the MU100R as supplementary tone generator with your MIDI key-
board and play the Voices of both instruments in a layer together. Or, use the
convenient Performance mode, and play four Voices on the MU100R at once.
You can split the four Voices across the keyboard, playing each from a dif-
ferent register. Or you can create sophisticated velocity splits, in which a
different Voice is heard depending on how strongly you play the keyboard.
Or use keyboard and velocity splits together for even greater flexibility.
Using With a Computer or Sequencer
Home Studio Setup
The MU100R integrates instantly and easily into any existing setup. If you have a
MIDI keyboard, computer and sequencing software, the MU100R with its high-
quality Voices and multi-timbral capabilities can expand your home studio system.

6
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
Carry It With You
If you have a laptop computer (and sequencing software), simply connect the
MU100R, plug in some headphones and you’ve got a complete, high-powered
music making system that’s ready to go wherever you go. Use it for composing,
arranging, practicing or making/playing demos for your band.
Use It on a Gig
Similarly, you can connect a laptop or a MIDI data filer and playback song data with
the MU100R’s Voices. Plug a microphone into one of the A/D inputs and a guitar
into the other, and you can mix your own live performance with the sequencer tracks.
What’s more, you can produce automatic vocal harmonies with the Harmony effect
— controlled either from a keyboard or directly from one of the sequencer tracks!
Multimedia
Since it’s compatible with General MIDI and XG, the MU100R is a natural for
multimedia applications. Bring it with you to a presentation — since the com-
puter interface is built-in to the MU100R, it hooks up instantly and easily to the
computer’s serial port or printer port, without the need for any other equipment.
About the Modes of the MU100R
The MU100R has two main operating modes: Multi and Performance. In
Multi mode, the MU100R is a 32-Part multi-timbral tone generator; in Per-
formance mode, the MU100R effectively functions as four tone generators
controlled over a single MIDI channel.
Which mode the MU100R is in depends on the selected Sound Module
mode. If XG, TG300B or C/M are selected, the MU100R automatically sets
itself to the Multi mode. When PFM is selected, the MU100R is in the Per-
formance mode. (For information on selecting the Sound Module mode, see
page 172.)
Each mode provides compatibility with different music software and hard-
ware.
XG: This stands for Extended General MIDI and provides the full
potential of the MU100R, giving you access to the 1074 XG Voices
plus the VL Voices.
TG300B: This mode provides compatibility with the GM-B mode of the
TG300 Tone Generator.
C/M: This mode provides compatibility with most computer music soft-
ware not supported by the other two Multi modes.
PFM: This mode (Performance) lets you play four Voices simultaneously
over a single MIDI channel. (For more information on using the
Performance mode, see page 43.)

The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
7
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
The bottom right of the display indicates the currently selected Sound Mod-
ule mode.
Selected Sound Module mode.
NOTE
When set to the TG300B mode, the MU100R may not be able to play TG300-spe-
cific song data with complete accuracy. However, MIDI data designed for other
computer music tone generators is compatible with the MU100R.
Play Modes and the Part Controls
Once the operating mode of the MU100R is set (Multi or Performance),
there are two main ways you can use the MU100R: playing and editing. In
the Play modes, you play the Voices; in the various Edit modes, you change
their settings.
Within the Play modes are the Part controls. These let you make basic
settings for the Parts. The Single Part controls allow you to make indepen-
dent settings for each Part, while the All Part controls allow you to change
the overall settings of all Parts. (See pages 96 and 98 for more information.)
The MU100R has several different Edit modes, each with various menus
and operations:
Part Edit Mode
The Part Edit mode allows you to change certain settings for each individual
Part, such as those of the Filter, EG (Envelope Generator), and many other
settings. The internal Voices can be sounded during editing, allowing you to
hear the effects of your edits.
Utility Mode
The Utility mode lets you set functions related to the overall operation of the
MU100R, such as Master Tune, display Contrast and reception of certain
MIDI messages that affect the entire instrument. Included also are miscella-
neous operations, such as sending bulk data to a data storage device, initial-
izing of the MU100R settings, and playing the special Demo song.
XG
TG300B
C/M
PERFORM

8
The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
Modes and Function Tree
Modes and Function Tree
Multi Play Mode
P. 96
P. 98
P. 129
P. 100
P. 100
P. 102
P. 105
P. 114
P. 106
P. 119
P. 107
P. 128
P. 131
P. 131
P. 134
P. 135
P. 135
P. 135
P. 135
P. 135
P. 137
P. 138
P. 140
[SELECT </>] Multi Part Control
[SELECT </>] Multi All Part Control
[SELECT </>] Performance Control
[SELECT </>] Performance Part Control
[EDIT]
Performance Edit Mode
[SELECT <] Common Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT <] Filter Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] EG Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] EQ Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Vibrato Edit [ENTER]
P. 136
[SELECT >] Plugin Edit (
Only when VL Part is selected.
) [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Others Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Part Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Copy [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Store [ENTER]
[SELECT >] Recall [ENTER]
[PLAY]
[PLAY]
[EDIT]
Multi Part Edit Mode
[SELECT <] Filter Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] EQ Edit (Only when Normal or VL Part is selected.) [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Drum Setup Edit
(Only when Drum Part is selected.)
[ENTER]
[SELECT >] Plugin Edit
(Only when VL Part is selected.)
[ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Vibrato Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Others Edit [ENTER]
P. 127
P. 95
[PART++-]
[SELECT </>] EG Edit [ENTER]
[PART++-]
( When the sound module mode is “XG”, “TG300B”, or “C/M”)
Performance Play Mode (
When the sound module mode is ”PFM”)

The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do
9
Modes and Function Tree
P. 156
: Mode
: Submode
[SELECT <] System Setup [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Dump Out [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Initialize [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Demo Song Play [ENTER]
[UTIL]
[MODE]
[EFFECT]
[EQ]
P. 157
P. 172
P. 172
P. 172
P. 172
P. 172
P. 142
P. 143
P. 144
P. 146
P. 146
P. 147
P. 155
P. 161
P. 165
P. 168
[SELECT >] Plugin [ENTER]
P. 169
[SELECT </>] Chorus Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Variation Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Insertion 1 Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT </>] Insertion 2 Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT >] Plugin Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT <] Reverb Edit [ENTER]
[SELECT <] or [VALUE-] XG
[SELECT </>] or [VALUE+/-] TG300
[SELECT </>] or [VALUE+/-] C/M
P. 141
[SELECT >] or [VALUE+] PFM
Push on the SELECT buttons either < or > for SELECT < / >.
Push on the PART + and - simultaneously for PART ++ -.
Utility Mode
Sound Module Mode
Effect Mode
Equalizer Mode

G
UIDED
T
OUR
When using your MU100R for the first time, read through
this short section of the manual. It guides you step-by-step in
using many of the basic operations: setting the instrument up,
connecting it properly to other equipment, and — most im-
portantly — playing it. It also introduces you to most of the
other, advanced features and operations of the instrument —
enabling you to quickly and effectively get the most out of
your new MU100R.

12
Guided Tour
Setting Up Your MU100R
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Connect the MU100R in the most basic setup — with a MIDI keyboard
and an external amplifier/speaker system.
Other setup examples are covered in later sections; for example, setting up
for use with a computer is on page 19. Once you’ve set up the MU100R, we
urge you to play the Demo song (page 15) and hear what the instrument is
capable of.
What You’ll Need
☛ The MU100R and the included PA-5B power adaptor.
☛ A MIDI keyboard, electronic piano, or any instrument that can output
MIDI data.
☛ An amplifier/speaker system, preferably stereo. Alternately, you can use
a set of stereo headphones.
☛ Audio connecting cables.
☛ A MIDI cable.
Making the Connections
CAUTION!
Before making any connections, turn all related equipment off, and make sure the
MU100R power adaptor is not connected to an electrical outlet.
Operation
1 Connect the MIDI cable.
Connect the MIDI OUT terminal of the MIDI keyboard to the
MIDI IN-A of the MU100R (as shown in the illustration).
2 Connect the audio cables.
Connect the R and L/MONO OUTPUT jacks of the MU100R to
the appropriate inputs on the amplifier speaker system (as shown
in the illustration).
•If the amplifier has only one input, use the L/MONO jack on the
MU100R. If you are using stereo headphones, connect them to
the front panel PHONES jack.
Setting Up Your MU100R

Guided Tour
13
3 Set the HOST SELECT switch.
Set this rear panel switch to MIDI (see illustration).
4 Connect the AC power adaptor.
Plug the DC output cable of the PA-5B into the DC IN terminal
on the rear panel, then plug the adaptor into an appropriate
electrical outlet.
•Wrap the DC output cable of
the adaptor around the cable
clip (as shown below) to pre-
vent accidental unplugging of
the cable during operation.
CAUTION!
• Do not attempt to use an AC adaptor other than the PA-5B. The use of an in-
compatible adaptor may result in irreparable damage to the MU100R, and even
pose a serious shock hazard.
• Be sure to disconnect the power adaptor from the outlet when the MU100R is
not in use.
Now that you’ve set up the MU100R, we urge you to go on to the next
section, turn on the instrument, and play the Demo song (page 15) to hear
what the instrument is capable of. If you need information on setting up the
MU100R for a different type of system, refer to “Setting Up the MU100R
in Your Music System” on page 17.
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN-A
MIDI CABLE
R
Amplifier
Speaker System
PHONES
DC INL/MONO
Power
Adaptor
STOP CONTINUE START
SOUND
OFF
MERGE
ON/OFF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0
TRANSPOSE
HEXA
DECIMAL
DECIMAL
DC IN
OCTAV E
OCTAVE SHIFT
OCTAV E
RESET
PITCH
ASSIGNABLE
IN MIDI OUT
ENTER
DRUM
NUMBER
NRPN
CONTROLLER
RPN
FIXED
VELOCITY
MIDI
CH
PROGRAM
CHANGE
BANK
SELECT
TEMPO
PROGRAM RESET SYSTEM WHEEL ASSIGNSEQUENCER
POWER ON OFF
SHIFT
GM
ON
XG
ON
MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1
CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST
122 COARSE TUNING
(NRPN)
(RPN)
120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY
121 FINE TUNING
123 VIBRATO RATE
124 VIBRATO DEPTH
125 VIBRATO DELAY
126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
127 FILTER RESONANCE
128 EG ATTACK TIME
129 EG DECAY TIME
130 EG RELEASE TIME
131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE
133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE
134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE
135 DRUM PITCH COARSE
136 DRUM PITCH FINE
137 DRUM LEVEL
138 DRUM PAN
139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH
140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH
141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH
142 CHANNEL PRESSURE
143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE
144 MASTER VOLUME
145 MASTER BALANCE
146 MASTER TUNING
147 VELOCITY
148 TEMPO
OTHERS
74 BRIGHTNESS
84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL
91 REVERB DEPTH
92 TREMOLO DEPTH
93 CHORUS DEPTH
94 VARIATION DEPTH
95 PHASER DEPTH
73 ATTACK TIME
1 MODULATION DEPTH
5 PORTAMENTO TIME
6 DATA ENTRY
7 MAIN VOLUME
8 BALANCE CONTROL
10 PANPOT
CONTROL CHANGE
2 BREATH CONTROL
4 FOOT CONTROL
64 HOLD1(DAMPER)
65 PORTAMENTO
66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD)
67 SOFT PEDAL
69 HOLD2 (FREEZE)
71 HARMONIC CONTENT
72 RELEASE TIME
11 EXPRESSION
POWER
ON/ OFF
Setting Up Your MU100R

14
Guided Tour
Powering Up
Admittedly this is a simple operation, but you should be careful to follow the
instructions below to avoid possible damage to your equipment and speakers.
Operation
1 Turn on the power of your MIDI keyboard.
2 Turn on the power of the MU100R.
Press the POWER switch.
After the animated greeting display finishes, the following dis-
play appears:
3 Turn down all volume controls.
This includes the MU100R and any connected equipment.
4 Turn on the amplifier/speaker system.
5 Set the volume controls.
First, set the volume control on the MU100R to about the mid-
way position, then set the volume on the amplifier to a suitable
level.
Powering Down
When you turn the power off, make sure to do it in the following order:
1) Amplifier/speaker system
2) MU100R
3) Other connected equipment (MIDI keyboard, etc.)
This prevents possible damage to the speakers.
Powering Up

Guided Tour
15
Playing the Demo Song
Now that you’ve set everything up properly, try playing the built-in Demo
song. This showcases the high-quality Voices and the AWM2 tone genera-
tion system of the MU100R. It also is an excellent demonstration of the 32-
part multi-timbral capacity and the various expressive controls and effects
that can be used simultaneously. Most importantly, the Demo song will give
you an idea of how powerful the MU100R can be in your own MIDI/com-
puter music setup.
Operation
1 Press the [UTIL] button.
2 Select and open the DEMO menu.
Use the [SELECT -/>] buttons to select “DEMO” (the menu
icon flashes), then press the [ENTER] button.
3 Start the Demo song.
Press the [ENTER] button. The Demo Song starts playing imme-
diately and repeats indefinitely until stopped (in step 4 below).
Playback of the individual Parts of the song is shown graphically
by the “level meter” bars in the display.
NOTE
During Demo Song playback, none of the panel controls (with the exception of
the [EXIT] button and the VOLUME control) can be used.
Playing the Demo Song

Guided Tour
17
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System
As you learned in the section The MU100R — What It Is and What It
Can Do on page 4, the MU100R can be integrated into a variety of setups. It
would be impossible to cover all connection possibilities in a short manual
as this; however, the section below will help in quickly setting up the MU100R
and using it in your system.
Connecting to MIDI Devices
The MU100R is equipped with MIDI IN, OUT, and THRU terminals, allow-
ing you to use it in any MIDI system. Moreover, the two MIDI IN terminals
are independent 16-channel ports, effectively giving you two tone genera-
tors in one. Here are some common connection examples using the built-in
MIDI interface. Refer to the example that most closely matches your setup,
then read the Operation steps at the end of this section.
• MIDI keyboard
In this setup, you can play the sounds of the MU100R from the connected
keyboard.
• Hardware sequencer
In this setup, a hardware sequencer (such as the Yamaha QY700) is used.
The main advantage of such a setup is its portability.
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN-A or B
MIDI CABLE
STOP CONTINUE START
SOUND
OFF
MERGE
ON/OFF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0
TRANSPOSE
HEXA
DECIMAL
DECIMAL
DC IN
OCTAVE
OCTAVE SHIFT
OCTAVE
RESET
PITCH
ASSIGNABLE
IN MIDI OUT
ENTER
DRUM
NUMBER
NRPN
CONTROLLER
RPN
FIXED
VELOCITY
MIDI
CH
PROGRAM
CHANGE
BANK
SELECT
TEMPO
PROGRAM RESET SYSTEM WHEEL ASSIGNSEQUENCER
POWER ON OFF
SHIFT
GM
ON
XG
ON
MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1
CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST
122 COARSE TUNING
(NRPN)
(RPN)
120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY
121 FINE TUNING
123 VIBRATO RATE
124 VIBRATO DEPTH
125 VIBRATO DELAY
126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
127 FILTER RESONANCE
128 EG ATTACK TIME
129 EG DECAY TIME
130 EG RELEASE TIME
131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE
133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE
134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE
135 DRUM PITCH COARSE
136 DRUM PITCH FINE
137 DRUM LEVEL
138 DRUM PAN
139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH
140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH
141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH
142 CHANNEL PRESSURE
143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE
144 MASTER VOLUME
145 MASTER BALANCE
146 MASTER TUNING
147 VELOCITY
148 TEMPO
OTHERS
74 BRIGHTNESS
84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL
91 REVERB DEPTH
92 TREMOLO DEPTH
93 CHORUS DEPTH
94 VARIATION DEPTH
95 PHASER DEPTH
73 ATTACK TIME
1 MODULATION DEPTH
5 PORTAMENTO TIME
6 DATA ENTRY
7 MAIN VOLUME
8 BALANCE CONTROL
10 PANPOT
CONTROL CHANGE
2 BREATH CONTROL
4 FOOT CONTROL
64 HOLD1(DAMPER)
65 PORTAMENTO
66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD)
67 SOFT PEDAL
69 HOLD2 (FREEZE)
71 HARMONIC CONTENT
72 RELEASE TIME
11 EXPRESSION
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN-A
MIDI CABLE
OCT
DOWN
OCT
UP
OCT
DOWN
OCT
UP
ON
BASS
F
#
E FGAB C
D
M
add9
M7
add9
a
m
mM7
m6
c
C
#
D
#
REST
TRACK
DOWN
TRACK
UP
SOLOMUTE
EDIT
CONTRAST
OUT BOUT AIN B
IN B
MIDI
MIDI
OUT BOUT A
IN A
IN A
PLAYREC
JOB
LOC 2LOC 1
TIE
7
(
#
5)
7
(
b
5)
7
(
#
9)
7
sus4
sus4
SECTION
A
G
b
D
b
E
b
7
(
b
9)
m7
(
b
5
)
M7
(9)
6
6
(9)
7
7
(9)
m7
(9)
m7
dim
ZWV
/
HGF
UTSRQPO
#
N
CBA
?
MLK
_
!
S
%
&
E
)
D
(
_
YX
aug
7
(
b
13
)
7
(13)
7
(
#
11)
JI
m7
(11)
ORG
BASS
CAPS
SHIFT
SPACE
3
DEL
YESNO
c
G
#
A
b
A
#
B
b
789
456
123
0
-
VOICE
SHIFT F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 SHIFT EXIT
-1 +1
MAX
VOLUME
EFFECT
DISK
SONG
PITCH ASSIGNABLE
PATTERN
UTILITY
3
B C D E F G H
FOOT SWRL/MONO
OUTPUT
MUSIC SEQUENCER
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System

18
Guided Tour
• MIDI data storage device
This setup is used for backing up your important data — including original
Performances you’ve created, as well as settings you’ve changed in the Part
Edit, Effect, EQ, or Utility modes.
In this example, a Yamaha MDF2 MIDI Data Filer is used. To back up
data, connect the MIDI IN of the MDF2 to the MIDI OUT of the MU100R.
To restore the data to the MU100R, connect the MIDI OUT of the MDF2 to
the MIDI IN of the MU100R. Refer to the owner’s manual of the MDF2 (or
your particular data storage device) for specific operating instructions in
receiving or sending data.
With the MDF2, you can also play compatible song data on the MU100R
directly from the MDF2 itself, without the need of a sequencer. In this case,
the MIDI OUT of the MDF2 should be connected to the MIDI IN of the
MU100R.
• Computer equipped with a MIDI interface
In this setup, you can control the MU100R from a computer (using sequenc-
ing or other song playback software). In a variation on this, you can connect
the computer to MIDI-A and a keyboard to MIDI-B. This allows you to play
parts live over sequencer playback — even if the sequencer uses all 16 MIDI
channels.
MDF2
MIDI IN
MIDI OUT
MIDI CABLE
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN-A
MIDI CABLE
Computer

Guided Tour
19
Operation
1 Set the HOST SELECT switch to MIDI.
2 Connect the MU100R to the appropriate MIDI device.
Refer to the illustrations above. Use a standard MIDI cable (see
page 92).
3 Turn on the the connected device, then the MU100R.
4 If you are using a computer, start up your music software, and
set up the appropriate options on the software for operation with
the MU100R.
Connecting Directly to a Computer
The MU100R features a built-in host computer interface, allowing you to
directly connect it to your computer — eliminating the need of installing a
special MIDI interface to your computer. The MU100R can be used with the
following computers: Apple Macintosh and compatibles, IBM PC/AT and
compatibles.
If your computer has a MIDI interface you may want to connect the
MU100R to it, rather than using the host computer interface on the MU100R.
(See the section “Connecting to MIDI Devices” on page 17.)
Depending on the computer or interface used, set the HOST SELECT
switch to the appropriate setting: MIDI, PC-1, PC-2 (IBM and compatibles),
or Mac (Macintosh and compaibles). For information on the types of cables
that can be used for connection, see the section “MIDI/Computer Con-
necting Cables” on page 92.
Macintosh and Compatibles
Follow these instructions if you have an Apple Macintosh not equipped with
an external MIDI interface. Connect the TO HOST terminal on the MU100R
to the Modem or Printer port on the Macintosh.
Modem or
Printer Port
Macintosh
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System

20
Guided Tour
Operation
1 Set the HOST SELECT switch to Mac.
2 Connect the MU100R to the host computer.
Refer to the illustration above. Use a standard Macintosh cable
(8-pin Mini DIN on both ends; see page 92).
3 Turn on the the host computer, then the MU100R.
4 Start up your music software.
If necessary, set up the appropriate options on the software for
operation with the MU100R. The relevant settings may be found
in menu(s) called “Studio Setup,” “System Setup,” or “MIDI
Setup.”
In this menu, you should be able to set separate MIDI outputs to access the
two MIDI ports on the MU100R. For example, the device for MIDI OUT 1
should be set to “Yamaha MU100” (or “MU80,” if “MU100” is not avail-
able).
Other options you may have to set include:
MIDI Interface Type
g
Standard MIDI Interface
MIDI Time Piece
g
On (for controlling all 32 Parts of the MU100R)
Clock
g
1 MHz
(The specific menu/parameter names may differ depending on your particu-
lar music software. For detailed instructions, refer to the owner’s manual or
on-line help of the software.)
Hint
If you have a second multi-timbral tone generator (such as the MU50), you can
connect it to the MIDI OUT terminal of the MU100R and have three independent
MIDI ports (for 48-channel operation). The software settings above apply here as
well: Set the device for MIDI OUT 3 to “Yamaha MU50” (or similar). (For more
information, see page 159.)
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System

Guided Tour
21
IBM PC/AT and Compatible
Serial Port
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System
IBM PC/AT and Compatibles
Follow these instructions if you have an IBM PC/AT or compatible com-
puter not equipped with an external MIDI interface. Connect the TO HOST
terminal on the MU100R to one of the computer’s serial ports, COM 1 or
COM 2.
The instructions below assume you are running Windows95 on your PC. For
using the TO HOST connection with other software and operating systems,
consult your Yamaha dealer. If your computer and music software cannot
recognize the TO HOST connection, you can still use the MU100R by in-
stalling a MIDI interface (internal card or external) to the computer.
Operation
1 Install the included driver software.
For Windows95
Install the included Yamaha CBX Driver for Windows95.
The driver software is on a floppy disk included with the MU100R.
Make sure to thoroughly read the “A:\MIDIDRV\README_E.TXT”
on the disk. This contains essential information on installing and
setting up the driver to your computer.
For Windows3.1
Install the included Yamaha CBX Driver for Windows3.1.
The driver software is on a floppy disk included with the
MU100R. Make sure to thoroughly read the “A:\IBMPC\
CBXT3.WRI” on the disk. This contains essential information on
installing and setting up the driver to your computer.
2 Set the HOST SELECT switch to PC-2.
3 Connect the MU100R to the host computer.
Refer to the illustration above. Use a standard computer cable
(8-pin Mini DIN to 9-pin D-SUB; see page 92).
4 Turn on the the host computer, then the MU100R.

22
Guided Tour
5 Start up your music software.
If necessary, set up the appropriate options on the software for
operation with the MU100R. The relevant settings may be found
in menu(s) called “Studio Setup,” “System Setup,” or “MIDI
Setup.”
In this menu, you should be able to set separate MIDI outputs to access the
two MIDI ports on the MU100R. For example, MIDI OUT 1 should be set
to “Yamaha CBX A Driver” (or “Windows MIDI, Output 1”). Similarly,
MIDI OUT 2 should be set to “Yamaha CBX B Driver” (or “Windows MIDI,
Output 2”).
(The specific menu/parameter names may differ depending on your particu-
lar music software. For detailed instructions, refer to the owner’s manual or
on-line help of the software.)
Hint
If you have a second multi-timbral tone generator (such as the MU50), you can
connect it to the MIDI OUT terminal of the MU100R and have three independent
MIDI ports (for 48-channel operation). The software settings above apply here as
well: Set MIDI OUT 3 should be set to “Yamaha CBX C Driver” (or “Windows MIDI,
Output 3”). (For more information, see page 159.)
Once you’ve set up the MU100R in your system, check that the MU100R is
properly receiving data.
Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System

Guided Tour
23
Selecting and Playing the Performances
As pointed out on page 43, the Performances of the MU100R let you play
four Voices together over one MIDI channel. These specially programmed
Performances (100 Preset and 100 Internal) take full advantage of the
MU100R dynamic Voices and flexible editing functions — giving you ex-
ceptionally powerful and expressive sounds for live performance situations.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Call up the Performance mode.
© Select and play Performances.
Calling Up the Performance Play Mode and
Playing the Performances
Operation
1 Press the [MODE] button.
2 Select “PFM” (PERFORMANCE) in the display.
Use the [SELECT -/>] buttons, [VALUE -/+] buttons or data
dial.
The Performance mode setting is also shown by the arrow at the
bottom right of the display.
NOTE
For more information on the sound module modes, see page 6.
Indicates Performance mode.
Selecting and Playing the Performances
XG
TG300B
C/M
PERFORM

24
Guided Tour
3 Press the [PLAY] button to go to the Performance Play mode.
You can press the [EXIT] button for this as well.
If the All Part display above (with the keyboard player icon) is not
shown, press both [PART-/+] buttons simultaneously.
4 Select the desired bank of Performances — Preset or Internal.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Bank parameter,
then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons to select the desired bank,
Preset (Pre) or Internal (Int).
• Preset bank
• Internal bank
“All” and keyboard player icon indicate All Part display
of Performance Play mode.
The upper body of the keyboard player icon is black,
indicating the Preset bank.
The upper body of the keyboard player icon is
white, indicating the Internal bank.
Selecting and Playing the Performances

Guided Tour
25
5 Select the desired Performance.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Program Number
parameter, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to
select the desired Performance number.
6 Play the connected MIDI keyboard.
Make sure that your keyboard is transmitting over MIDI channel
1. (Refer to the owner’s manual of that instrument if necessary.)
If you’ve carefully followed all instructions up to now, the “level
meter” bars in the display should move — and you should be
able to hear the sound of the MU100R as you play.
Go on to select other Performances in the same bank and play those
as well. To try out Performances in the other bank, return to step #4
above.
Performance number
The “level meter” bars indicate the “level” (velocity) of the incom-
ing MIDI data.
These numbers indicate the four Parts of the Performance.
Selecting and Playing the Performances

26
Guided Tour
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices
The MU100R has a stunningly huge variety of Voices — a total of 1267. In
this section, you’ll select and play Voices in the XG mode, which features
1074 different Voices. The MU100R also features a built-in VL tone genera-
tor that provides 256 Voices using the sophisticated Virtual Acoustic Syn-
thesis system (page 63).
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Call up the XG mode.
© Select Voice banks and Voices from the panel controls.
© Change the Play mode display to suit your preference.
© Select and play Voices from a MIDI keyboard.
Calling Up the XG Mode
Operation
1 Press the [MODE] button.
2 Select “XG” in the display.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, [VALUE -/+] buttons or data
dial.
The XG mode setting is also shown by the arrow at the bottom right
of the display.
3 Press the [PLAY] button to go to the Play mode.
You can press the [EXIT] button for this as well.
Indicates XG mode.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices
XG
TG300B
C/M
PERFORM

Guided Tour
27
About the Modes — Multi and Performance
The MU100R has two main operating modes: Multi and Performance. You
used the Performance mode earlier when playing Performances — playing
four Voices over one MIDI channel. The Multi mode is primarily used in
sequencer and computer music applications, since it allows you to play all 32
Parts independently over different MIDI channels.
Which mode the MU100R is set to depends on the selected Sound Module
mode. The XG, TG300B and C/M settings are all Multi mode. When PFM is
selected, the MU100R is in the Performance mode.
Selecting Voice Banks and Voices From the Panel
Operation
1 Select a Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Depending on the selected Part,
one of the displays below will appear:
• For Parts 1 – 16 and the A/D Parts:
• For Parts 17 – 32:
For this example, select Part 1. Press the appropriate button until
“01” appears in the PART section of the display.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices

28
Guided Tour
2 Select the bank number.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the bank number
parameter (as shown below).
3 Change the bank number.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Notice that the
bank numbers “jump” as they are selected — the MU100R skips
bank numbers that have the same Voice as bank “000.”
In the XG mode, several banks of Voices are available. Each bank
contains up to 128 different Voices, for a total of 1074 Voices.
4 Select the program (Voice) number.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program
number parameter (as shown below).
Bank number. Dark arrow
indicates bank number is
selected.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices
Instrument icon. Arrow at top
left of icon indicates bank
number is selected.
Program number.

Guided Tour
29
5 Change the program number.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. In the example dis-
play below, Voice number 25 has been selected.
6 Play the Voice.
Play this new Voice from the connected MIDI keyboard. (Make
sure that the keyboard is transmitting on channel 1.) If you’ve
carefully followed all instructions up to now, the “level meter”
of the Part should move — and you should be able to hear the
sound of the MU100R as you play. Try selecting other Voice
banks and Voices and play them as well. Each Voice bank con-
tains some different Voices, some of which are variations, some
unique.
Details
• The MU100R’s Voices and program numbers follow the GM (General MIDI)
format. This means that you can select a Voice type by its number, then select
Voice variations by bank. For example, all the nylon guitar Voices are at pro-
gram number 25.
• In the XG mode, the Voices are conveniently organized in the banks according
to their type. For example, Voices having stereo variations or brighter variations
are found in the “Stereo” and “Bright” banks, respectively. (See the “Sound List
& MIDI Data” booklet.)
• Banks MSB 48, 46 and above feature Voices that are not simply variations, but
use different instrument samples. (See the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.)
Program number. Dark arrow
indicates program number is
selected.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices
Bank number.
Instrument icon, indicating the type of
Voice. Arrow at top right of icon indi-
cates program number is selected.

30
Guided Tour
• Notice that as you increase the bank number, at some point beyond the XG
Voice banks (above bank 127) the bank number returns to “000” and the fol-
lowing icon appears in the display:
Banks showing this icon are MU100 Exclusive Voice banks, and are different
than the same numbered XG Voice banks. (See the “Sound List & MIDI Data”
booklet.)
• VL Voice banks may also be selected if VL Voice selection for the Part has been
enabled. (See page 69.)
• Though the MU100R skips over bank numbers with identical Voices (see step
#3 above), it can be set to not skip bank numbers, if desired. (See page 160:
Utility mode/System/Display Bank Select.)
Changing the Play Mode Display
The MU100R lets you view the Parts in three ways, depending on your prefer-
ence.
Press the [PLAY] button repeatedly.
Each press of the [PLAY] button switches among the three displays below.
1) Full level meters
2) All Parts, with half level meters
3) All Parts, with full level meters
This shows the level meters at their maximum height,
but only displays half of the Parts.
This displays all Parts, but the level meters are at half the height.
This displays all Parts with the level meters at maximum height.
However, the Voice name and number are not displayed.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices

Guided Tour
31
Selecting Voices From a MIDI Keyboard
You can also select Voices remotely from a connected MIDI keyboard. Though
the actual operation may differ depending on the keyboard used, the general
procedure is the same. These instructions also apply to use with a computer.
(Refer to the owner’s manual of your specific instrument or software for
detailed instructions.)
Operation
1 Make the necessary settings on the keyboard.
Make sure that the keyboard is set to transmit over the desired
MIDI channel (the same as that of the selected Part), and that it
is set up to send Program Change messages.
2 Select a program number on the keyboard.
The Voice number and name on the MU100R will change, and
will be the same number as the program number you selected
on your keyboard.
Details
• Depending on what keyboard you are using to control the MU100R, you may
need to be careful in selecting program numbers. The MU100R’s program num-
bers start at “001,” but some keyboards have different numbering systems. For
example, some start at “0” — which means that selecting “25” on the keyboard
will select Voice 026 on the MU100R.
• Part 10 is reserved for playing drum “kits.” This is the default factory setting for
all of the Multi modes (XG, TG300B, and C/M). For more information on drum
Parts, see page 39.
Selecting and Playing Individual Voices

32
Guided Tour
Editing in the Multi Mode
This section takes you step-by-step through an example editing session in
the Multi mode. The operations and techniques you learn here enable you to
perform any editing operation in the Multi mode.
There are two separate sections of the Multi mode that are devoted to
editing: the Single/All Part controls, and the Edit menus.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Select a Part for editing.
© Use the Single Part controls — to change the MIDI channel of a Part, and
change its Volume and Pan settings.
© Use the Edit menu parameters — to change the filter and EG (Envelope
Generator) settings of a Part.
© Use the Drum Setup controls — to edit change the Part settings for a
drum kit.
Hints
• Editing Parts, not Voices
It is important to remember that in editing you are not changing the Voice itself,
but rather the Part the Voice is assigned to. This means that when you change the
Voice of the Part, the edited settings apply to the new voice, whether they’re
appropriate or not.
You can use this to your advantage by recording all Multi settings to your se-
quencer, before the actual song data. This lets you instantly reconfigure the
MU100R and all its settings for each song.
• Saving your edits
Keep in mind that any edits you make in the Multi mode are automatically saved
as the power on defaults. In other words, the next time you turn on the power, the
previous condition of all Parts is automatically recalled. If you want to save one
“set” of edits (for example, for use with a specific song) before creating another
set, you must first save the current setup to a sequencer or MIDI data filer. (For
details, see page 161.)
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
33
Single Part Controls
You can make changes to each individual Part by using the Single Part con-
trols. These are displayed in the Multi Play mode, and give you at-a-glance
confirmation and control of the important basic settings of the selected Part.
If the Multi mode was active when you last turned the power off, the next
time you turn the power on, the Single Part controls are automatically called
up.
Let’s take a look at the Play display again:
PART MIDI
BANK/PGM#
VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY
Each of these settings are made independently for each Part. For example,
each Part could have a different Volume setting, or a different Pan setting.
Try going through the brief sections below and making some changes in the
Part controls yourself.
Voice name, bank number and program number.
Note Shift
(key transpose).
Chorus Send.
Reverb Send.
Variation Send.
Pan (stereo position).
Expression.
MIDI receive
channel.
Volume.
Part number. (Change this with the [PART -/+] buttons.)
Editing in the Multi Mode

34
Guided Tour
Changing the Volume and Pan settings of a Part
Here, we’ll change the Volume and Pan settings of one Part’s Voice.
Operation
1 Select the desired Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons to select Part 1.
2 Select the desired control.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Volume control.
3 Change the setting.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial, and play the key-
board as you edit so you can hear the change in the sound.
Now, let’s change the Pan setting for the Part:
4 Select the desired control.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Pan control.
5 Change the setting.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to change the set-
ting, and play the keyboard again as you make changes.
6 Return to “home base.”
Pressing the [EXIT] button from any of the Single Part controls
automatically returns to the Voice name/program number dis-
play. This is a convenient way to instantly return to “home base”
from a “distant” control.
Current Volume setting.
Current Pan setting.
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
35
On Your Own...
If you want to, try making changes to some of the other Part controls. The
procedure is the same:
1) Select a Part with the [PART -/+] buttons.
2) Select a control for editing with the [SELECT </>] buttons.
3) Change the setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
4) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to “home base” — Voice name
and number.
Hint
• You can easily edit the same control for different Parts. To do this, simply remain
at the selected control and use the [PART
-
/
+
] buttons to change the Part to be
edited.
• Setting different Parts to the same MIDI channel is a way to build “fat,” richly
textured sounds — like the four-Voice sounds created in the Performance mode.
The advantage to this method here is that you are not limited to four Voices. The
disadvantage is that you can only create and use one of these “monster” sounds
at a time. (However, you can store/load your Multi mode settings to/from a com-
puter or data filer; see page 17.)
To do this:
1) Select the desired Part (by using the [PART
-
/
+
] buttons).
2) Select the Receive Channel (“Rcv CH”) control (by using the [SELECT
<
/
>
]
buttons).
3) Set the Receive Channel value (by using the [VALUE
-
/
+
] buttons or data dial).
4) With the Receive Channel still selected, select a different Part (with the [PART
-
/
+
] buttons), and set it to the same value as the other Part.
5) Repeat step #4 above for as many other Parts as desired.
For example, if you’ve set both Parts 1 and 2 to MIDI channel 1, both of their “level
meters” should move together as you play. And, if the two Parts are set to different
Voices, you should hear two different Voices sound at the same time. (For instruc-
tions on changing the Voice for a Part, refer back to “Selecting and Playing Indi-
vidual Voices” on page 26.)
For more information on the specific Part controls, see page 96.
All Part controls
The instructions in this section show you how to change the settings for indi-
vidual Parts; these are the Single Part controls. The All Part controls, on the
other hand, let you change certain global settings affecting all the Parts.
To select the All Part controls, simultaneously press both [PART -/+] but-
tons. (For more information on the All Part controls, see page 98.)
Editing in the Multi Mode

36
Guided Tour
Edit Menu Parameters
The Edit menu parameters provide more detailed and advanced controls over
the Parts. These are powerful tools that let you subtly enhance or fine-tune
the sound of a Voice — or radically change its character for some wild and
unique sounds.
Changing the Filter and EG Settings of a Part
Operation
1 Select the desired Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Also, for the sake of these in-
structions, select the “SquareLd” Voice, #081. (See page 27.)
2 Call up the Edit menu.
Press the [EDIT] button.
3 Select “FILTER” in the display.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. The Edit menu has five items:
FILTER, EG (Envelope Generator), EQ (Equalizer), VIBRATO, and
OTHERS. The “flag” next to the item flashes when selected.
Details
• When a drum Part is selected, the EQ menu item is replaced by “DRUM.” (See
page 114 for information on editing drum Parts.)
• When a VL Voice Part is selected, the “PLUGIN” menu item also appears in the
display.
4 Call up the Filter parameters.
Press the [ENTER] button.
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
37
5 Select the “LPF Cutoff” parameter.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons.
6 Adjust the value while listening to the sound.
Hold down a note on the connected keyboard and turn the data dial
to adjust the value, swinging between the maximum (+63) and
minimum (-64) values. Notice how the timbre of the sound changes.
Before going to the next step, set LPF Cutoff to “+63.”
7 Select “LPF Reso” and change the value.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. Then, do the same as you did in the
last step, holding a note and changing the value with the data dial.
Hint
• Try holding notes or chords in different octaves of the keyboard as you adjust the
parameters, since the Filter effects depend on the pitch or frequency of the sound.
Details
• The effect of the Filter parameters also differs depending on the selected Voice.
(For more information on the Filter parameters, see page 100.)
Now, let’s change one of the EG parameters:
8 Go back to the Edit menu.
Press the [EXIT] button.
9 Select and call up “EG.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “EG,” then press the
[ENTER] button.
; Select the “Attack Time” parameter.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons.
The bars graphically indicate pa-
rameter values for each Part.
Editing in the Multi Mode
Indicates additional parameters
are available (to the right).
Indicates no other parameters
are available (to the left).
Selected Part
flashes.

38
Guided Tour
a Adjust the value while listening to the sound.
Try setting this to around “+30” and play the keyboard. Notice
how the attack of the sound has become slower.
b Select and adjust the “Release Time” parameter.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then set this to around “+50.”
Play some notes on the keyboard and release them. Notice how the
sound sustains after you release each key.
Details
• The effect of the EG parameters differs depending on the selected Voice. (For
more information on the EG parameters, see page 102.)
On Your Own...
While you’re at it, try making changes to some of the other Edit parameters.
The procedure is the same:
1) Select the desired Part with the [PART -/+] buttons.
2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button.
3) Select the desired menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press
[ENTER].
4) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and
change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
5) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu.
Hint
You can select different Parts (by using the
[PART -/+]
buttons) at any point in the
editing session, no matter which Edit menu or parameter is selected. This lets you
quickly shuttle among the various parts and effectively edit the desired parameters.
The selected Part is always indicated at the bottom left of the display.
For more information on the specific Edit parameters, see page 100.
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
39
Editing Drum Kits — with the Drum Setup Controls
The Drum Setup controls provide a comprehensive set of tools for control-
ling and changing the drum kit Voices. Many of these parameters can be set
individually for each sound in a Drum Part. Up to four of your original edit-
ing setups can be permanently stored.
Unless you’ve set them otherwise, Parts 10 and 26 are automatically set
to play a Drum Part and the MIDI channel for both is set to 10. (General
MIDI song data is standardized for playing drum/percussion sounds over
channel 10.)
For the sake of these instructions, we’ll simply select Part 10 and edit the
existing Drum Part. However, you can set up additional Drum Parts on any
of the Part numbers; refer to the box section below.
Remember that once a Part is assigned a Drum Part, different drum kit
Voices can be selected. (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.)
Assigning a Drum Part
This operation allows you to assign a Drum Part to any of the Part numbers —
letting you use two or more different drum kits within the same song.
1. Select the desired Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons.
2. Call up the Edit menu.
Press the [EDIT] button.
3. Select and call up the OTHERS menu.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER].
4. Select the Part Mode parameter.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons.
5. Set the parameter to “drumS1.”
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. As long as you select one of
the “drum sets” (drumS1 – drumS4), any edits you make will automatically
be saved to the selected set.
Details
• The “normal” setting is for normal Voices; the “drum” setting selects the
Drum Part, but cannot be edited. (For more information on the Part Mode,
see page 108.)
6. Press the [EXIT] button.
Press it once to return to the Edit menus, twice to return to the Play dis-
play.
Editing in the Multi Mode

40
Guided Tour
Making Changes to Individual Drum Sounds — the “Drum” Parameters
The Drum parameters provide extraordinary flexibility, since they allow you
to make independent settings for the individual drum/percussion sounds in a
Drum Part. We’ll explore a couple of the possiblilities here:
Operation
1 Select “DRUM” from the Edit menus (with the [SELECT </>]
buttons) and press [ENTER].
2 Select “E3: Conga L.”
Play E3 on the connected MIDI keyboard, or use the [PART -/
+] buttons to select “E3.”
Details
• In the Drum parameters you cannot use the
[PART -/+]
buttons to select a
Part; they are reserved for selecting notes/sounds only.
3 Select the Pitch Coarse parameter, and set it to “-22.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then the
[VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. This setting creates a deep
log drum sound.
4 Select the Velocity Pitch Sensitivity parameter (VelPchSens), and
set it to “+12.”
Again use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then the [VALUE -/+]
buttons or data dial. Play the key softly to strongly and notice
how the pitch changes according to key velocity.
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
41
5 Select “F#3: Timbale L.”
Play F#3 on the connected keyboard, or use the [PART -/+]
buttons to select “F#3.”
6 Select the LPF Cutoff parameter, and set it to –40.
7 Select the LPF Resonance (LPF Reso) parameter, and set it to
+63.
8 Select the Velocity LPF Sensitivity parameter (VelLPFSens), and
set it to +16.
Play the key softly to strongly and notice how key velocity
changes the timbre of the sound for a “wah-wah” effect.
More Drum Editing
Try some of the other parameters in the edit menus (FILTER, EG, VIBRATO,
OTHERS) on your own and hear how they affect the drum sounds. Keep in
mind that these are applied to the entire Part, and cannot be set individually
for each sound.
As a springboard for further exploration, try editing the following parameters
in the OTHERS menu:
1. With a drum Part selected, call up the OTHERS parameters.
Press [EDIT], select “OTHERS,” then press [ENTER].
2. Select “PitBndCtrl” and set the value to +24.
Play with the pitch bend wheel on the connected keyboard while playing
different keys.
3. Select “MW LFOPMod” and set the value to 090.
Play with the modulation wheel on the connected keyboard while playing
different keys.
Select and change other parameters in the same way.
NOTE
Some of the parameters (such as Release Time in the EG menu) may not have
any affect on the drum sounds at all. Also, the effect of a parameter may differ
depending on the specific drum sound. (For more information on editing Drum
Parts, see page 114.)
Editing in the Multi Mode

42
Guided Tour
On Your Own...
1) Select a Drum Part with the [PART -/+] buttons.
2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button.
3) Select the “DRUM” menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press
[ENTER].
4) Select the desired drum sound, either by playing the corresponding key
of the MIDI keyboard or by using the [PART -/+] buttons.
5) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and
change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
6) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu.
Hint
Use of a connected MIDI keyboard is an exceptionally fast and convenient way to
edit Drum Parts. It not only lets you quickly shuttle among the various sounds while
editing, it also lets you hear the sound being edited and see the sound name.
For more information on the specific Drum parameters, see page 114.
Editing in the Multi Mode

Guided Tour
43
Editing in the Performance Mode
The Performance mode is an exceptionally powerful and flexible mode that
allows you to combine four different Voices (including both A/D inputs) and
play them from a single MIDI channel.
The potential applications of the Performance mode are enormous, and
we’ll touch on some of the main ones here. As the name suggests, the Per-
formance mode is primarily intended for live performance situations. The
four Voices can be played altogether in a huge, “fat” layer, or can be split
across the keyboard in different zones, or can be switched according to key
velocity.
A total of 200 Performances are available: 100 Preset, which are reserved
for only factory settings, and 100 Internal, to which you can save your own
original Performances.
This section takes you step-by-step through an example editing session
in the Performance mode. The operations and techniques you learn here
enable you to perform any editing operation in the Performance mode.
As with the Multi mode, the Performance mode has two separate sec-
tions that are devoted to editing: the Single/All Part controls, and the Edit
menus.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Use the All Part controls — to transpose the overall key of a Performance.
© Use the Single Part controls — to select different Voices for the
Performance.
© Use the Edit menu parameters to create a “fat” two-Voice sound.
© Use the Mute/Solo button for effective editing.
© Set up a keyboard split — with individual Voices playable from different
sections of the keyboard.
© Set up a Performance for “playing” filter sweeps with the modulation
wheel on your keyboard.
© Save your original Performance.
Editing in the Performance Mode

44
Guided Tour
All Part Controls
You can make changes to the overall Performance by using the All Part con-
trols. These are displayed in the Performance Play mode, and give you at-a-
glance confirmation and control of some important basic settings of the se-
lected Performance.
In the Performance mode, the All Part controls are automatically called
up whenever you turn the power on or select the Performance mode.
Let’s take a look at the All Part Performance Play display:
PART MIDI
BANK/PGM#
VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY
For more information on the All Part controls, see page 128.
Performance name, bank (Preset or Internal), and
program number.
System Transpose
(key transpose
setting for entire
Performance).
Reverb Return.
Variation Return.
Performance Pan
(stereo position of entire Performance).
Expression
(not available; always set to maximum).
System Channel (MIDI receive channel for entire Performance).
Performance Volume.
Indicates All Part control.
Chorus Return.
Editing in the Performance Mode

Guided Tour
45
Transposing the Overall Key of a Performance
In this example, you’ll change the System Transpose setting for the “Rich
Piano” Performance. This All Part control is useful for instantly changing
the key to match the range of a vocalist, or for ease in playing difficult keys.
Operation
1 Select the “Rich Piano” Performance.
First select the Preset bank (“Pre”), then select Performance
number 002 (“Stereo Grand”). (For instructions on selecting Per-
formances, see steps #4 and #5 on page 24.)
2 Select the System Transpose control.
Use the [SELECT >] buttons to move the cursor arrow to the ap-
propriate control. (“SysTran” appears in the display.)
3 Change the System Transpose setting as desired.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. (The “+00” setting
is normal; ±“12” is up/down one octave.)
Play the connected keyboard and try other transpose settings as you
play.
Current System transpose setting (in semitones).
Editing in the Performance Mode

46
Guided Tour
Single Part Controls — Selecting Different
Voices for the Performance
In this next section, you’ll use the Single Part controls to change the Voice
settings of the Performance.
Operation
1 Call up the Single Part controls.
Simultaneously press both [PART -/+] buttons.
PART MIDI
BANK/PGM#
VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY
For more information on the Single Part controls, see page 129.
2 Select the desired Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons.
Keep in mind that you should select only from the active Parts —
the ones with a dark bar in the display. Other Parts can be selected
and changed; however, they will not sound in the Performance.
3 Select the desired bank and Voice.
Do this in the same way as you did in the Multi mode. (See steps
#2 and #3 on page 28.)
Performance name, bank (Preset or Internal), and
program number.
Note Shift
(key transpose
setting for
selected Part).
Reverb Send.
Variation Send.
Part Pan
(stereo position of selected Part).
Expression
(not available; always set to maximum).
(Not available in Single Part.)
Part Volume.
Selected Part number. (Change this with the [PART -/+] buttons.)
Chorus Send.
Indicates active Part(s) of the
Performance.
Editing in the Performance Mode

Guided Tour
47
Details
• Drum Parts are not available in the Performance mode. However, percussive
Voices (numbers 113 – 120) can be selected.
When editing a Performance:
• Decide how many Parts you want.
When creating a Performance, choose a preset that uses the same number of
Parts (Voices) you intend to use. (You can easily tell how many Parts a Per-
formance has by looking at the “level meters”; a dark bar appears above the
Part numbers that are active.)
• Start with a similar sound.
When editing, it’s a good idea to start with a sound that’s relatively similar to
the one you intend to create. For example, if you want to create an soft, ethe-
real strings pad, you probably wouldn’t start with a brash preset such as
“Dance Chord”! This is not a hard and fast rule, however, since each preset is
only a basic “template” over which you can easily change Voices and create a
completely different sound.
On Your Own...
If you want to, try making changes to some of the other Part controls. The
procedure is the same:
1) Select a Part with the [PART -/+] buttons.
2) Select a control for editing with the [SELECT </>] buttons.
3) Change the setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons.
4) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to “home base.” (When editing
in Single Part, pressing once returns to Voice name and number; pressing
once again returns to All Part.)
For more information on the specific Part controls, see page 96.
Editing in the Performance Mode
Two active Parts

48
Guided Tour
Edit Menu Parameters — Creating a Two-Voice Layer
Editing a Performance is almost identical to editing Parts in the Multi mode.
The Edit menu tree is slightly different, and certain parameters are different
as well. (For a full list and description of Performance Edit parameters, see
page 131.)
In the following instructions, you’ll use the Edit menu parameters to cre-
ate a two-Voice Performance and “fatten” the sound using Detune.
Operation
1 Select the desired Performance.
For this example, select the Preset bank, then Performance
number 027, “Jump-off.”
2 Select Part 1.
Call up the Single Part controls (simultaneously press both
[PART -/+] buttons), then select Part 1.
3 Solo the selected Part.
Press the [MUTE/SOLO] button twice (or repeatedly until the
display below appears) to solo the selected Part.
Dark bar indicates Part 1 is being soloed.
Editing in the Performance Mode
Using Mute/Solo for effective editing:
The [MUTE/SOLO] button is a convenient tool, especially in editing Perform-
ances. Make sure that the Single Part controls are selected, then use the button
to switch among the following three conditions. (In All Part, the [MUTE/
SOLO] button simply mutes/un-mutes all Parts.)
Mute: Lets you hear what the other Parts of the Performance sound
like, minus the selected Part.
Solo: Lets you hear what the selected Part sounds like by itself.
Normal: Lets you hear all Parts together.
Use this function regularly as you edit the sound. While you’re editing, you should
solo the Part, so you can clearly hear the changes. Make sure to frequently use
Normal (all Parts on), so you can hear the total effect of your edits.
For more on Mute/Solo, see page 85.

Guided Tour
49
4 Select Part 1 and select a new Voice for it: “HeavySyn” (082).
5 Select Part 2 and select the “HeavySyn” Voice for it as well.
6 Select the “OTHERS” parameters.
Press the [EDIT] button. From the first Edit menu, select and call
up “PART,” then select and call up “OTHERS.”
7 Select and set the Detune parameter for Part 2.
Use the [SELECT <] buttons to select the parameter, then the
[VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. With Part 2 selected, in-
crease this to “+2.2.”
8 Set the Detune parameter for Part 1.
Keep the display at the Detune parameter and select Part 1. De-
crease this setting to “–2.2.”
This produces a “fat” layered sound. You can check how much
this changes the sound by exiting to the Single Part display and
using [MUTE/SOLO] button to listen to the Parts by themselves
and together.
Now, try changing some other parameters.
9 Exit to the second Edit menu and call up the “VIBRATO” param-
eters.
Press the [EXIT] button once, then select and call up the “VI-
BRATO” parameters.
First Edit menu.
Second Edit menu.
Editing in the Performance Mode

50
Guided Tour
; Change the Vibrato Rate, Depth, and Delay settings.
Select one of the Parts and set the Vibrato parameters as follows:
Rate: +15
Depth: +04
Delay: +15
This produces a delayed vibrato for Part 1; in other words, the
vibrato effect starts after the keys have been held for a while.
Notes played staccato have no vibrato.
a Exit back to the Single Part control display.
Press the [PLAY] button.
Setting Up a Keyboard Split
In the following steps, you’ll assign two different Parts to separate sections
of the keyboard.
Operation
1 Select Part 2 and select a new Voice for it: “NewAgePd” (089).
From the Single Part display, use [PART -/+] buttons to select
Part 2. Then select Voice 089 in the normal way. (Keep Part 1’s
Voice set to “HeavySyn,” 082, as set in step #4 of “Creating a
Two-Voice Layer” above.)
2 Change the Note Limit High setting for Part 1.
The Note Limit parameters determines the range of notes over
which the Part will sound. To set this:
1) In Edit menu select and call up the “PART” menu, then do
the same with the “OTHERS” menu.
2) Select Part 1.
3) Select and change the “NoteLimitH” setting to “B2.” (Leave
the “NoteLimitL” setting unchanged.)
3 Change the Note Limit Low setting for Part 2.
1) Select Part 2.
2) Select and change the “NoteLimitL” setting to “C3.” (Leave
the “NoteLimitH” setting unchanged.)
Playing notes below middle C on the keyboard plays the synth bass
sound, while notes above middle C play the “New Age” pad.
Hint
• You may want to raise the octave setting of Part 1. To do this, exit to Single Part,
select Part 1, then use the
[SELECT >]
buttons to select the Note Shift control.
For a higher “HeavySyn” Voice, set this to “+00.”)
Editing in the Performance Mode

Guided Tour
51
If you wish to save this newly created Performance, refer to “Saving
Your Original Performance” on page 52.
On Your Own...
While you’re at it, try making changes to some of the other Edit (part) pa-
rameters. The procedure is the same:
1) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button.
2) Select “PART” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER].
3) Select the desired menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press
[ENTER].
4) Select the desired Part with the [PART -/+] buttons.
5) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and
change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
6) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu.
Using the Assignable Controller in a Performance
In this section, you’ll set up a Performance in which the modulation wheel
on your connected keyboard can be used to “play” dynamic filter sweeps.
This is done with the Assignable Controller functions. Here, we’ll simply
show you what steps to follow; for more detailed information on the Assign-
able Controller and using it in the Multi mode, refer to page 59.
Operation
1 Select the “Dark Pad” Performance (Preset #025).
2 Select and call up “COM” (Common) from the first Edit menu.
3 From the Common menu, select the “AC1 CC No.” parameter
and set it to “01.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then use the [VALUE -/+]
buttons or data dial.
4 Select the “AC1FilCtrl” parameter and set it to “+63.”
5 Select Part 1 and change some of its Filter settings.
The Filter settings determine how the Part responds to the
“AC1FilCtrl” setting above. To set these:
1) In Edit menu select and call up the “PART” menu, then do
the same with the “FILTER” menu.
Editing in the Performance Mode

52
Guided Tour
2) Select Part 1.
3) Select and change these parameters:
LPF Cutoff: –64
LPF Reso: +50
Provided your connected keyboard has a modulation wheel (most
do), and all other settings are appropriate, you can create wide, dy-
namic filter sweeps by holding notes and moving the modulation
wheel.
Saving Your Original Performance
Once you’ve edited a Performance, you can give it a different name and save
it for future recall. The MU100R has 100 Internal memory locations for
your original Performances.
For instructions on naming a newly created Performance, see page 132.
Operation
1 Press the [EDIT] button.
2 Select “STORE.”
Either Preset or Internal Performances can be edited, but they can
only be saved to the Internal bank.
3 Select a different Internal number, if desired.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
4 Press the [ENTER] button to save the Performance, or press the
[EXIT] button to cancel.
Saving the new Performance will erase the old one. You can re-
store the factory-programmed Internal Performances from in-
cluded floppy disk.
Editing in the Performance Mode

Guided Tour
53
Assignable Controller (AC1)
The Assignable Controller (AC1) is one of the more powerful features of the
MU100R — it gives you extraordinarily flexible and expressive real-time
control over the Voices.
In this section, you’ll:
© Learn about MIDI controllers and control numbers, and how they can
affect the Voices.
© Set up your system for using the Assignable Controller.
© Try out some specific controller application examples, such as:
* Varying degrees of brightness on a Part
* Filter sweep and “wah” effects
* “Expression pedal” control of volume
* Variable filter control of specific drum sounds
Hint
A good way to introduce yourself to some of the Assignable Controller applications is to
explore the Performances — many of them feature Assignable Controller settings that let
you change some aspect of the sound (usually with the modulation wheel on the con-
nected keyboard). (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet, and select/play Per-
formances that mention “MW” in the “Description” section of the lists.)
Controllers and Control Numbers
In the MIDI world, “controllers” are used to change some aspect of the sound.
In this section, we’ll work with “continuous” controllers — so named be-
cause they let you add musical, expressive effects that change smoothly over
time (such as crescendos and decrescendos).
The illustration below shows some continuous controllers you’re likely
to see on a MIDI keyboard.
NOTE
Your own MIDI instrument may not have all the controllers shown in the illustration.
Assignable Controller (AC1)
Modulation wheel
Volume pedal
Foot controller
Breath controller
Data entry slider
MIDI Keyboard

54
Guided Tour
The actual, physical means of controlling (such as foot pedals, modulation
wheels, etc. on a connected keyboard) are generally assigned to specific
“virtual” control numbers. A few examples of these include the modulation
wheel (at control number 1), foot controller (control number 4), and volume
pedal (control number 7).*
Control Numbers and the Actual Sound
The control numbers described above are in turn assigned to some specific
aspect of the sound on the connected tone generator (for example, to vol-
ume, pitch modulation, dry/wet balance of an effect, etc.). As you might
expect, control number 7 (Volume) affects the volume of the connected tone
generator.
Physical controller
(volume pedal)
In this example, the foot controller of a keyboard controls the volume on the MU100R.
Assignable Controller (AC1)
* On some instruments, the control number for the physical controllers
is fixed; some instruments allow you to assign a different control
number to the existing control. (Refer to the owner’s manual of your
instrument for details. Also for more on control numbers, see the list
on page 126 of this manual, and the “Sound List & MIDI Data” book-
let.)
STOP CONTINUE START
SOUND
OFF
MERGE
ON/OFF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0
TRANSPOSE
HEXA
DECIMAL
DECIMAL
DC IN
OCTAV E
OCTAVE SHIFT
OCTAV E
RESET
PITCH
ASSIGNABLE
IN MIDI OUT
ENTER
DRUM
NUMBER
NRPN
CONTROLLER
RPN
FIXED
VELOCITY
MIDI
CH
PROGRAM
CHANGE
BANK
SELECT
TEMPO
PROGRAM RESET SYSTEM WHEEL ASSIGNSEQUENCER
POWER ON OFF
SHIFT
GM
ON
XG
ON
MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1
CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST
122 COARSE TUNING
(NRPN)
(RPN)
120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY
121 FINE TUNING
123 VIBRATO RATE
124 VIBRATO DEPTH
125 VIBRATO DELAY
126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
127 FILTER RESONANCE
128 EG ATTACK TIME
129 EG DECAY TIME
130 EG RELEASE TIME
131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE
133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE
134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE
135 DRUM PITCH COARSE
136 DRUM PITCH FINE
137 DRUM LEVEL
138 DRUM PAN
139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH
140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH
141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH
142 CHANNEL PRESSURE
143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE
144 MASTER VOLUME
145 MASTER BALANCE
146 MASTER TUNING
147 VELOCITY
148 TEMPO
OTHERS
74 BRIGHTNESS
84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL
91 REVERB DEPTH
92 TREMOLO DEPTH
93 CHORUS DEPTH
94 VARIATION DEPTH
95 PHASER DEPTH
73 ATTACK TIME
1 MODULATION DEPTH
5 PORTAMENTO TIME
6 DATA ENTRY
7 MAIN VOLUME
8 BALANCE CONTROL
10 PANPOT
CONTROL CHANGE
2 BREATH CONTROL
4 FOOT CONTROL
64 HOLD1(DAMPER)
65 PORTAMENTO
66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD)
67 SOFT PEDAL
69 HOLD2 (FREEZE)
71 HARMONIC CONTENT
72 RELEASE TIME
11 EXPRESSION
“Virtual” controller:
control number 7
(MIDI Volume)
STOP CONTINUE START
SOUND
OFF
MERGE
ON/OFF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0
TRANSPOSE
HEXA
DECIMAL
DECIMAL
DC IN
OCTAVE
OCTAVE SHIFT
OCTAVE
RESET
PITCH
ASSIGNABLE
IN MIDI OUT
ENTER
DRUM
NUMBER
NRPN
CONTROLLER
RPN
FIXED
VELOCITY
MIDI
CH
PROGRAM
CHANGE
BANK
SELECT
TEMPO
PROGRAM RESET SYSTEM WHEEL ASSIGNSEQUENCER
POWER ON OFF
SHIFT
GM
ON
XG
ON
MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1
CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST
122 COARSE TUNING
(NRPN)
(RPN)
120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY
121 FINE TUNING
123 VIBRATO RATE
124 VIBRATO DEPTH
125 VIBRATO DELAY
126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
127 FILTER RESONANCE
128 EG ATTACK TIME
129 EG DECAY TIME
130 EG RELEASE TIME
131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY
132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE
133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE
134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE
135 DRUM PITCH COARSE
136 DRUM PITCH FINE
137 DRUM LEVEL
138 DRUM PAN
139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH
140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH
141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH
142 CHANNEL PRESSURE
143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE
144 MASTER VOLUME
145 MASTER BALANCE
146 MASTER TUNING
147 VELOCITY
148 TEMPO
OTHERS
74 BRIGHTNESS
84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL
91 REVERB DEPTH
92 TREMOLO DEPTH
93 CHORUS DEPTH
94 VARIATION DEPTH
95 PHASER DEPTH
73 ATTACK TIME
1 MODULATION DEPTH
5 PORTAMENTO TIME
6 DATA ENTRY
7 MAIN VOLUME
8 BALANCE CONTROL
10 PANPOT
CONTROL CHANGE
2 BREATH CONTROL
4 FOOT CONTROL
64 HOLD1(DAMPER)
65 PORTAMENTO
66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD)
67 SOFT PEDAL
69 HOLD2 (FREEZE)
71 HARMONIC CONTENT
72 RELEASE TIME
11 EXPRESSION
POWER
ON/ OFF
MIDI Keyboard
MIDI OUT
MIDI Keyboard
MU100R
MIDI IN
MIDI OUT

Guided Tour
55
Assigning the Assignable Controller
The Assignable Controller on the MU100R lets you specify the control num-
ber to be used and determine which aspect or aspects of the sound will be
affected. It also lets you set the degree to which the controller affects the
sound.
The best way to understand all this is to go through some actual examples,
so go on to the next section and set up your system:
Physical Controllers Controllers Parameters
Modulation wheel,
Foot controller,
Breath controller, etc.
Filter Control
Amplitude (level) Control
Variation Effect Control
Insertion 1 Effect Control
Insertion 2 Effect Control
(In Performance mode:)
Filter Control
Amplitude Control
LFO Filter Modulation Depth
Assignable Controller (AC1)

56
Guided Tour
Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up
Operation
1 Set up the MIDI keyboard or instrument.
Connect the foot controller to the appropriate jack, and make
sure that the instrument is set to transmit over MIDI channel 1.
(If your instrument doesn’t have a foot controller, use another
controller as described in the next step.)
2 Select the desired Part.
From the Multi Play mode, use the [PART -/+] buttons. For
the sake of these instructions, select Part 1.
3 Call up and set the Assignable Controller number.
The control number of your instrument’s controller must match
the Assignable Controller control number. In this example and
all the following instructions in this section, we’ll use the foot
controller. Since the foot controller is control number 4, the As-
signable Controller must be set to “04.”
To do this:
1) Press the [EDIT] button.
2) Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “OTHERS,” then
press [ENTER].
3) Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “AC1 CC No.”
4) Set the value to “04” with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data
dial.
If you don’t have a foot controller, you can use another controller,
such as the modulation wheel (01) or volume pedal (07) — making
sure that the Assignable Controller number matches.
Keep in mind that this setting applies only to the selected Part.
Other Parts can have separate control number settings.
Assignable Controller (AC1)
ATTACK
PHONES L/MONO
OUTPUT
R DC IN POWER
FOOT
VOLUME
FOOT
CONTROLLER
FOOT
SWITCH
TO HOST HOST SELECT IN OUT
MIDI
THRU
AMP EG
RELEASE ASSIGN 1/DATAVOLUME
CUTOFF
FILTER
RESONANCE ASSIGN 2
2
MW/FC
1
SCENE
ARPEGGIO
HOLD SHIFT
OCTAVE
PART/LAYER/
+
PRESET USER
VWX
PROGRAM
+
PERFORMANCE STORE
MULTI
PRESET USER ARPEGGIATOR
UTILITY
7
YZ'
8
&
*
9
MNO
4
PQR
5
STU
6
DEF
1
GHI
2
JKL
NO/
QUICK PC
YES
3
ABC
0
SPACE
ENTER
PERFORMANCE MULTI
DEMO
STORE UTILITY
TYPE
BANK
P BEND
RANGE
NOTE
SFT
ATK
TIME
ATK
TIME
MASTER
TUNE
TEMPO
ARPEGGIATOR PERFORM
LEVEL
EFECT
PROGRAM
SYSTEM MIDI ASSIGN
PMOD
DETUNE
DCY
TIME
DCY
TIME
KBD
TRANS
SUB
DIVIDE
VOLUME
FMOD
REV
TYPE
CUTOFF
FC PORTA
VEL ASSIGN2
LFO
PEG
CHO
TYPE
VARI
EF
VARI
TYPE
SWITCH
VARI
PARAM
TIME
VARI
DATA
MW
FMOD
LIMIT
LOW
TUNE
AEG
FEG
NOTE
DCY
LEVEL
DCY
LEVEL
VEL
CURVE
PAN
CUTOFF
LIMIT
HIGH
REL
TIME
REL
TIME
VEL
FIX
REV
SEND
LIMIT
LOW
AMOD
INIT
LEVEL
TRANS
CH
CHO
SEND
LIMIT
HIGH
PMOD
ATK
TIME
EFFECT
RCV
CH
VARI
SEND
OFFSET
FMOD
ATK
LEVEL
DEVICE
NO
CUTOFF
FILTER
DEPTH
WAVE
DCY
TIME
LOCAL
REZ
PARAM
SPEED
REL
TIME
BULK
DUMP
PERFORM
NAME
POLY/
MONO
ASSIGN1
PARAM
DATA
PHASE
INIT
REL
LEVEL
CTRL
NO
COMMON
LAYER
UTILITY
PITCH MODULATION
CS1X

Guided Tour
57
Modulation Wheel
The modulation wheel is the most common controller, and can be found on
nearly every MIDI keyboard. It is usually used to produce LFO effects (regular
wavering of the sound, like vibrato and tremolo). Since it is so common, the
MU100R features various parameters that are reserved strictly for modulation
wheel control.
In the Multi mode, the modulation wheel can control Pitch LFO. The Per-
formance mode features both Pitch LFO and Filter LFO. For more information
on these parameters, see page 132.
Using the Assignable Controller —
Some Applications
Changing the Brightness on a Piano Voice
Though you can use the Equalizer (page 80) to adjust the brightness of a
Part’s Voice, you may find it convenient to be able to change the character of
the sound “on the fly,” as you play. This uses the AC1 Filter Control param-
eter. Try this with the Grand Piano Voice (001:GrandP #).
Operation
1 Call up the Edit menu.
From the Multi Play mode, press the [EDIT] button.
2 Select and call up “OTHERS.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER].
3 Select “AC1FilCtrl” and set it to “+63.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Filter Control pa-
rameter, then set the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or
data dial. Playing the Part at the minimum pedal position results
in mellow “lounge” piano sound; maximum position results in a
bright “rock’n’roll” piano.
Minimum position —
mellow sound.
Maximum position —
bright sound.
Assignable Controller (AC1)

58
Guided Tour
4 Try the setting on other Voices.
Exit to the Multi Play mode display (press the [PLAY] button) and
select other Voices, trying out the new setting, and moving the
foot controller up and down as you play. Try out some of these
Voices, and notice how the sound changes:
SynBass2 (040), Saw Ld (082), Warm Pad (090) — for a
“wah” filter sweep effect.
SynVoice (055), NewAgePd (089) — for gradually fading in a
breathy sound.
For details on the AC1 Filter Control parameter, see page 112.
Details
• Keep in mind that the degree and character of the AC1 Filter Control depends
also on the Filter parameter settings for the Part (see page 112). Some Voices
may not change at all unless these parameters are set appropriately. However,
all of the example Voices above should clearly change in response to AC1 (if
the Filter parameters are all at their default setting of 00).
Resetting the parameter values
The simple operation below lets you instantly restore the factory preset values.
Since it automatically cancels any edits you’ve made, you should use it with
care.
1. Press the [MODE] button.
2. Select a different mode, then re-select the original one.
For example, if you were editing in the XG mode, use the [SELECT </>]
buttons to move the cursor to “TG300,” then back to “XG.”
Doing this automatically resets all Part settings to the factory-programmed con-
dition and cancels any edits you made in the Multi mode (including whatever
Voices you selected).
Assignable Controller (AC1)

Guided Tour
59
Expressive Volume Control of a Part
This example shows you how to use the foot controller as an expression
pedal. This may come in handy when use of MIDI Volume (#7) or Expres-
sion (#11) is unavailable.
Operation
1 Select the desired Part and Voice.
Keep the settings you made to Part 1 (in the last example), and
select a new Part/Voice for this example. From the Multi Play
mode, select Part 2 with the [PART -/+] buttons. (This should
be set to MIDI channel 2; set the MIDI channel on the con-
nected keyboard accordingly.) A good Voice for this application
would be PercOrg# (018); select this with the [VALUE -/+]
buttons or data dial.
2 Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part.
Set this to “04.” (Refer to step #3 in “Using the Assignable Con-
troller — Setting Up” above.)
3 From the “OTHERS” parameters, select “AC1AmpCtrl” and set it
to “+63.”
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Amplitude (level)
Control parameter, then set the value with the [VALUE -/+]
buttons or data dial.
Now, play the organ sound and use the foot controller to play ex-
pressive volume swells. For details on the AC1 Amplitude Control
parameter, see page 113.
Expressive Control of Individual Drum Sounds
In this example, the foot controller is used to produce expressive timbre
changes and filter sweeps on selected drum sounds, using the Filter Control
parameter.
Operation
1 Select a Drum Part.
Select Part 10 with the [PART -/+] buttons, and make sure
that the connected keyboard is set to transmit over MIDI chan-
nel 10.
2 Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part.
Set this to “04.” (Refer to step #3 in “Using the Assignable Con-
troller — Setting Up” above.)
Assignable Controller (AC1)

60
Guided Tour
3 Set the AC1 Filter Control to “+63.”
Since you’ve called up the “OTHERS” parameters in the previ-
ous step, select “AC1FilCtrl” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons)
and set it to “+63” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial).
4 Select the “DRUM” parameters.
Call up the Edit menu, then select “DRUM” (with the [SELECT
</>] buttons) and press [ENTER].
5 Select “A3: Cabasa.”
Play A3 on the connected keyboard, or use the [PART -/+]
buttons to select “A3.”
6 Set some of the filter parameters for the Cabasa sound.
Select using [SELECT </>] button and set the two parameters
below as indicated:
LPF Cutoff: –40
LPF Reso: +60
Now, play the sound and move the foot controller as you play. No-
tice how this gives you dynamic, expressive control over the timbre
of the selected sound — without affecting the other sounds of the
drum kit.
Hints
• Since virtually all sequencers record controller data as well as note data, you can
record these expressive sound changes into your song tracks — either while you
record the notes themselves, or separately for a previously recorded track.
• The negative values of the AC1 parameters let you control the sound by moving
the controller in the opposite direction. For example, moving the foot controller
to the minimum position produces the greatest change in the sound.
An application of this might be to create a pedal-controlled crossfade between
two Parts.
To do this:
1) Set two Parts to the same MIDI channel. (See page 96.)
2) Set each Part to a different Voice.
3) Set the “AC1AmpCtrl” parameter for one Part to “–64,” and the same param-
eter for the other Part to “+64.”
• The Assignable Controller can also be used to control one parameter of a se-
lected effect.
Assignable Controller (AC1)

Guided Tour
61
On Your Own...
While you’re at it, try making some of your own settings. The procedure is
the same:
1) Select the desired Part and Voice.
2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button.
3) Select “OTHERS” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press
[ENTER].
4) Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part.
5) Select the appropriate parameters with the [SELECT </>] buttons.
• If you are using the AC1 Filter Control, make sure to appropriately set
other filter settings (in “FILTER” parameters, page 100, and/or “DRUM”
parameters, page 114).
•Select the AC1 parameters in the “OTHERS” parameters. (In the
Performance mode, these are in the “COMMON” parameters; see page
133.)
• If you are using a Drum Part, select the desired drum sound, either by
playing the corresponding key or by using the [PART -/+] buttons.
6) Change the value, with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
7) Use the [EDIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu.
Assignable Controller (AC1)

62
Guided Tour
Playing and Editing VL Voices
The VL section of the MU100R is a tone generator incorporating Yamaha’s
revolutionary “Virtual Acoustic Synthesis” tone generation system. Based
on sophisticated computer physical modeling technology, Virtual Acoustic
Synthesis produces sound that is more realistic, more expressive, and more
musical than any other system to date.
The VL section is a monophonic* tone generator, with its own set of
separate controls, yet is completely integrated with the other Parts of the
MU100R. VL Voices can be used only in the XG and Performance modes,
and only one Part can be used to play a VL Voice at a time.
For more details on VL Voices, see “About the VL Voice Section,” below.
* A “monophonic” tone generator plays only one note at a time.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Learn about the VL.
© Select VL Voice banks and VL Voices.
© Edit VL Voices.
About the VL Voice Section
Main Features
• Allows you to play back song data which has been programmed with
the VL-XG Voice data.
• Allows you to simulate the sound of acoustic musical instruments by ed-
iting the VL parameters directly from the MU100R (page 119).
• Allows you to play VL Voices with a WX11 Wind MIDI Controller (via
BT7) connected by MIDI to the MU100R.
VL Voice Edit
• Editing VL-XG Voices
If you want to edit the existing MIDI files using VL Voices from the VL tone
generator section, you’ll need to use an external sequencer which is capable
of editing system exclusive messages and transmitting the parameter changes
to the VL tone generator section. See MIDI Data Format for more informa-
tion on system exclusive messages.
Playing and Editing VL Voices

Guided Tour
63
Playing and Editing VL Voices
Virtual Acoustic Synthesis
Unlike previous tone generation systems which use oscillators, function gen-
erators, preset waveforms or samples to produce sound, Yamaha Virtual
Acoustic (“VA”) Synthesis applies sophisticated computer-based “physical
modeling” technology to musical sound synthesis. In the same way that com-
puter “models” are used to simulate weather systems or the flight character-
istics of aircraft in the design stage, the VL tone generator section simulates
the very complex vibrations, resonances, reflections and other acoustic phe-
nomena that occur in a real wind or string instrument.
VA Advantages
The VL tone generator section offers many advantages in terms of musical per-
formance. Not just in terms of sound, but also in terms of the “behavior” that
makes acoustic instruments so … well, musical! Yamaha Virtual Acoustic Syn-
thesis is simply the most musical tone generation system ever created.
• The VL tone generator section sounds better, has more depth, and is
more realistic in the musical sense than any other tone generation sys-
tem.
• Simply playing a note in the same way does not always produce pre-
cisely the same sound. The instrument is responsive and “alive”.
• Note-to-note transitions have the same continuity exhibited by acoustic
instruments. What goes on in between the notes is just as important mu-
sically as the notes themselves.
• It has extraordinary expressive capability. Rather than simply control-
ling parameters like volume or pitch, you can control characteristics
such as breath and reed pressure with appropriate complex effects on the
timbre of the sound.
VL Tone Generator Model
The overall VL Tone Generator model or “algorithm” consists of three main
blocks: the instrument, controllers, and modifiers. In schematic form these
blocks are arranged as follows:
Sound out
Controllers (also envelopes)
Instrument Modifiers

64
Guided Tour
The Instrument
The key block in this algorithm is the instrument, since it is here that the
fundamental tone or “timbre” of the sound is defined. The instrument model
consists primarily of a driver — the reed/mouthpiece, lip/mouthpiece, or
bow/string system — and a resonant system corresponding to the tube and
air column or string.
Playing and Editing VL Voices
One of the remarkable features of the Virtual Acoustic Synthesis system is
that just about any driver can be used with any type of pipe or string.
NOTES
• The sound thus produced is amplified and sustained by the body of the instru-
ment.
• The pitch of the sound is determined by the length of the air column or string, and the
timbre is a complex product of the driving source (reed, lip, air, string), the shape of
the resonant cavity, the materials from which the instrument is made, etc.
In all these instruments pressure applied
here (the driving point) causes vibration
which results in sound.
Reed vibration
Lip vibration
Air vibration
String vibration
Drivers Pipes/String

Guided Tour
65
The Controllers
The input to an acoustic wind instrument comes from the player’s lungs,
trachea, oral cavity, and lips. In a string instrument it comes from the player’s
arm movement, transmitted to the string via a bow. These elements actually
form an important part of the sound generating system and, in the VL tone
generator section, are included in the controllers block. The player also in-
fluences the sound of the instrument by playing the keys, tone holes, or
frets, and this aspect of control constitutes another part of the controllers
block. These and other control parameters provided by the VL tone genera-
tor section are listed in the illustration below.
In essence, the controller parameters determine how the instrument
“plays”. All of these parameters can be assigned to any external controller
that can be used with the VL tone generator section: breath controller, foot
controller, modulation wheel, etc. The pressure parameter, for example, will
normally be assigned to a breath controller so the player can control the
dynamics of the instrument by varying the breath pressure applied to the
controller — a natural, instinctive way to play wind-instrument Voices. At
the same time the growl and throat parameters might also be assigned to the
breath controller in order to achieve life-like response and effects.
Playing and Editing VL Voices
Embouchure
The tightness of the lips
against the reed or against
each other, or the force of
the bow against the string.
Tonguing
Simulates the half-tonguing
technique used by saxo-
phone players by changing
the “slit” of the reed.
Pitch
Changes the length of the
air column or string, and
thereby the pitch of the
sound.
Damping & Absorption
Simulate the effects of air
friction in the pipe or on
the string, and of high-
frequency losses at the end
of the pipe or string.
Throat
Controls the characteristics
of the “player’s” throat or
bowing arm.
Pressure
The amount of breath
pressure applied to the reed
or mouthpiece, or bow
velocity applied to the
string.
Growl
A periodic pressure (bow
velocity) modulation which
produces the “growl” effect
often heard in wind
instruments.
Scream
Drives the entire system
into chaotic oscillation,
creating effects that can
only be achieved with
physical modelling
technology.

66
Guided Tour
The Modifiers
The modifiers block consists of 4 sections as shown in the diagram. Al-
though these may appear to be simple effects, they are actually intimately
related to the VL’s sound-producing model and have a significant effect on
the sound.
Harmonic Enhancer
The Harmonic Enhancer determines the
harmonic structure of the sound to the
extent that it can produce radical timbral
variations within an instrument “family”
(e.g., saxophones).
Dynamic Filter
This section is similar to the dynamic fil-
ters found in many conventional synthe-
sizers, with high-pass, bandpass, band
elimination, and low-pass modes. Some
filter parameters are available via the VL
tone generator section controls.
Frequency Equalizer
This is a 5-band parametric equalizer with frequency, Q (bandwidth), and
level control. The equalizer also has pre-EQ high- and low-pass filters as
well as key scaling capability for precise response control throughout the
instrument’s range.
Resonator
The Resonator uses simulated “resonator” pipes or strings and delays to
produce a “woody” resonance effect — although it has little or no effect on
some Voices. The Resonator is employed as one of the preset Voice param-
eters.
Playing and Editing VL Voices
Harmonic
Enhancer
Dynamic
Filter
Frequency
Equalizer
Resonator

Guided Tour
67
Voice Organization
The VL Voices have each program number and are organized into 13 banks.
Refer to the Voice list in the “SoundList & MIDI Data” booklet.
• Banks 112 through 119: VL-XG Banks
(Bank Select MSB: 81 or 97)
The Voices from the PRESET 1 and PRESET 2 banks are assigned to MIDI
banks and program change numbers conforming to the Yamaha XG format.
IMPORTANT
Since the VL tone generator section does not have a full set of XG-compatible Voices,
however, some Voice numbers will be skipped (e.g., 22, 23, 25, 27, etc.). If the
truncated number is designated, no sound will be produced (when Bank Select
MSB is 81) or the XG Voice in the bank 1 will sound instead (when Bank Select MSB
is 97).
• Bank 000: PRESET 1
The PRESET 1 bank contains 128 preset Voices which have been created
primarily to be played via a keyboard.
• Bank 001: PRESET 2
The PRESET 2 bank contains 128 preset Voices which have been created to
provide maximum expressive capability when played with a breath control-
ler or a WX-series Wind MIDI Controller.
• Bank 002: CUSTOM
The CUSTOM bank has 6 memory locations (program numbers 001 - 006)
in which you can load the Voices created by the Yamaha VL70-m.
The loaded Voices cannot be backed up. When the MU100R is turned on,
the Voices are reset to their defaults, the sound-effect type Voices from the
PRESET banks.
• Bank 003: INTERNAL
The internal Voices of the VL70-m can be received and loaded (bulk data).
The Internal bank has 64 memory locations in which Voices you have edited
can temporarily be stored.
The loaded Voices cannot be backed up. When the MU100R is turned on,
the Voices are reset to their defaults, the Voices from the Preset banks, set up
to be played via a WX-series Wind MIDI Controller.
IMPORTANT
The edited Voices cannot be stored in the Internal Voice bank. If you want to keep
your edited Voice, save it as a part of the song data using the sequencing software
which is capable of editing and transmitting system exclusive messages.
Playing and Editing VL Voices

68
Guided Tour
NOTE
• If you save the MU100R Performance mixed and layered with a VL Voice, the VL
Voice number and its VL parameter setting edited on the MU100R panel will be
stored.
• Note that the “program numbers” here are 001~128 and the “MIDI program change
numbers” are 000~127. When selecting Voices (programs) using an external MIDI
device, subtract a value of “1” from the “program number” to match the “MIDI
program change numbers.”
Selecting Banks
• Use the MIDI bank MSB (control number 00) and LSB (control number
32) numbers listed at right to select VL banks from an external MIDI
device.
BANK MSB LSB
BANK 112 97 or 81 112
BANK 113 97 or 81 113
BANK 114 97 or 81 114
BANK 115 97 or 81 115
BANK 116 97 or 81 116
BANK 117 97 or 81 117
BANK 118 97 or 81 118
BANK 119 97 or 81 119
PRESET 1 33 0
PRESET 2 33 1
CUSTOM 33 2
INTERNAL 33 3
Playing and Editing VL Voices

Guided Tour
69
Playing and Editing VL Voices
Selecting VL Voice banks and VL Voices
The VL Voices can be selected in the much the same way as the XG Voices.
Selecting VL Voices from an External Device
If you want to control the MU100R including the VL tone generator section by
using sequencing software and/or use the tone generator without panel but-
tons (e.g., sound card), you’ll need to transmit the MIDI messages such as XG
System On, Bank Select MSB/LSB and program change to the MU100R by us-
ing the sequencing software which is capable of editing and transmitting sys-
tem exclusive messages. Refer to the MIDI Data Format in the “Sound List &
MIDI Data” booklet.
Operation
1 Make sure that the XG or Performance mode is selected.
For information on selecting the Sound Module mode, see page
172.
2 Assign one of the Parts for playing VL Voices.
Only one Part can be used for the VL Voices, and this must be
properly assigned.
To do this:
1) Press the [UTIL] button.
2) Select “PLUGIN” (with the [SELECT >] button) and press
the [ENTER] button.
3) Select “PLG100-VL” (VL Voices) with the [SELECT <] but-
ton, and press [ENTER] again.
4) Select the Part Assign parameter (with the [SELECT <]
button).
5) Set the desired Part number (01– 16 for XG, 01 – 04 for
Performance) with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.

70
Guided Tour
3 Return to the Play mode, and select the approriate Part.
Press the [PLAY] button, then use the [PART -/+] buttons to
select the same Part as you assigned in step #2 above.
4 Select one of the VL bank numbers.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the bank number
parameter, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to
select one of the VL Voice banks. (The VL Voice banks follow
the “SFX” bank. For this example, select VL bank 000.)
5 Select the desired Voice.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program
number parameter, then use the[VALUE -/+] buttons or data
dial to select one of the VL Voices.
6 Play the Voice.
Play this new Voice from the connected MIDI keyboard. Go on
to select other VL Voices in this bank, and from other banks as
well. For details on the available VL Voice banks, see page 68.
VL Voice icon.
Playing and Editing VL Voices
Bank number. Program number.

Guided Tour
71
Editing a VL Voice
This section shows you the basic steps in editing VL Voices. The VL param-
eters here are completely different from those of the normal Voices, the ones
you edited on page 36. (For more information on the VL Edit parameters,
see page 119.)
Keep in mind that in editing the VL Voices, you are not changing the
Voice itself, but rather the Part the Voice is assigned to. This means that
when you select a different VL Voice for the Part, the edited settings apply to
the new Voice, whether they’re appropriate or not.
You can use this to your advantage by recording all VL Part settings to
your sequencer, before the actual song data. This ensures that the VL Part
will play exactly as intended for each song.
Also remember that any edits you make to the VL Part are automatically
saved as the power on defaults. In other words, the next time you turn on the
power, the previous condition of the VL Part is automatically recalled. If
you want to save one “set” of edits (for example, for use with a specific
song) before creating another set, you must first save the current setup to a
sequencer or MIDI data filer. (For details, see page 18.)
NOTE
The VL Edit parameters are not available for the normal Voices or Drum Voices.
Operation
1 Select the VL Part.
In order to edit the VL Voice, you must first select the Part to
which the VL Voice has been assigned. Also make sure that a
VL Voice has been selected for the Part. (See “Selecting VL
Voice banks and VL Voices” above.)
2 Call up the Edit menu.
Press the [EDIT] button.
3 Call up the VL Edit menu.
Use the [SELECT >] button to select “PLUGIN” in the display,
then press [ENTER].
Playing and Editing VL Voices

72
Guided Tour
Playing and Editing VL Voices
4 Select the desired parameter.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter for edit-
ing. For complete descriptions and details of all VL Edit param-
eters, see page 119.
5 Change the parameter value or setting.
Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to change the value
or setting.
6 Return to the Play mode after finishing editing.
Press the [PLAY] button to return to the Play mode.
NOTE
There are additional VL-related parameters in the Utility mode. For more informa-
tion on these parameters, refer to page 169.
To call up these parameters:
1. Press the [UTIL] button.
2. Use the [SELECT
>
] button to select “PLUGIN,” then press [ENTER].
3. If it isn’t already selected, select “PLG100-VL” with the [SELECT
<
] button,
then press [ENTER].
4. Select and edit the parameters in the normal way, using the [SELECT
<
/
>
]
buttons, then the [VALUE
-
/
+
] buttons or data dial.

Guided Tour
73
Effects
To complement the huge variety of Voices and the 32-Part multi-timbral
capacity, the MU100R features a built-in multi-effect processor with seven
independent digital effects: Reverb, Chorus, Variation, Insertion 1 and 2,
Harmony, and EQ. (In this section, we’ll examine the first five; Harmony
and EQ are covered on pages 77 and 80, respectively.)
These high-quality effects provide an enormous amount of sound pro-
cessing power and flexibility. Combine these with the Part controls in the
Multi mode, and you have a “virtual” 34-channel mixer at your disposal,
with per-channel EQ, master EQ, and six effect sends — complete with six
independent effect units!
The following instructions assume that the XG mode is selected (page
26). However, using effects in the Performance mode and the other modes is
done in virtually the same way.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Set the Reverb Type and adjust the amount applied to a Part.
© Set the Chorus Type and adjust the amount applied to a Part.
© Use the Variation effects to apply distortion to a Part.
Using Reverb and Chorus
Judicious use of Reverb creates a sense of space and enhances the realism of
the Voices. The selected Reverb Type is applied to all Parts; however, the
amount of Reverb for each Part can be adjusted. This lets you add special
textures to the mix of a song, such as “drenching” one Part in Reverb while
another Part is kept “dry.”
The Chorus effect section features a variety of pitch modulation effects. These
let you subtly enhance or “fatten” the sound, or completely transform the
sound in wild and unique ways. As with Reverb, only one Chorus Type can
be used for all Parts; however, the amount of Chorus for each Part can be
adjusted.
Effects

74
Guided Tour
Operation
1 First, set the Send and Return controls to appropriate levels.
Before you actually change the Reverb or Chorus settings, you
should set the Send and Return controls, in order to properly
hear the effect and the changes you make.
To do this:
1) Select the desired Part from the Multi Play mode Single
Part display. (Use the [PART -/+] buttons.)
2) Select “RevSend” (Reverb Send) or “ChoSend” (Chorus
Send) with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and set it to “40”
or higher.
3) Select the All Part display (by pressing both [PART -/+]
buttons).
4) Select “RevRtn” (Reverb Return) or “ChoRth” (Chorus Re-
turn) with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and set it to “60”
or higher.
2 Call up the Effect Edit mode.
Press the [EFFECT] button.
3 Select and call up the desired effet section.
Select “REV” (Reverb) or “CHO” (Chorus) with the [SELECT </
>] buttons.
4 Select and change the Type parameter.
Use the [SELECT <] button to select “Type,” then change the
setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
5 Edit other parameters as desired.
Once you’ve selected a Reverb or Chorus Type, you can adjust
the other parameters.
For Reverb, try changing the Reverb Time and HPF Cutoff and
listen to how the changes affect the Reverb sound. For Chorus,
the parameters differ depending on the selected Chorus Type.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then ad-
just the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
For a list of Reverb Types and other information on Reverb, see page
142. For a list of the available parameters for each Reverb Type, re-
fer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.
For a list of Chorus Types and other information on Chorus, see
page 143. For a list of the available parameters for each Chorus
Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.
Effects

Guided Tour
75
Applying Distortion to a Part —
Using the Variation Effects
The Variation effect section provides a wealth of additional effects. With a total
of 70 different Types, it features some of the same effects found in the Reverb,
Chorus and Insertion sections. This is not mere redundancy; it allows you to use
two Types of Reverb or Chorus on different Voices. For example, you may want
to have a Symphonic effect on one Voice and Phaser on another. Variation also
gives you many special effects not found in the Reverb and Chorus sections,
such as Delay, Gate Reverb, Wah and Pitch Change.
The Variation effect can be applied either to all Parts (as with Reverb and
Chorus), or to a single selected Part (as described below).
Operation
1 Set Variation Connection to “INS” (Insertion).
To use Variation with a single Part, the Variation Connection pa-
rameter should be set to Insertion.
To do this:
1) Press the [EFFECT] button.
2) Select “VAR” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and press
[ENTER].
3) Select “VarConnect” (with the [SELECT >] button), and
change the setting to “INS” (with the [VALUE -/+] but-
tons or data dial).
2 Select the desired Part and set its Variation Send control to “on.”
To do this:
1) Return to the Multi Play mode Single Part display (press
the [PLAY] button), then select the desired Part (with the
[PART -/+] buttons).
2) Select “VarSend” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons), and
set it to “on” (with the [VALUE-/+] buttons or data dial).
3 Return to the Variation parameters, select the Distortion Type,
and make other necessary settings.
To do this:
1) Press the [EFFECT] button.
2) Select “VAR” (with the [SELECT -/+] buttons) and press
[ENTER].
3) Select “Type” (with the [SELECT <] button), and change
the setting to “DISTORTION” (with the [VALUE -/+]
buttons or data dial).
Effects

76
Guided Tour
4) If you cannot hear the Distortion effect clearly, select the
“Dry/Wet” parameter (with the [SELECT </>] buttons)
and adjust it (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial)
until the sound is appropriate.
5) Using the same method (as in step #4), select and adjust
other important Distortion parameters as needed, such as
“Drive” and “OutputLvl” (Output Level).
Now, play the Part and hear how Distortion affects the sound. Se-
lect other Types and play with them as well.
The Variation parameters differ depending on the selected Vari-
ation Type. For a list of Variation Types and other information on
Variation, see page 144. For a list of the available parameters for
each Variation Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.
Details
• When Variation is set for use with a single Part (Insertion), only Variation Send is
available. (The Dry/Wet parameter in Variation Edit effectively performs the same
function as Variation Return in this case; see page 145.) Also, Variation Send can
be set to “on” for only one Part.
• When Variation is set for use with all Parts (System), both Variation Send and
Return must be set to appropriate values. (The operation is the same as step #1 in
“Using Reverb” and “Using Chorus” above.)
For more information, refer to “About the Effect Connections — System
and Insertion” on page 152.
Insertion 1 and 2 Effect Sections
The Insertion 1 and 2 sections provide additional signal processing power.
Each of the Insertion sections can be applied to a single selected Part, and
each features 43 effect Types.
For a list of Insertion Types and other information on Insertion, see page 146.
For a list of the available parameters for each Insertion Type, refer to the
“Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.
Effects

Guided Tour
77
Harmony Effect
This sophisticated effect takes the sound of your voice (via a microphone
and one of the A/D inputs) and reproduces it as a harmony vocal, providing
up to four-part harmonies (including your original voice).
You can pre-program the pitch interval of the harmony, or you can “play”
the harmony from your connected MIDI keyboard (or sequencer), and even
have the harmony interval change, depending on the chord you play. As long
as your own voice is in pitch and you play the appropriate chords, the
MU100R ensures that the harmony “voices” will be enharmonically correct
and stay in pitch with the chord changes of the song.
Though the Harmony effect can be applied to any Part, it is designed
primarily to be used with vocal input. It also includes a “gender changer”
effect that turns a male voice into a female voice (or vice versa), and a vi-
brato effect that automatically adds a warm, natural vibrato to your voice.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Set up your system and the MU100R for the Harmony effect.
© Select a Harmony Type and Mode.
© “Play” vocal harmonies from a connected MIDI keyboard, to match the
melody you sing.
Using the Harmony Effect
Operation
1 Set up the MIDI keyboard.
Connect a MIDI keyboard (as described on page 17) and set the
MIDI transmit channel to 1.
Hint
• Alternately, you could set up a sequencer in this step and use the sequencer’s
song data to control the Harmony effect and determine specific harmony notes.
In this way, when you play back the song and sing along with it, all the appro-
priate backing harmonies will be produced automatically.
2 Connect a microphone to the MU100R and set up the A/D Part.
Connect a microphone to the A/D INPUT 1 jack, select Part
“A1,” then select the “Mic” preset (bank #000, program #002).
(Refer to the section “Using the A/D Inputs” on page 87, for de-
tailed instructions.)
Harmony Effect

78
Guided Tour
3 Call up the Harmony System menu (in the Utility mode).
To do this:
1) Press the [UTIL] button.
2) Select “PLUGIN” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and
press the [ENTER] button.
3) Select “PLG100-VH” (Harmony) with the [SELECT >] but-
ton, and press the [ENTER] button.
4 Set the Harmony Channel to 1.
Use the [SELECT <] button to select “Harmony Ch” (Harmony
Channel), then set the parameter to “01” to match it with the
transmit channel of the connected MIDI keyboard.
5 Call up the Harmony Edit menu.
To do this:
1) Press the [EFFECT] button.
2) Select “PLG” (with the [SELECT >] button) and press the
[ENTER] button.
3) At the “PLG100-VH” (Harmony) menu, press [ENTER]
again.
6 Set the Harmony Insert Part to the corresponding A/D Part.
Use the [SELECT >] button to select “Ins Part” (Insert Part), then
set the parameter to “AD01”.
Harmony Effect

Guided Tour
79
7 Set the Harmony Type to Chordal.
Select “Type” (with the [SELECT <] button), then set the param-
eter to “CHORDAL HM” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data
dial). When set to Chordal, chords you play on the connected
MIDI keyboard determine the notes of the Harmony effect. (For
more information on Chordal and the other Types, see page 147.)
8 Set the Harmony Mode to “trio above”.
Select “Mode” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons), then set the
parameter to “trio above” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or
data dial).
9 Sing into the microphone and play chords on the MIDI keyboard.
The Harmony function recognizes thirty-four different chord
types. Chords can be played at any register on the keyboard and
result in the same harmonies. Experiment with different chord
types (major, minor, seventh, etc.) and hear how the harmonies
change — even while holding the same pitch with your voice.
Hints
• Keep in mind that you don’t need to hold the chord down — simply play it once
at the point you want the harmony to change, then release it and continue
singing until the next chord change.
• If another Part is set to MIDI channel 1, you’ll hear its Voice playing the chord.
To keep this Voice from sounding, use the [MUTE/SOLO] button to mute the
part, or turn its Volume setting down.
On Your Own...
Here is a summary of the steps you should follow when using the Harmony
effect:
1) Set up one of the A/D input Parts, and select one of the presets.
Do this if you want to apply Harmony to an external source (such
as a microphone or guitar). (See page 87.)
2) Set the Harmony Channel to match the transmit channel of a connected
MIDI keyboard.
Do this if you want to control the Harmony effect via MIDI.
Path: UTILITY
g
“PLUGIN”
g
“PLG100-VH”
g
“Harmony Ch”
3) Set the Insert Part to the corresponding Part.
For the A/D inputs, this would be set to “AD01” or “AD02.”
Path: EFFECT
g
“PLG”
g
“PLG100-VH”
g
“Ins Part”
4) Make other appropriate settings in the “PLG100-VH” menu (called up in
step #3 above).
Most important of these are Harmony Type, Harmony Mode, and
Lead/Harmony Balance. (See page 147.)
Harmony Effect

80
Guided Tour
Equalizer (EQ)
The MU100R features an extensive set of equalization controls that give
you comprehensive control over the tone quality — both of individual Parts
and over the entire instrument sound.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Use the Part EQ edit parameters to adjust the tone of a specific Part.
© Use the main EQ to adjust the overall tone of the MU100R.
Adjusting the Tone of a Specific Part — Part EQ
The Part EQ parameters give you two-band (low and high frequencies) con-
trol over the sound of individual Parts. These can be used in both the Multi
mode and the Performance mode.
NOTE
When a Drum Part is selected, the EQ menu is not available. However, the same
EQ parameters can be adjusted for each individual drum sound in the “DRUM”
menu. (See page 117.)
Operation
1 Select the desired Part.
From the Multi mode Single Part display, use the [PART -/+]
buttons to select the desired Part (excepting Drum Parts).
2 Call up the EQ parameters.
Press the [EDIT] button, then select “EQ” (with the [SELECT </
>] buttons) and press the [ENTER] button.
3 Select the general frequency range — low or high.
In this example, we’ll boost the bass of the Part, so select “Low
Freq” (Low Frequency) with the [SELECT </>] buttons.
Equalizer (EQ)

Guided Tour
81
4 Set the specific frequency to be adjusted.
For this example, set the Low Frequency value to “315” (Hz).
5 Select the Low Gain parameter and adjust the value.
For this example, set the Low Gain value to “+35.” Play the
Voice (especially in the lower octaves) and hear how the sound
has changed.
NOTE
Depending on the Voice selected for the Part (and depending in which octave you
play the Voice), you may or may not hear very much change in the sound at
certain frequencies.
If you want, try adjusting the High Frequency/Gain parameters as
well.
EQ in the Performance Mode
The EQ settings of individual Parts in the Performance mode can be adjusted
in the same way:
1) Select a Part (in the Single Part controls).
2) Press the [EDIT] button.
3) Select “PART”, then press the [ENTER] button.
4) Select “EQ”, then press the [ENTER] button, and edit the parameters as
shown in steps #3 – #5 above.
Equalizer (EQ)

82
Guided Tour
Adjusting the Overall Tone — Main EQ
The main EQ section gives you five-band control (at specific frequencies)
over the entire sound of the MU100R. Special presets are also available for
instantly changing the tone to suit different types of music.
Operation
1 Call up the “EQ TYPE” parameter and select the desired EQ pre-
set.
First press the [EQ] button, then use the [SELECT </>] buttons
to select the parameter. Then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or
data dial to select the desired preset.
2 If desired, change the values of the five different bands.
Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then
change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial.
The changes you make to a selected EQ preset are maintained even
when the power is turned off. However, selecting another preset au-
tomatically cancels your original settings.
For more information on the Equalizer effects, see page 155. Also,
refer to the Multi Mode Equalizer Lock parameter (page 158).
Equalizer (EQ)
1) The graphic EQ display shows the EQ curve.
2) The EQ icon’s sliders indicate current settings and move
as the value is adjusted.

Guided Tour
83
Individual Outputs
This convenient feature allows you to send the output of a selected Part or
Parts to the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. For Drum Parts, you can even select
specific drum sounds to be output through these jacks.
In general, the extensive built-in effects and other Part controls of the
MU100R provide all you need for processing and mixing complex multi-
Part songs. However, there may be times (in studio recording, for instance)
when you want to “sweeten” or process a certain Voice or sound with a favor-
ite outboard effect unit, or record a Part to a separate track of a tape recorder.
The individual outputs are designed just for these kinds of applications.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Set up the MU100R so that two Parts are independently routed to the
two INDIV. OUTPUT jacks.
Using the Individual Outputs
Operation
1 Make the necessary audio connections.
In the example illustration below, the INDIV. OUTPUT 1 jack is
connected to the input of an effect unit. The output of the effect
unit is then connected to a channel on a mixing console, along
with the main OUTPUT jacks of the MU100R.
In a variation of this, INDIV. OUTPUT 1 could be connected di-
rectly to a separate input channel on the mixing console, then proc-
essed with an outboard effect using the send/return connections on
the mixer.
Hint
If you don’t have an external mixer yet want to use the individual output and an
external effect to process a Part, you can do so and return the output from the
effect device back into the MU100R via one of the A/D inputs. (For information on
using the A/D inputs, see page 87.)
Individual Outputs
Effect unit MU100R
Mixing Console
(3) INDIV. OUTPUT
(4) OUTPUT L and R(2) In(1) Out

84
Guided Tour
2 Select the desired Part.
From the Multi mode Single Part display, use the [PART -/+]
buttons to select the desired Part for using with the individual
output.
3 Set the Output Select parameter to the desired setting.
Here, we’ll set the selected Part to output from the INDIV. OUT-
PUT 1 jack.
To do this:
1) Press the [EDIT] button.
2) Select “OTHERS” with the [SELECT >] button, and press
the [ENTER] button.
3)
Select “OutPtSel” (Output Select) with the [SELECT >] but-
ton.
4) Set the parameter to “ind1” with the [VALUE -/+] but-
tons or data dial.
The selected Part will now be output only through the INDIV. OUT-
PUT 1 jack. (Output through the main OUTPUT jacks and PHONES
jack is cancelled.)
To select another Part for individual output, repeat steps #2 and
#3 above. You can set additional Parts to be output through the
same jack, or select “ind2” to output a Part or Parts through INDIV.
OUTPUT 2.
For more information on the individual outputs, refer to the Output
Select parameter (page 113) and the Output Select Lock parameter
(page 158).
Routing Drum Sounds to the Individual Outputs
Individual drum sounds can also be routed to the individual outputs.
To do this:
1) Select a Drum Part.
2) Press the [EDIT] button.
3) Select “DRUM,” and press the [ENTER] button.
4) Select the desired drum sound (either from the connected MIDI keyboard
or with the [PART -/+] buttons).
5) Call up the Output Select parameter (with the [SELECT >] button) and
make the desired setting (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial).
For more information on using Drum Parts with the individual outputs, refer to
the Output Select parameter (page 118).
Individual Outputs

Guided Tour
85
Mute/Solo
The MU100R has convenient Mute and Solo functions for selectively mut-
ing or soloing any of the 32 normal Parts and the A1 and A2 A/D Parts. This
is especially useful when playing back several Parts from a connected com-
puter or sequencer. Mute lets you silence one Part to hear how all of the
other Parts sound without it. Solo lets you isolate a single Part, to hear how
that Part sounds by itself.
In the Performance mode, Mute and Solo are especially effective tools
that help you as you edit the Parts, since they allow you to better hear how
the changes you make affect specific Voices as well as the overall sound of
the Performance.
Using Mute/Solo
Operation
1 Select the desired Part.
Make sure the Single Part mode is active (see page 108), then
use the [PART -/+] buttons to select the Part.
2 Press the [MUTE/SOLO] button.
While playing the keyboard (or during playback of a song from
a sequencer), press the [MUTE] button. Each press cycles
through the three functions: Mute, Solo and Normal operation.
Selected Part number.
The selected Part is muted, while all other Parts sound normally.
Mute/Solo

Guided Tour
87
A/D Inputs
The MU100R features a special A/D (Analog-to-Digital) input function that
allows you to connect up to two different external signals (microphone, elec-
tric guitar, CD player, etc.), mix those signals with the MU100R’s Voices. A/
D input is perfect for singing along with your keyboard performance, since
it allows you to blend the two signals without the need for an external mixer.
Or you can use it to sing or play guitar over backing tracks played from a
MIDI sequencer.
There are two A/D Parts (A1 and A2) and they can be manipulated in
much the same way as the other parts — for example, they can have inde-
pendent Volume, Pan, and effect send settings. What’s more, you can control
certain parameters automatically via a connected MIDI sequencer. (See page
17.)
The two A/D Parts include several specially programmed presets, com-
plete with proper gain settings and suitable effects — using the built-in ef-
fects of the MU100R.
In this section, you’ll learn how to:
© Set up the MU100R for using the A/D inputs.
© Call up the A/D input presets.
Using the A/D Inputs
Operation
1 Turn down the A/D INPUT VOLUME control on the front panel.
CAUTION!
Before connecting an external input, always turn the VOLUME control down.
2 Connect the microphone or instrument to one of the A/D INPUT
jacks.
For this example, connect to the A/D INPUT 1 jack. (Depending
on the equipment being used, appropriate conversion adaptors
may be necessary; the A/D INPUT jacks accept 1/4” phone plugs.)
A/D Inputs

88
Guided Tour
3 Select the corresponding Part.
Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Since you connected to the A/D
INPUT 1 jack above, select Part A1 in this step.
4 Select the appropriate bank of presets.
Do this in the normal way, using the [SELECT </>] buttons to
highlight the bank number parameter, then using the [VALUE -
/+] buttons to change the bank.
The selected bank determines the type of input and sets the appro-
priate gain level. Each bank/type is indicated by an icon in the LCD:
Bank 000
For input of a microphone (or other mic level instruments).
A/D Inputs

Guided Tour
89
Bank 001
Bank 002
Bank 003
Bank 018
For input of an electric or electric/acoustic guitar
(or other mic level instruments).
For input of a keyboard (or other line level instruments, such as
tone generators, rhythm machines, etc.).
For input of audio equipment (such as CD players, cassette decks, etc.).
For input of a stereo keyboard (or other stereo signals from line level
instruments, such as tone generators, rhythm machines, etc.).
A/D Inputs

90
Guided Tour
Bank 019
CAUTION!
Do not use line level signals (such as from keyboards, etc.) with the mic level
banks. The signal may be too high, resulting in damage to the MU100R.
5 Select the desired preset.
Do this in the normal way (as you selected Voices), using the
[SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program number param-
eter, then using the [VALUE -/+] buttons to select the preset.
The available presets have been specially programmed to suit
the type of input selected. For example, presets for Mic input in-
clude Karaoke and Vocal; Guitar input presets include Tube,
Stack and Phaser. Explore some of these settings on your own
with a microphone and different instruments. (For a list of all
available A/D input presets, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI
Data” booklet.)
6 Turn up the level.
If the connected source has a volume control, first set it to an
appropriate level, then slowly bring up the A/D INPUT VOL-
UME control on the MU100R while playing the instrument (or
singing into the microphone), until the level is appropriate.
For input of stereo audio equipment
(such as CD players, cassette decks, etc.).
A/D Inputs

Guided Tour
91
Data Flow Block Diagram
When HOST SELECT switch is set to MIDI (31,250 bps):
Sound
Module
A1~16CH
TO HOST IN-B IN-A OUT THRU
Sound
Module
B1~16CH
When HOST SELECT switch is set to
PC-1/MAC (31,250 bps) or PC-2 (38,400 bps):
Sound
Module
A1~16CH
TO HOST IN-B IN-A OUT THRU
Sound
Module
B1~16CH
Data Flow Block Diagram

92
Guided Tour
MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables
MIDI
Standard MIDI cable. Maximum length 15 meters.
DIN 5-PIN DIN 5-PIN
4
2
5
4
2 (GND)
5
Mac
Apple Macintosh Peripheral cable (M0197). Maximum length 2 meters.
MINI DIN
8-PIN
MINI DIN
8-PIN
1
2
3
2 (HSK i)
1 (HSK o)
5 (RxD –)
4 4 (GND)
5 3 (TxD –)
6 8 (RxD +)
7 7 (GP i)
8 6 (TxD +)
PC-1
8-pin MINI DIN to D-SUB 25-pin cable. If your PC-1 type computer has a
9-pin serial port, use the PC-2 type cable. Maximum length 1.8 meters.
MINI DIN
8-PIN
D-SUB
25-PIN
1
2
3
5 (CTS)
4 (RTS)
3 (RxD)
4 7 (GND)
8
5 2 (TxD)
PC-2
8-pin MINI DIN to D-SUB 9-pin cable. Maximum length 1.8 meters.
MINI DIN
8-PIN
D-SUB
9-PIN
1
2
3
8 (CTS)
7 (RTS)
2 (RxD)
4 5 (GND)
8
5 3 (TxD)
This concludes your basic tour of the important functions of the MU100R. To find out
more about how to best use your MU100R, look through the Reference section that
follows and try out some of the functions and operations that interest you.
MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables

Multi Mode
95
Multi Mode
In the Multi mode, the MU100R performs as a multi-timbral tone generator
capable of playing up to 32 Parts simultaneously, over 32 MIDI channels.
Normally, the MU100R should be set to Multi mode when using it with a
sequencer and General MIDI song data. There are three Multi modes: XG,
TG300B and C/M. (For information on selecting these, see pages 6 and
172.)
Part Controls
Part Controls ................................................................................ 95
Single Part Control................................................................ 96
All Part Control..................................................................... 98
Multi Edit Mode.......................................................................... 100
Filter (FIL) ........................................................................... 100
Envelope Generator (EG) .................................................... 102
Equalizer (EQ)..................................................................... 105
Vibrato ............................................................................... 106
Others ................................................................................ 107
Drum Setup Controls ...........................................................114
VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin) ........................................119
Part Controls
The Part controls in the Play mode give you tools for adjusting the basic
sound and settings for each Part. The MU100R lets you adjust the various
settings for each Part individually (Single Part control) or together (All Part
control). Each of these types is explained in greater detail below.
NOTE
In the Multi mode, no settings can be permanently saved to the internal memory
of the MU100R. However, you can use the Dump Out function to save Multi
settings to a MIDI data storage device. (See page 18.)

96
Multi Mode
Single Part Control
The Single Part controls include: MIDI Receive Channel, Bank Number,
Program Number, Volume, Expression, Pan, Reverb Send, Chorus Send,
Variation Send and Note Shift. For basic information on using the Single
Part control, see page 33.
MIDI Receive Port/Channel
Settings: A1 — A16, B1 — B16, OFF
This determines the MIDI IN port (A or
B) and the receive channel (1 — 16) for
the selected Part.
Bank Number
Settings:
A1 (A/D Input part):
000 — 003, 018, 019
A2 (A/D Input part):
000 — 003
Normal part:
XG: 000, 001, 003, 006, 008, 012,
014, 016 — 022, 024 — 029,
032 — 043, 045, 048, 052 —
054, 064 — 088, 096 — 101,
126, 127
[icon-MU100] 000, 008, 016,
024, 048, 056, 064, 072, 080,
088, 096, 104, 120
[icon-SFX] SFX
[icon-VL] 000 — 003, 112 —
119
TG300B: 000, 001 — 011, 016 — 019,
024 — 026, 032, 033, 040,
126, 127
C/M: Fixed (only one bank)
Drum part:
XG: 126, 127
TG300B: 000
C/M: Fixed (only one bank)
This determines the bank number of the
selected Part’s Voice. (Refer to the SOUND
LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.)
For more information on selecting banks,
see page 28 and Display Bank Select pa-
rameter, page 160.
Program (Voice) Number
Settings:
A1 (A/D Input part): 001 — 013
A2 (A/D Input part): 001 — 005
Normal part: 001 — 128
This determines the Voice for the selected
Part. (Refer to the SOUND LIST & MIDI
DATA booklet.)
Volume
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the Volume setting for
the selected Part’s Voice.
Part Controls

Multi Mode
97
Expression (Expresn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the Expression setting for
the selected Part’s Voice.
Pan
Settings: Rnd (Random),
L63 — C — R63
This determines the stereo position of the
selected Part’s Voice. A setting of “Rnd”
(Random) randomly assigns the Voice to
a pan position. This is useful when you
want to have different Voices sound from
different random parts of the stereo im-
age. (The Random setting does not affect
the A/D input Parts and VL Voice Parts.)
Reverb Send (RevSend)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
Part’s Voice that is sent to the Reverb ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a com-
pletely “dry” Voice sound.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter
to work as intended. (See page 142.)
Part Controls
Chorus Send (ChoSend)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
Part’s Voice that is sent to the Chorus ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a completely
“dry” Voice sound (no Chorus effect).
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter
to work as intended. (See page 143.)
Variation Send (VarSend)
Settings: off, on (when Variation Con-
nection is set to INS);
000 — 127 (when Variation
Connection is set to SYS)
This determines whether the selected Part’s
Voice is sent to the Variation effect or not.
A setting of “off” or “000” results in no
Variation effect being applied to the Voice.
Note Shift (NoteSft)
Range: –24 — +24 semitones
This determines the key transposition set-
ting for the Part’s Voice.

98
Multi Mode
All Part Control
The All Part controls include: Device Number, Master Volume, Master At-
tenuator, Reverb Return, Chorus Return, Variation Return and Transpose.
Keep in mind that these controls affect all Parts equally, and either add to or
subtract from their individual values. For example, if Note Shift on one Part
is set to –12, and Transpose (in All Part) is set to +12, that Part’s pitch value
will actually be 0 or normal. For basic information on using the All Part
controls, see page 35.
Part Controls
Device Number (DevNo.)
Settings: 1 — 16, all
This determines the Device Number for
the MU100R, a kind of MIDI “identifi-
cation” number to distinguish between
multiple units. For example, if you are
using more than one MU100R, set a dif-
ferent Device Number for each. This set-
ting only applies to the data dump fea-
tures. (See page 161.) If you have only
one MU100R, set this to “all.”
Master Volume (M.Volum)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the overall Volume of the
Parts.
Master Attenuator (M.Attn)
Range: 000 (maximum volume) —
127 (minimum volume)
This determines the level of all Parts, but
functions as an attenuator; the greater the
value, the lower the volume. This is useful
when you are playing several songs and
want to keep their overall level consistent.
Reverb Return (RevRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Reverb
return in the overall mix.
Chorus Return (ChoRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Chorus
return in the overall mix.

Multi Mode
99
Variation Return (VarRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Variation
return in the overall mix. Variation Re-
turn is only available when the Variation
Connection parameter is set to SYS. (See
page 145.)
Transpose (Trans)
Range: –24 — +24 semitones
This determines the overall Transpose
setting of the Parts.
Part Controls

100
Multi Mode
Multi Edit Mode
The Multi Edit mode features various parameters for controlling the Filter,
the EG (Envelope Generator), the EQ, and Vibrato. It also features a variety
of other miscellaneous controls grouped in the Others parameters. When a
Drum Part is selected, Drum-related parameters are also available. When
the VL Voices are assigned to the selected Part, the VL Edit parameters
(“PLUGIN”) are also available (page 119).
For basic information on using the Multi Edit mode, see page 36.
NOTE
When a VL Voice is selected, the following Multi Edit parameters are not available:
HPF Cutoff — in Filter menu
Low Frequency and High Frequency — in EQ Menu (However, both Gain
parameters are effective.)
Element Reserve, Velocity Limit Low and Velocity Limit High — in Others
menu
Filter (FIL)
Path: [EDIT] button → “FILTER” (“FIL” when a VL Part is selected.)
Filter ——————————————————————————
●
LPF Cutoff Frequency
●
LPF Resonance
●
HPF Cutoff Frequency
The MU100R features a digital filter that can be used to change the tim-
bre of the Voices. The filter is affected (together with the level) by the EG
(Envelope Generator), which allows you to change the timbre over time
as well. (See EG, page 102.)
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
101
LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the cutoff frequency of
the low pass filter (LPF). The LPF filters
out frequencies higher than the cutoff
point and “passes” the lower frequencies.
Lower cutoff values create a deeper, more
rounded tone, while higher values create
a brighter tone.
Frequency
Level
These frequencies are
“cut” or filtered out.
These frequencies
are “passed” or let
through.
LPF Cutoff Frequency
setting
LPF Resonance (LPF Reso)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the amount of filter reso-
nance or emphasis of the LPF Cutoff Fre-
quency above. Higher values make the
filter effect more pronounced and stron-
ger, creating a resonant peak around the
cutoff frequency.
Frequency
Level
Resonance
LPF Cutoff Frequency setting
HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the cutoff frequency of the
high pass filter (HPF). The HPF filters out
frequencies lower than the cutoff point and
“passes” the higher frequencies. Lower cut-
off values preserve the fundamental and
lower overtones of the sound, while higher
values create a thinner, brighter tone.
Frequency
Level
These frequencies
are “cut” or
filtered out.
HPF Cutoff Frequency
setting
These frequencies are
“passed” or let through.
Multi Edit Mode

102
Multi Mode
Envelope Generator (EG)
Path: [EDIT] button → “EG”
EG (Envelope Generator) —————————————————
Level/Filter EG Parameters ..................................... 103
●
EG Attack Time
●
EG Decay Time
●
EG Release Time
Pitch EG Parameters .............................................. 103
●
Pitch EG Initial Level
●
Pitch EG Attack Time
●
Pitch EG Release Level
●
Pitch EG Release Time
The EG parameters allow you to shape the sound of a Part’s Voice — or,
in other words, set how the level and timbre of the Voice changes over
time. This section also includes independent Pitch Envelope Generator
(PEG) parameters for controlling how the pitch of a Part’s Voice changes
over time.
The relationship of the main EG parameters — Attack, Decay and Re-
lease — are shown in the illustration below. These parameters not only
affect the sound level, but also the timbre (with the Filter parameters; see
page 100).
Multi Edit Mode
1) Short Attack, Decay, Release times:
Level
Attack
Decay Release
Time
Ke
y
is releasedKe
y
is
p
ressed
Min.
Max.
Level
Attack Decay Release
Time
Ke
y
is releasedKe
y
is
p
ressed
Min.
Max.
2) Long Attack, Decay, Release times:
Even though the key is held for the same length of time in both examples,
the sound of the second example slowly reaches full volume and decays
over a longer time. It also sustains longer after the key is released.
Keep in mind that the EG parameters affect each other, and are affected
by how long a note is held. For example, if Decay is set to a low value
and the note is held for a long time, you may not be able to hear changes
made to the Release parameter.

Multi Mode
103
Level/Filter EG Parameters
EG Attack Time
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the Attack Time of the
EG, or how long it takes for the sound to
reach full volume when a note is played.
For the Filter, this determines how long
it takes for the sound to be affected by
the maximum Filter values.
EG Decay Time
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the Decay Time of the
EG, or how rapidly the sound dies out as
a note is held. For the Filter, this deter-
mines how long it takes for the Filter ef-
fect to die out.
EG Release Time
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the Release Time of the
EG, or how long the sound sustains after
a note is released. For the Filter, this de-
termines how long the Filter effect con-
tinues after a note is released.
Pitch EG Parameters
The Pitch EG parameters determine how
the pitch of a Part’s Voice changes over
time. This lets you produce subtle or pro-
nounced pitch changes as a note is played.
In the example Pitch EG settings below,
a played note is gradually bent up to its
normal pitch, and kept there as the note
is held. When the note is released, the
pitch rapidly climbs up.
Normal
Pitch
Time
Key is released
Low
High
NOTE
The Pitch EG parameters may have little or
no effect, depending on the particular Voice
used and the settings made to the main EG
parameters.
Pitch EG Initial Level (PEGInitLvl)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the initial pitch of the Part’s
Voice, when the note is first played. A set-
ting of 00 corresponds to normal pitch.
Multi Edit Mode

104
Multi Mode
Pitch EG Attack Time (PEGAtakTime)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the Attack Time of the
Pitch EG, or how long it takes for the pitch
to return to normal (from the pitch value
set in Initial Level above).
Pitch EG Release Level (PEGReleLvel)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the final pitch of the
Part’s Voice, or the pitch that is reached
after the note is released. A setting of 00
corresponds to normal pitch.
NOTE
The Pitch EG Release Level and Time param-
eters may have no effect if the Voice itself
does not sustain after the note is released.
(Short percussive Voices may fall into this
category.) Also make sure that the main EG
Release Time is set to an appropriate value
so that the sound sustains.
Pitch EG Release Time (PEGReleTime)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the Release Time of the
Pitch EG, or how long it takes for the pitch
to change to the pitch value set in Release
Level above.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
105
Multi Edit Mode
Equalizer (EQ)
Path: [EDIT] button → “EQ”
EQ (Equalizer) ——————————————————————
●
EQ Low Frequency
●
EQ Low Gain
●
EQ High Frequency
●
EQ High Gain
The EQ parameters let you adjust and set the tonal quality of a Part’s
Voice, such as boosting the bass sound, or making it brighter. This is a
two-band equalizer with wide frequency variation for each band, and is
independent of the overall EQ controls (see page 155).
EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq)
Range: 32 Hz — 2.0 kHz
This determines the frequency which is
boosted or cut (in the Low Gain param-
eter below) for each Part.
EQ Low Gain
Range: –64 — +00 — +63
This determines the level of the selected
frequency (in Low Freq above). Positive
values boost the level of the selected fre-
quency and negative values attenuate it.
EQ High Frequency (High Freq)
Range: 500 Hz — 16 kHz
This determines the frequency which is
boosted or cut (in the High Gain param-
eter below) for each Part.
EQ High Gain
Range: –64 — +00 — +63
This determines the level of the selected
frequency (in High Freq above). Positive
values boost the level of the selected fre-
quency and negative values attenuate it.

106
Multi Mode
Vibrato
Path: [EDIT] button → “VIBRATO”
(“VIB” When a VL Part is selected)
Vibrato —————————————————————————
●
Vibrato Rate
●
Vibrato Depth
●
Vibrato Delay
Vibrato produces a quavering, vibrating sound in the Part’s Voice, by regu-
larly modulating the pitch. You can control the speed and depth of the Vi-
brato, as well as the time it takes before the Vibrato effect is applied.
Vibrato Rate
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the speed of the Vibrato
effect. Higher values result in a faster Vi-
brato sound.
Vibrato Depth
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the depth of the Vibrato
effect. Higher values result in a stronger,
more pronounced Vibrato sound.
Vibrato Delay
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the delay in the onset of
the Vibrato effect. Delay is effective es-
pecially on stringed instrument Voices.
For example, violin players often use de-
layed vibrato, especially while playing
long notes. The Delay parameter is use-
ful in recreating this effect, producing a
more natural, lifelike sound. Higher val-
ues result in a longer Delay time.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
107
Others
Path: [EDIT] button → “OTHERS”
Others —————————————————————————
Detune .................................................................. 108
●
Detune
Assignment Parameters .......................................... 108
●
Part Mode
●
Mono/Poly Mode
Portamento Parameters .......................................... 109
●
Portamento Switch
●
Portamento Time
Element ................................................................. 109
●
Element Reserve
Note Limit Parameters ........................................... 110
●
Note Limit Low
●
Note Limit High
Dry Level ............................................................... 110
●
Dry Level (VarConnect=SYS)
Velocity Sensitivity Parameters .............................. 110
●
Velocity Sensitivity Depth
●
Velocity Sensitivity Offset
Velocity Limit Parameters ...................................... 111
●
Velocity Limit Low
●
Velocity Limit High
Pitch Bend, Modulation Wheel,
Assignable Controller ............................................ 111
●
Pitch Bend Control
●
MW LFO Pitch Modulation Depth
●
AC1 Control Change Number
●
AC1 Filter Control
●
AC1 Amplitude Control
Output Assignment ................................................ 113
●
Output select
The Others section of parameters contains miscellaneous controls, in-
cluding those related to tuning, Part Mode, velocity, portamento, note
range, etc.
Multi Edit Mode

108
Multi Mode
Detune
Detune
Range: –12.8 — +12.7
This determines the fine tuning of the
Part’s Voice.
HINT
Detune could be used to slightly detune a Voice
compared to the tuning of the rest of the Voices
for a richer sound. It could also be used to
detune two different Voices being played in
unison. For example if two different Parts are
set to the same MIDI channel (see page 96) and
same Voice, a naturally thick chorusing effect
can be obtained by slightly detuning each Voice
in opposite directions here.
Assignment Parameters
Part Mode
Settings: normal, drum, drumS1 — S4
(When Sound Module mode
is set to C/M, both Parts 10
and 26 are set to drumS1.)
This determines the mode for the Part. A
setting of normal allows selection of the
normal instrument Voices. (See the
SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.)
The drum setting allows selection of the
drum kits. (See the SOUND LIST &
MIDI DATA booklet.) The drumS1 —
S4 settings are locations for storing spe-
cially programmed drum setups. These
setups can be edited by using the Drum
Setup controls in the Multi Edit mode.
Multi Edit Mode
(See page 114.) The drum and drumS1
— S4 settings are not available in the Per-
formance mode (all Parts are fixed to
“normal”).
The Part Mode settings differ depending
on the Sound Module mode selected, as
described below.
For XG (Extended General MIDI) mode:
All settings described above are available.
When normal is selected, any of the ba-
sic or the extended set of Voices can be
used for the Part.
For TG300B mode:
The settings normal and drumS1 — S4
are available; drum cannot be selected.
When normal is selected, either the ba-
sic or the extended set of Voices (for the
TG300B mode) can be used for the Part.
For C/M mode:
The Part Mode settings are fixed in this
mode and cannot be changed: Parts 10
and 26 are set to drumS1, and all other
Parts are set to normal. The MIDI Re-
ceive Channel setting for Parts 1 and 17
is set to off. The 128 Voices of C/M Type
1 can be used for Parts 1 — 9 and 17 —
25; the 64 Voices of C/M Type 2 can be
used for Parts 11 — 16 and 27 — 32.
For PFM (Performance) mode:
All four Parts are set to normal; none of
the drum settings are available. Any of
the basic or the extended set of Voices can
be used for each Part.
NOTE
When two or more different Parts are set to
the same editable drum setup (drumS1 — S4),
any edits made to that drum setup automati-
cally affect all those Parts. For example, when
two Parts are set to drumS1, any changes
made to drumS1 affect both Parts.
Height of bars indicates selected Part Mode
setting for each Part. (A single bar indicates
“normal” setting.)

Multi Mode
109
Multi Edit Mode
Mono/Poly Mode
Settings: mono, poly
This determines whether the Part’s Voice
is played monophonically (only one note
at a time) or polyphonically (up to 64
notes at a time). This parameter is not
available when the Part Mode is set to
Drum.
Portamento Parameters
Portamento is a function that creates a
smooth pitch glide from one note to an-
other.
Portamento Switch (PortametSw)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether Portamento is
on or off for the Part. (This parameter is
not available for Drum Parts.)
Portamento Time (PortametTm)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the time of the
Portamento effect, or how long it takes to
glide the pitch from one note to the next.
Higher values result in a longer pitch glide
time. (This parameter is not available for
Drum Parts.)
Element
Element Reserve (ElemReserv)
Range: 00 — 64
This determines the minimum number of
sound elements that are reserved for the
Part. This setting ensures that when the
maximum simultaneous polyphony of 64
notes (or elements) is exceeded, the se-
lected Part will still play up to the num-
ber of elements set here. For example, if
the Element Reserve of a Part is set to
10, the sounds for that Part (up to 10 si-
multaneous notes) will not be cut off, even
if the maximum polyphony is exceeded.
The total number of Element Reserve
values for all of the Parts cannot exceed
64.
This parameter is useful when playing
back dense song data, and it ensures that
the most important Parts in the song data
will play properly without being cut off.
Height of bars indicates selected Mono/Poly
Mode setting for each Part. (A single bar
indicates “mono” setting, while full height
indicates “poly”.)
Height of bars indicates selected Portamento
Switch setting for each Part. (A single bar
indicates “off” setting, while full heignt
indicates “on.”)

110
Multi Mode
Note Limit Parameters
The Note Limit Low and High parameters
allow you to set the range of notes for a
Part’s Voice. Notes outside the range will
not be played.
HINT
Note Limit can be used to set up keyboard
splits. Set two Parts to the same MIDI chan-
nel (see page 96), but give them Note Limit
settings so that one Part is played from the
left side of the keyboard and the other is
played from the right.
Note Limit Low (NoteLimitL)
Range: C-2 — G8
This determines the lowest responding
note for the Part. Notes below this value
will not be played.
Note Limit High (NoteLimitH)
Range: C-2 — G8
This determines the highest responding
note for the Part. Notes above this value
will not be played.
Dry Level
Dry Level
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the unproc-
essed sound of the Voice (sound with no
effect processing). This parameter is only
available when the Variation Connection
parameter is set to SYS. (See page 145.)
Velocity Sensitivity Parameters
Velocity Sensitivity Depth (VelSensDpt)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the degree to which ve-
locity affects the Part’s Voice. Higher val-
ues make the Voice more sensitive to
changes in velocity.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
111
Velocity Sensitivity Offset (VelSensOfs)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the volume range over
which velocity affects. For lower values,
the velocity affects a volume range from
minimum to medium-loud. For higher
values, velocity affects a range from me-
dium-soft to maximum.
Level
127
127
0
at 127
at 64
at 0
Velocit
y
NOTE
Depending on the Voice used, if Velocity Sen-
sitivity Offset is set to too low of a value, the
Voice may not sound, no matter how strong
the velocity.
Velocity Limit Parameters
The Velocity Limit Low and High param-
eters allow you to set the effective veloc-
ity range for a Part’s Voice. Velocity val-
ues outside the range will not be played.
(Velocity is generally the strength at
which notes are played from a MIDI key-
board.)
HINT
Velocity Limit can be used to set up velocity
splits. A velocity split allows you to have one
Part’s Voice sound when you play the con-
nected keyboard strongly, and a different
Voice sound when you play softly. Set two
Parts to the same MIDI channel (see page 96),
but give them different Velocity Limit settings
so that one or the other sounds depending
on how strongly you play the keyboard.
Multi Edit Mode
Velocity Limit Low (VelLimitLo)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the lowest velocity value
at which the Part’s Voice will play. The
higher the value, the harder the keyboard
must be played for the Voice to sound.
Velocity Limit High (VelLimitHi)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the highest velocity value
at which the Part’s Voice will play. The
lower the value, the less strength needed
(in playing the keyboard) to get maximum
volume.
no
sound
no
sound
1 127
VelLimitLo VelLimitHi
Pitch Bend, Modulation Wheel,
Assignable Controller
Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl)
Range: –24 — +24 semitones
(+/– 2 octaves)
This determines the Pitch Bend range for
the Part’s Voice. (Pitch Bend is usually
controlled by a pitch bend wheel on a
MIDI keyboard.)

112
Multi Mode
Modulation Wheel — LFO Pitch
Modulation Depth (MW LFOPMod)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines how widely the pitch is
modulated by the LFO (low frequency os-
cillator). This is generally controlled from
a modulation wheel on a MIDI keyboard
and produces a vibrato effect. The higher
the value, the deeper the pitch modula-
tion, and hence, the more pronounced the
vibrato effect.
Assignable Controller 1 Control
Change Number (AC1 CC No.)
Range: 00 — 95
This determines the which MIDI control
change number is assigned to the Assign-
able Controller (AC1) for the selected
Part. AC1 can be used to affect the Filter
(page 112), volume (Amplitude; page
113), LFO (page 133) or the Variation ef-
fect (page 145). Make sure that param-
eters you don’t want to be affected by AC1
are properly set to 00.
HINT
Though this parameter allows you to assign
any control change number from 0 to 95, only
a few of these are in common use. The con-
trollers most likely to be encountered include:
01 — Modulation wheel or lever
02 — Breath controller
04 — Foot controller
07 — Volume controller
Some or all of these may be available on your
MIDI instrument, and can be used to control cer-
tain functions on the MU100R in real time. Some
Multi Edit Mode
MIDI instruments allow you to change the con-
trol change number for a particular controller:
for example, setting the modulation wheel (nor-
mally 01) to control Volume (07). Refer to the
owner’s manual of your particular instrument for
more information. Also see page 62 in the VL
Voice section for more details on controllers.
Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control
(AC1 FilCtrl)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the degree to which Assign-
able Controller 1 (AC1) affects the Cutoff
Frequency of the Low Pass Filter for each
Part. For maximum effect, this should be
set to one of the extreme values, negative
or positive. A setting of 00 results in no con-
trol over the Filter, even when AC1 is oper-
ated (or control change data is received).
Negative settings affect the Filter negatively;
in other words, when the controller is at the
minimum position, control over the Filter
is greatest (see illustration below). (The con-
trol number used for AC1 is set in the As-
signable Controller 1 Control Change Num-
ber parameter above.)
For positive values: For negative values:
Minimum
effect
Maximum
effect
Maximum
effect
Minimum
effect
HINT
Positive and negative values can be most ef-
fectively used by setting two different Parts to
opposite settings. In this way, moving the con-
troller (for example, a foot controller) one way
will affect one Part and moving it the oppo-
site way will affect the other Part.

Multi Mode
113
Multi Edit Mode
Output Assignment
Output Select (OutPtSel)
Settings: stereo, ind1+2, ind1, ind2
This determines the output configuration
for the selected Part. When set to “ste-
reo,” the Part is output (with effects)
through the main OUTPUT and PHONES
jacks. When set to one of the “ind” (indi-
vidual) settings, it is output through the
INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. In this case, only
Insertion effects can be applied; System
effects cannot be applied to the INDIV.
OUTPUT jacks. When set to “ind1+2,”
the Part is output in stereo (1: left, 2:
right). Settings of “ind1” and “ind2” out-
put the Part in mono to the correspond-
ing jack. (Parts output through the
INDIV. OUTPUT jacks cannot be heard
through the PHONES jack.)
NOTE
●
The Output Select Lock parameter (page
158) must be set to “off” in order to change
this setting via MIDI.
●
When the Part Mode parameter (page 108)
is set to “drum” or “drum S1 — S4”, this
setting is inactive.
Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude
Control (AC1 AmpCtrl)
Range: 64 — +63
This determines the degree to which As-
signable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the
volume (Amplitude) for each Part. For
maximum effect, this should be set to one
of the extreme values, negative or posi-
tive. A setting of 00 results in no volume
control, even when AC1 is operated (or
control change data is received). Nega-
tive settings affect the volume negatively;
in other words, when the controller is at
the minimum position, control over the
volume is greatest. (The control number
used for AC1 is set in the Assignable
Controller 1 Control Change Number
parameter above.)
NOTE
For more information on using positive and
negative values, see the illustration and hint in
Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (page
112).

114
Multi Mode
Drum Setup Controls
The Drum Setup controls allow you to make a wide variety of settings for
the drum sounds in a Drum Part. These settings include Pitch controls,
Level, Pan, effect send, filter controls and EG (Envelope Generator),
among others. Moreover, these parameters can be set to completely inde-
pendent values for each of the drum sounds in a Part.
The Drum Setup controls can only be called up by first selecting a Part to
which a Drum Part is assigned. (For basic information on using the Drum
setup controls, see page 39.)
Parh: [EDIT] button → “DRUM”
Drum Setup Controls ———————————————————
Pitch Parameters .................................................... 115
●
Pitch Coarse
●
Pitch Fine
●
Velocity Pitch Sensitivity (VelPchSens)
Level...................................................................... 115
●
Level
Pan ........................................................................ 115
●
Pan
Effect Send Parameters........................................... 115
●
Reverb Send (Rev Send)
●
Chorus Send (Cho Send)
●
Variation Send (Var Send)
Filter Parameters .................................................... 116
●
LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff)
●
LPF Resonance (LPF Reso)
●
Velocity LPF Cutoff Sensitivity (VelLPFSens)
●
HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff)
EQ Parameters ....................................................... 117
●
EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq)
●
EQ Low Gain
●
EQ High Frequency (High Freq)
●
EQ High Gain
EG Parameters ....................................................... 117
●
EG Attack
●
EG Decay 1
●
EG Decay 2
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
115
Multi Edit Mode
Pitch Parameters
Pitch Coarse
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the coarse pitch setting
of the selected drum sound.
Pitch Fine
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the fine pitch setting of
the selected drum sound.
Velocity Pitch Sensitivity (VelPchSens)
Range: –16 — +16
This determines the degree to which pitch
changes of the selected drum sound respond
to velocity. In other words, you can control
how much the pitch of the sound changes
by how hard or soft you play the keys of a
connected keyboard. Positive values raise
the pitch and negative values lower the pitch.
A value of 00 results in no pitch change,
whatever velocity is received.
Level
Level
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the volume of the se-
lected drum sound.
Pan
Pan
Settings: Rnd (Random), L63 — C —
R63
This determines the stereo position of the
selected drum sound. A setting of “Rnd”
(Random) randomly assigns the drum to a
pan position. This is useful when you want
to have different drums sound from differ-
ent random parts of the stereo image.
Effect Send Parameters
Reverb Send (Rev Send)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
drum sound that is sent to the Reverb ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a com-
pletely “dry” drum sound, no matter how
much Reverb is applied to the Drum Part.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter to
work as intended. (See page 142.) Also, the pa-
rameters Reverb Send in Single Part control
(page 97) and Reverb Return in All Part control
(page 98) must be set to appropriate values.
Assignment ............................................................ 117
●
Alternate Group
Note On/Off .......................................................... 118
●
Receive Note On (RcvNoteOn)
●
Receive Note Off
Output Assignment ................................................ 118
●
Output Select (OutptSel)
The Drum Setup parameters are only available when the Part Mode has
been set to drumS1 — S4. (See page 108.)

116
Multi Mode
Chorus Send (Cho Send)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
drum sound that is sent to the Chorus ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a com-
pletely “dry” drum sound, no matter how
much Chorus is applied to the Drum Part.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter to
work as intended. (See page 143.) Also, the pa-
rameters Chorus Send in Single Part control
(page 97) and Chorus Return in All Part control
(page 98) must be set to appropriate values.
Variation Send (Var Send)
Settings: off, on (when Variation Con-
nection is set to INS);
000 — 127 (when Variation
Connection is set to SYS)
This determines the level of the selected
drum sound that is sent to the Variation ef-
fect. A setting of off results in a completely
“dry” drum sound, no matter how much
Variation is applied to the Drum Part.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Variation effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter to
work as intended. (See page 144.) Also, the pa-
rameters Variation Send in Single Part control
(page 97) and Variation Return in All Part con-
trol (page 99) must be set to appropriate values.
Filter Parameters
LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff)
Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 —
127 (TG300B or C/M mode)
This determines the cutoff frequency of
the low pass filter (LPF) for the selected
drum sound. The LPF filters out frequen-
cies higher than the cutoff point and
“passes” the lower frequencies. Lower
cutoff values create a deeper, more
rounded tone, while higher values create
a brighter tone. (For more information,
see LPF Cutoff Frequency on page 101.)
LPF Resonance (LPF Reso)
Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 —
127 (TG300B or C/M mode)
This determines the amount of filter reso-
nance or emphasis of the LPF Cutoff Fre-
quency above for the selected drum
sound. Higher values make the filter ef-
fect more pronounced and stronger, cre-
ating a resonant peak around the cutoff
frequency. (For more information, see
LPF Resonance on page 101.)
Velocity LPF Cutoff Sensitivity (VelLPFSens)
Range: –16 — +16
This determines the degree to which the
LPF Cutoff Frequency for the selected
drum sound changes in response to ve-
locity. In other words, you can shift the
LPF Cutoff Frequency of the filter up or
down (and thus change the timbre of the
sound) depending on how hard or soft you
play the keys of a connected keyboard.
Positive values raise the LPF Cutoff Fre-
quency and negative values lower it. A
value of 00 results in no frequency
change, whatever velocity is received.
HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the cutoff frequency of
the high pass filter (HPF) for the selected
drum sound. The HPF filters out frequen-
cies lower than the cutoff point and
“passes” the higher frequencies. Lower
cutoff values preserve the fundamental
and lower overtones of the sound, while
higher values create a thinner, brighter
tone. (For more information, see HPF
Cutoff Frequency on page 101.)
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
117
Multi Edit Mode
EQ Parameters
EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq)
Range: 32 Hz — 2.0 kHz
This determines the frequency which is
boosted or cut (in the Low Gain param-
eter below) for the selected drum sound.
EQ Low Gain
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the level of the selected
frequency (in Low Freq above). Positive
values boost the level of the selected fre-
quency and negative values attenuate it
for the selected drum sound.
EQ High Frequency (High Freq)
Range: 500 Hz — 16 kHz
This determines the frequency which is
boosted or cut (in the High Gain param-
eter below) for the selected drum sound.
EQ High Gain
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the level of the selected
frequency (in High Freq above) for the
selected drum sound. Positive values
boost the level of the selected frequency
and negative values attenuate it.
EG Parameters
EG Attack
Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode),
000 — 127 (TG300B or
C/M mode)
This determines the Attack Time of the
EG (Envelope Generator), or how long it
takes for the sound of the selected drum
sound to reach full volume when a note
is played. (See page 102 for more infor-
mation about the EG function; also see
illustration below.)
EG Decay 1
Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 —
127 (TG300B or C/M mode)
This determines the Decay 1 time of the
EG, or how rapidly the sound dies down
to the Decay 2 level. (See illustration be-
low.) Higher values result in a longer
Decay time.
EG Decay 2
Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 —
127 (TG300B or C/M mode)
This determines the Decay 2 time of the EG,
or how rapidly the sound dies out com-
pletely. (See illustration below.) Higher val-
ues result in a longer Decay time.
Level
EG Attack
EG Decay 1
EG Decay 2
Time
Assignment
Alternate Group
Settings: off, 001 — 127
This determines the group assignment of
the selected drum sound. Drums assigned
to the same group cannot be sounded si-
multaneously. In other words, if one drum
in a group is sounding while a second in
the same group is played, the first drum
sound will be cut off and the second will
sound.
HINT
The main use for this parameter is in creating
realistic hi-hat sounds. By assigning an open
hi-hat and a closed hi-hat to the same group,
you can “choke” or stop the open hi-hat
sound by simply playing the closed hi-hat —
just like pressing the pedal on an actual hi-
hat set.

118
Multi Mode
Note On/Off Parameters
Receive Note On (RcvNoteOn)
Settings: on, off
This determines how the selected drum
sound responds to MIDI Note On messages.
Normally, this should be set to on so that
the corresponding drum sound plays when
a MIDI Note On message is received. Set
this to off when you want to keep the se-
lected drum sound from playing.
Receive Note Off
Settings: on, off
This determines how the selected drum
sound responds to MIDI Note Off mes-
sages. When this is set to on, the selected
sound will stop in response to the corre-
sponding MIDI Note Off message. An on
setting is good for some sustained sounds
(like a whistle), whose duration you want
to control or for key-controlled cymbal
“chokes.” For most drum sounds, how-
ever, this should be set to off so that the
drum sound plays back in its entirety (is
not cut off).
Multi Edit Mode
Output Assignment
Output Select (OutPtSel)
Settings: stereo, ind1+2, ind1, ind2
This determines the output configuration for
the selected drum sound. When set to “ste-
reo,” the drum sound is output (with effects)
through the main OUTPUT and PHONES
jacks. When set to one of the “ind” (indi-
vidual) settings, it is output (without effects)
through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. When
set to “ind1+2,” the drum sound is output
in stereo (1: left, 2: right). Settings of “ind1”
and “ind2” output the drum sound in mono
to the corresponding jack. (Drum sounds
output through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks
cannot be heard through the PHONES jack.)
NOTE
The Output Select Lock parameter (page 158)
must be set to “off” in order to change this
setting.

Multi Mode
119
VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin)
The VL Voice Part parameters give you comprehensive tools for chang-
ing the character and expressive control of the VL Voices. As with the
other MU100R Voices, the edits that you make to these parameters affect
the Part and not the actual Voice itself. In other words, any parameter
changes made are applied to any other VL Voices you select. Make sure
that the Part to be edited is appropriately enabled for VL Voices. For
basic instructions on editing VL Voices, see page 62.
Path: [EDIT] → “PLUGIN”
Plugin —————————————————————————
Filter ...................................................................... 120
●
Filter Envelope Generator Depth
Pressure ................................................................. 120
●
Pressure Control Change Number
●
Pressure Control Depth
Embouchure .......................................................... 120
●
Embouchure Control Change Number
●
Embouchure Control Depth
Tonguing................................................................ 121
●
Tonguing Control Change Number
●
Tonguing Control Depth
Scream .................................................................. 121
●
Scream Control Change Number
●
Scream Control Depth
Breath Noise.......................................................... 122
●
Breath Noise Control Change Number
●
Breath Noise Control Depth
Growl .................................................................... 122
●
Growl Control Change Number
●
Growl Control Depth
Throat Formant ...................................................... 123
●
Throat Formant Control Change Number
●
Throat Formant Control Depth
Harmonic Enhancer............................................... 123
●
Harmonic Enhancer Control Change Number
●
Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth
Damping ............................................................... 124
●
Damping Control Change Number
●
Damping Control Depth
Absorption............................................................. 124
●
Absorption Control Change Number
●
Absorption Control Depth
Multi Edit Mode

120
Multi Mode
Filter
Filter Envelope Generator Depth (FilEG Dept)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by the
controller assigned to dynamic filter. The
higher the value the greater the variation. Posi-
tive values cause an increase in filter cutoff fre-
quency in response to higher controller values
(e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modu-
lation wheel position), while negative values
cause a decrease in filter cutoff frequency in
response to higher controller values.
Pressure
Pressure Control Change Number (Prs CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Pressure” corresponds to the amount of
breath pressure applied to a reed or mouth-
piece, or the speed of the bow applied to a
string. Pressure variations affect both vol-
ume and timbre. The “Prs CC No.” param-
eter specifies the controller to be used for
pressure control. When set to “off” maxi-
mum pressure is applied at all times.
Details
• Note that pressure affects not only volume,
but timbre and pitch as well. Accurate key-
board/controller pitch is produced only at
maximum pressure.
• The “PrsCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for pressure
control to have any effect.
Pressure Control Depth (PrsCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by the
controller assigned to pressure. The higher the
value the greater the variation. Positive values
cause an increase in pressure in response to
higher controller values (e.g., increased breath
pressure or higher modulation wheel position),
while negative values cause a decrease in pres-
sure in response to higher controller values.
Details
• Set this parameter to “+00” if you do not
intend to control pressure via a controller.
Embouchure
Embouchure Control Change Number
(Emb CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Embouchure” corresponds to the tightness
of the lips against the reed or against each
other. In a string instrument Voice, embou-
chure corresponds to how strongly the bow
is pressed against the string. This affects
both pitch and timbre. The “Emb CC No.”
parameter specifies the controller to be used
for embouchure control. When set to “off,”
medium embouchure is applied at all times.
Details
• Note that with many Voices, accurate key-
board/controller pitch is produced only at
medium embouchure.
• The “EmbCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to appropriate values (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for embouchure
control to have any effect.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
121
Multi Edit Mode
Embouchure Control Depth (EmbCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to embouchure.
The higher the value the greater the varia-
tion. Positive values cause an increase in
embouchure in response to higher con-
troller values (e.g., increased breath pres-
sure or higher modulation wheel posi-
tion), while negative values cause an de-
crease in embouchure in response to
higher controller values.
Tonguing
Tonguing Control Change Number
(Tng CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Tonguing” simulates the half-tonguing
technique used by saxophone players by
changing the “slit” of the reed. The slit is
the space between the tip of the reed and
the mouthpiece. The “Tng CC No.” pa-
rameter specifies the controller to be used
for tonguing control. When set to “off”
no tonguing is applied.
Details
• Note that accurate keyboard pitch is pro-
duced only when maximum tonguing is ap-
plied or the tonguing controller is turned
off.
• The “TngCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for tonguing
control to have any effect.
Tonguing Control Depth (TngCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to tonguing. The
higher the value, the greater the variation.
Positive values cause an decrease in
tonguing in response to higher controller
values (e.g., increased breath pressure or
higher modulation wheel position), while
negative values cause an increase in
tonguing in response to higher controller
values.
Scream
Scream Control Change Number
(Scr CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Scream” drives the entire system into
chaotic oscillation, creating effects that
can only be achieved with physical mod-
eling technology. The “Scr CC No.” pa-
rameter specifies the controller to be used
for scream control. When set to “off”, no
scream variation can be produced via a
controller, but a continuous scream value
is determined by the “ScrCtrlDpt” param-
eter below. (Negative values increase the
scream level.)
Details
• The “ScrCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for scream con-
trol to have any effect.

122
Multi Mode
Scream Control Depth (ScrCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to scream. The
higher the value the greater the variation.
Positive values cause an increase in
scream effect in response to higher con-
troller values (e.g., increased breath pres-
sure or higher modulation wheel posi-
tion), while negative values cause a de-
crease in scream effect in response to
higher controller values.
Breath Noise
Breath Noise Control Change Num-
ber (Bnz CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Breath Noise” can be used to add the
required amount of breath noise to a
Voice. The “Bnz CC No.” parameter
specifies the controller to be used for
breath noise control. When set to “off”,
no breath noise variation can be produced
via a controller, but a continuous breath
noise value is determined by the
“BnzCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative
values increase the breath noise level).
Details
• The “BnzCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for breath noise
control to have any effect.
Breath Noise Control Depth (BnzCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to breath noise.
The higher the value the greater the varia-
tion. Positive values cause an increase in
breath noise in response to higher con-
troller values (e.g., increased breath pres-
sure or higher modulation wheel posi-
tion), while negative values cause a de-
crease in breath noise in response to
higher controller values.
Growl
Growl Control Change Number (Grl
CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Growl” produces a periodic pressure
modulation which produces the “growl”
effect often heard in wind instruments.
The “Grl CC No.” parameter specifies the
controller to be used for growl control.
When set to “off”, no growl variation can
be produced via a controller, but a con-
tinuous growl value is determined by the
“GrlCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative
values increase the growl level).
Details
• The “GrlCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for growl con-
trol to have any effect.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
123
Growl Control Depth (GrlCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to growl. The higher
the value, the greater the variation. Positive
values cause an increase in growl effect in
response to higher controller values (e.g.,
increased breath pressure or higher modu-
lation wheel position), while negative val-
ues cause a decrease in growl effect in re-
sponse to higher controller values.
Throat Formant
Throat Formant Control Change Num-
ber (Thr CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Throat Formant” controls the characteris-
tics of the simulated player’s lungs, trachea,
and oral cavity and Can add a realistic
“roughness” to the sound. The “Thr CC No.”
parameter specifies the controller to be used
for throat formant control. When set to “off”,
no throat formant variation can be produced
via a controller, but a continuous throat
formant value is determined by the
“ThrCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative
values increase the throat formant level).
Details
•The “ThrCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for throat formant
control to have any effect.
• Throat Formant only applies to some reed-
type Voices.
Throat Formant Control Depth (ThrCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by the
controller assigned to throat formant. The
higher the value, the greater the variation. Posi-
tive values cause an increase in throat formant
effect in response to higher controller values
(e.g., increased breath pressure or higher
modulation wheel position), while negative
values cause a decrease in throat formant ef-
fect in response to higher controller values.
Harmonic Enhancer
Harmonic Enhancer Control Change
Number (Hrm CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
The Harmonic Enhancer can vary the har-
monic structure of the sound over a wide range.
The “Hrm CC No.” parameter specifies the
controller to be used for harmonic enhancer
depth (wet/dry balance) control. When set to
“off,” no harmonic enhancer depth variation
can be applied via a controller.
Details
• The “HrmCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for harmonic
enhancer control to have any effect.
• Since most VL Voices have sufficient natu-
ral harmonic content, the Harmonic En-
hancer is actually only used on a few
Voices. Therefore changing the controller
destination with many Voices will produce
either no change in the sound or a simple
change in amplitude.
Multi Edit Mode

124
Multi Mode
Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth
(HrmCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to the harmonic
enhancer. The higher the value, the greater
the variation. Positive values cause an
increase in harmonic enhancer depth in
response to higher controller values (e.g.,
increased breath pressure or higher modu-
lation wheel position), while negative
values cause a decrease in harmonic en-
hancer depth in response to higher con-
troller values.
Damping
Damping Control Change Number
(Dmp CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Damping” simulates the effect of damp-
ing due to losses within the body of a wind
instrument or in a string due to air fric-
tion. This affects both pitch and timbre.
The “Dmp CC No.” parameter specifies
the controller to be used for damping con-
trol. When set to “off,” no damping varia-
tion can be applied via a controller.
Details
• Note that accurate keyboard pitch is pro-
duced only when damping is maximum.
• The “DmpCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for damping
control to have any effect.
Damping Control Depth (DmpCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to damping. The
higher the value, the greater the variation.
Positive values cause a decrease in damp-
ing in response to higher controller val-
ues (e.g., increased breath pressure or
higher modulation wheel position), while
negative values cause an increase in
damping in response to higher controller
values.
Absorption
Apsorption Control Change Number
(Abs CC No.)
Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95,
AT, VEL, PB
“Absorption” simulates the effect of high-
frequency loss at the end of the air col-
umn or string. The “Abs CC No.” param-
eter specifies the controller to be used for
absorption control. When set to “off,” no
absorption variation can be applied via a
controller.
Details
• Note that accurate keyboard pitch is pro-
duced only at when absorption is maxi-
mum.
• The “AbsCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must
be set to an appropriate value (higher than
“+01” or lower than “-01”) for absorption
control to have any effect.
Multi Edit Mode

Multi Mode
125
Absorption Control Depth (AbsCtrlDpt)
Settings: -64 — +63
Sets the amount of variation produced by
the controller assigned to absorption. The
higher the value, the greater the variation.
Positive values cause a decrease in ab-
sorption in response to higher controller
values (e.g., increased breath pressure or
higher modulation wheel position), while
negative values cause an increase in ab-
sorption in response to higher controller
values.
Controllers
Here’s a list of some of the physical con-
trollers you might want to use with the
VL tone generator section:
Breath Controller
(MIDI control change no. 02)
A natural candidate for controlling pres-
sure, tonguing, throat formant, growl, and
other parameters.
Pitch Bend Wheel
The pitch bend wheel on your keyboard
or other MIDI device can be assigned to
a range of parameters, but it’s “standard”
function is pitch control. A controller pa-
rameter such as Embouchure can also be
assigned to the pitch bend wheel for more
realistic pitch variations.
Modulation Wheel
(MIDI control change no. 01)
Since the modulation wheel on your key-
board or other MIDI device can be as-
signed to any controller parameter, it can
be an important tool for musical expres-
sion. Use it in conjunction with a breath
controller or a foot controller for broad
expressive variation.
Foot Controller
(MIDI control change no. 04)
Like the modulation wheel, a foot con-
troller connected to your keyboard or
other MIDI device can be assigned to any
VL controller parameter.
Aftertouch
Keyboard aftertouch allows you to con-
trol any controller parameter by the pres-
sure you apply to a key after it is initially
pressed. This is perhaps the most “inti-
mate” type of keyboard expression con-
trol.
Multi Edit Mode

126
Multi Mode
MIDI Control Change Number Assignments
Control No. Controller
off(00) off
(used by Bank Select MSB)
01 Modulation Wheel
02 Breath Controller
03 Unassigned
04 Foot Controller
05 Portamento Time
06 Data Entry MSB
07 Volume Control
08~09 Unassigned
10 Panpot
11 Expression
12~31 Unassigned
off(32) off
(used by Bank Select LSB)
33~37 Unassigned
38 Data Entry LSB
39~63 Unassigned
64 Hold1
65 Portamento Switch
66 Unassigned
67 Soft Pedal
68~70 Unassigned
71 Harmonic Content
72 Release Time
73 Attack Time
74 Brightness
75~90 Unassigned
91 Effect Send Level
(Reverb Effect)
92 Unassigned
93 Effect Send Level 3
(Chorus Effect)
94 Effect Send Level 4
(Variation Effect)
95 Unassigned
AT After Touch
VEL Velocity
PB Pitch Bend
Multi Edit Mode
Velocity
Although normally assigned to pressure
(particularly in plucked string Voices),
keyboard velocity can also be assigned
to any other controller parameter.
Others
The MIDI protocol provides 119 control
change numbers, some of which are pre-
assigned to specific controllers — as
noted above, “01” is “Modulation
Wheel”, for example. 95 of these are
available for assignments to the VL con-
troller parameters, so any available MIDI
control devices can be used to full advan-
tage. A complete list of the available
MIDI control change numbers is given
below.

Performance Mode
127
Performance Mode
In the Performance mode, the MU100R performs as a four-Part tone gen-
erator, with all Parts controlled over a single MIDI channel. The Perfor-
mance mode is so named because it’s ideally suited to live performance
situations. It allows you to play four different Voices at the same time from
your MIDI keyboard — either in a layer, or in sophisticated keyboard and
velocity splits. It also gives you comprehensive control over each of the four
Parts for maximum performance flexibility. A total of 200 Performances are
available: 100 Preset and 100 Internal. For basic information on using the
Performance Mode, see page 23.
NOTE
Drum Parts are not available in the Performance mode.
Performance Part Control........................................................... 128
All Part ............................................................................... 128
Single Part .......................................................................... 129
Performance Edit Mode .............................................................. 131
Common ............................................................................ 131
Part..................................................................................... 134
Copy and Store Operations ........................................................ 137
Copy .................................................................................. 137
Store ................................................................................... 138
Recall Function .................................................................. 140

128
Performance Mode
System MIDI Channel (Sys CH)
Settings: 01 — 16
This determines the MIDI receive chan-
nel for all Parts of the Performance.
Performance Bank
Settings: Pre (Preset), Int (Internal)
This determines the bank of Performance
programs: Preset or Internal. Preset Perfor-
mances are those that have been created and
loaded at the factory; the Internal bank is
reserved for user-created Performances.
NOTE
When changing Performance banks, there may
be a slight delay before the sound changes.
Performance Number
Range: 001 — 100
This determines the Performance number.
NOTE
When changing Performance numbers, there
may be a slight delay before the sound changes.
Performance Part Control
All Part
For basic information on using the All Part controls in the Performance mode, see page
44.
Performance Volume (Pfm Vol)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the overall Volume of the
Performance.
Performance Pan (Pfm Pan)
Range: L63 — C — R63
This determines the overall Pan position
of the Performance.
Reverb Return (RevRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Reverb
return for the Performance in the overall
mix.
Performance Part Control

Performance Mode
129
Chorus Return (ChoRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Chorus re-
turn for the Performance in the overall mix.
Variation Return (VarRtn)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the amount of Variation
return in the overall mix of the Perfor-
mance. Variation Return is only available
when the Variation Connection param-
eter is set to SYS. (See page 145.)
System Transpose (SysTran)
Range: –24 — +24 semitones
This determines the overall Transpose
setting of the Performance.
Performance Part Control
Single Part
For basic information on using the Single Part controls in the Performance mode, see
page 46.
Bank Number
Settings:
A1 part: 000 — 003, 018, 019
A2 part: 000 — 003
1 — 4 part:
XG Voice banks,
MU100 Exclusive Voice banks,
VL Voice banks
This determines the bank number of the
selected Part’s Voice. Each bank contains
128 Voices. (Refer to the SOUND LIST
& MIDI DATA booklet.)
Program (Voice) Number
Range: 001 — 100
This determines the Voice for the selected
Part. (Refer to the SOUND LIST &
MIDI DATA booklet.)

130
Performance Mode
Volume
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the Volume setting for
the selected Part’s Voice.
Pan
Settings: Rnd (Random), L63 — C —
R63
This determines the stereo position of the
selected Part’s Voice. A setting of “Rnd”
(Random) randomly assigns the Voice to a
pan position. This is useful when you want
to have different Voices sound from differ-
ent random parts of the stereo image.
Reverb Send (RevSend)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
Part’s Voice that is sent to the Reverb ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a com-
pletely “dry” Voice sound.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter
to work as intended. (See page 142.)
Chorus Send (ChoSend)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the selected
Part’s Voice that is sent to the Chorus ef-
fect. A value of 000 results in a completely
“dry” Voice sound (no Chorus effect).
NOTE
Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be
properly enabled and set for this parameter
to work as intended. (See page 143.)
Variation Send (VarSend)
Settings:
off, on (when Variation Connection is
set to INS);
000 — 127 (when Variation Connec-
tion is set to SYS)
This determines whether the selected
Part’s Voice is sent to the Variation effect
or not. A setting of off or 000 results in
no Variation effect being applied to the
Voice.
Note Shift (NoteSft)
Range: –24 — +24 semitones
This determines the key transposition set-
ting for the Part’s Voice.
Performance Part Control

Performance Mode
131
Performance Edit Mode
The Performance Edit mode features various functions and parameters,
grouped in the following sections: Common (related to the Performance as a
whole), Part (related to each of the four Parts), and the Copy and Store op-
erations.
For basic information on using the Performance Edit mode, see page 43.
Common
Path: [EDIT] button → “ COM”
Common ————————————————————————
Performance Name................................................ 132
●
Performance Name (Perform Name)
Portamento Parameters .......................................... 132
●
Portamento Switch (PortamnSw)
●
Portamento Time (PortamnTm)
Modulation Wheel Parameters .............................. 132
●
LFO Pitch Modulation Depth (MW LEOPMod)
●
LFO Filter Modulation Depth (MW LFOFMod)
Pitch Bend ............................................................. 133
●
Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl)
A/D Part................................................................. 133
●
A/D Part
Assignable Controller Parameters .......................... 133
●
Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Num-
ber (AC1 CC No.)
●
Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (AC1 FilCtrl)
●
Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude Control
(AC1 AmpCtrl)
●
Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter Modulation
Depth (AC 1 LFOFMod)
The Common parameters allow you to name a Performance, enable the
A/D Parts for a Performance, and set the control change number for
realtime parameter control.
Performance Edit Mode

132
Performance Mode
Performance Edit Mode
Performance Name
Performance Name (Perform Name)
This allows you to give a name to your
edited Performance.
Operation
1 From the Performance Name dis-
play, press the ENTER button.
2 Use the SELECT </> buttons to
select the character position
(flashing character) in the name
and use the VALUE -/+ buttons
or data dial to change the charac-
ter at that position.
Up to 12 characters can be used
for the Performance name. Avail-
able characters include all letters
of the alphabet, in both upper and
lower case, numbers from 0 to 9,
and a variety of miscellaneous
characters.
Performance name
Flashes to indicate character position.
Use these to move among character positions.
Use these to change character at selected position.
3 Press the EXIT button to return to
the previous display (or press the
PLAY button to return to the Play
display).
After creating and naming a Per-
formance, you’ll probably want to
save that Performance for future
recall. For instructions on saving a
Performance, refer to the Store
operation on page 138.
Portamento Parameters
Portamento Switch (PortamnSw)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.)
Portamento Time (PortamnTm)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.)
Modulation Wheel Parameters
Modulation Wheel — LFO Pitch
Modulation Depth (MW LFOPMod)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 112.)

Performance Mode
133
Modulation Wheel — LFO Filter
Modulation Depth (MW LFOFMod)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines how widely the Filter
(page 135) is modulated by the LFO (low
frequency oscillator). This is generally
controlled from a modulation wheel on a
MIDI keyboard, and depending on the
Voice used, it creates a “swoosh” or
“wah-wah” filter sweep effect. Higher
values result in deeper filter modulation,
creating a more pronounced filter sweep
effect.
Pitch Bend
Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.)
A/D Part
A/D Part
Settings: off, on
Height of bars indicates A/D Part setting.
(A single bar indicates “off” setting,
while full height indicates “on.”)
This determines whether A/D Parts are
enabled for the Performance or not. When
set to “on,” Parts 3 and 4 are automati-
cally set as A/D Parts (A1 and A2).
HINT
You can use the MU100R strictly as an effect
processor for the A/D input (for example, your
guitar or microphone) by Soloing the appro-
priate A/D Part (A1 or A2).
Assignable Controller Parameters
Assignable Controller 1 Control
Change Number (AC1 CC No.)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode (page 112), with the
exception that AC1 in the Performance
mode can also control LFO filter modu-
lation (see Assignable Controller 1 LFO
Filter Modulation Depth below).
Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control
(AC1 FilCtrl)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 112.)
Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude
Control (AC1 AmpCtrl)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 113.)
Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter
Modulation Depth (AC1LFOFMod)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the degree to which As-
signable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the
LFO modulation of the Filter. This cre-
ates a regular and continuous “wah-wah”
or filter sweep effect. The higher the
value, the greater the LFO filter modula-
tion. (The control number used for AC1
is set in the Assignable Controller 1 Con-
trol Change Number parameter above.)
Performance Edit Mode

134
Performance Mode
Part
Path: [EDIT] button → “ PART”
PART —————————————————————————
■
FILTER
●
LPF Cutoff Frequency
●
LPF Resonance
●
HPF Cutoff Frequency
■
EG (Envelope Generator)
Level/Filter EG Parameters
●
EG Attack Time
●
EG Decay Time
●
EG Release Time
Pitch EG Parameters
●
Pitch EG Initial Level
●
Pitch EG Attack Time
●
Pitch EG Release Level
●
Pitch EG Release Time
■
EQ (Equalizer)
●
EQ Low Frequency
●
EQ Low Gain
●
EQ High Frequency
●
EQ High Gain
■
Vibrato
●
Vivrato Rate
●
Vivrato Depth
●
Vivrato Delay
■
Others
Detune .................................................................. 136
●
Detune
Assignment ............................................................ 136
●
Mono/Poly Mode
Note Limit Parameters ........................................... 136
●
Note Limit Low
●
Note Limit High
Dry Level ............................................................... 136
●
Dry Level (VarConnect=SYS)
Velocity Parameters ............................................... 136
●
Velocity Sensitivity Depth
●
Velocity Sensitivity Offset
●
Velocity Limit Low
●
Velocity Limit High
■
Plugin
The Part menu contains the Filter, EG, Vibrato, Others and Plugin pa-
rameters for the Performance.
Performance Edit Mode

Performance Mode
135
■
Filter
Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “FILTER” (“FIL” when a VL Part
is selected)
The Filter section of Performance Edit parameters are the same as the
corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 100.)
■
EG
Path:[EDIT] → “PART” → “EG”
The EG section of Performance Edit parameters are the same as the cor-
responding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 102.)
■
EQ
Path:[EDIT] → “PART” → “EQ”
The EQ Performance Edit parameters are the same as the corresponding
parameters in the Multi Edit mode (See page 105).
■
Vibrato
Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “VIBRATO” (“VIB” when VL
Part is selected)
The Vibrato Performance Edit parameters are the same as the correspond-
ing parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 106.)
■
Others
Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “OTHERS”
The Others Performance Edit parameters contains miscellaneous con-
trols, including those related to tuning, velocity, note range, etc. With a
few omitted parameters, these are the same as the parameters in the Multi
Edit mode.
NOTE
The Part Edit parameter (available in Multi Edit) is not available in Performance
Edit mode. No Drum Parts can be selected for a Performance.
Performance Edit Mode

136
Performance Mode
Performance Edit Mode
Detune
Detune
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 108.)
Assignment
Mono/Poly Mode
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.)
Note Limit Parameters
Note Limit Low (NoteLimitL)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.)
Note Limit High (NoteLimitH)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.)
Dry Level
Dry Level
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.) This
parameter is only available when the
Variation Connection parameter is set to
SYS. (See page 145.)
Velocity Parameters
Velocity Sensitivity Depth (VelSensDpt)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.)
Velocity Sensitivity Offset (VelSensOfs)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.)
Velocity Limit Low (VelLimitLo)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.)
Velocity Limit High (VelLimitHi)
Same as the corresponding parameter in
the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.)
■
Plugin
Path: [EDIT] button → “PART” → “PLUGIN”
The VL Voice section parameters of Performance Edit are the same as
the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 119.)

Performance Mode
137
Copy and Store Operations
The Copy and Store operations allow you to save and organize the Perfor-
mances you’ve created.
Copy
The Copy operation allows you to copy the settings of one Performance
program (Preset or Internal) to another Performance number (Internal
only).
Operation
1 From the Performance Edit menu, use the SELECT </> buttons
to select “COPY.” Then, press the ENTER button to call up the
Copy operation.
2 Use the SELECT </> buttons to select the desired parameter:
memory location, source number or destination number. (The
selected parameter flashes.) Then use the VALUE -/+ buttons
or data dial to change the value.
Copy and Store Operations

138
Performance Mode
3 Press the ENTER button to actually execute the Copy operation.
An “Executing…” message flashes in the display during the
operation. When the data has been copied, the MU100R returns
to the Performance Edit menu.
To cancel the operation without copying, press the EXIT button
(before pressing ENTER).
Store
Once you’ve edited or created a Performance, you can save that new
Performance for future recall by using the Store operation. Performances
can be saved to any one of the 100 Internal memory locations. With the
exception of the Receive Channel and Transpose (Note Shift) settings
made from the Play screen, all parameter settings in the Play screen and
in the Edit, Effect and EQ modes are saved to the selected Performance
number.
Operation
1 From the Performance Edit menu, use the SELECT </> buttons
to select “STORE.” Then, press the ENTER button to call up the
Store operation.
Copy and Store Operations
Memory location (P = Preset, I = Internal)
Source Performance number
Destination Performance number
Use these to select desired parameter.
Use these to change value.

Performance Mode
139
2 Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to change the destination
Performance number.
3 Press the ENTER button to actually execute the Store operation.
An “Executing...” message flashes in the display during the
operation. When the data has been stored, the MU100R returns to
the Performance Edit menu.
To cancel the operation without saving, press the EXIT button
(before pressing ENTER).
Performance number
Use these to change Performance number.
Copy and Store Operations

140
Performance Mode
Recall Function
Recall is a convenient function that allows you to recover an accidently
deleted Performance. For example, if you are editing a Performance and
inadvertently select a different Performance, the edited Performance
would normally be lost. By using Recall before turning off the MU100R
or editing another Performance, you can recover the previously edited
Performance data.
To use Recall:
1 Select RECALL in the Performance Edit Mode menu, then press
the ENTER button.
The following display briefly appears:
2 At the “Are you sure?” prompt above, press the ENTER button
again to execute the function.
If no previously edited Performance data exists, the following
display briefly appears, indicating no Performance can be recalled.
Copy and Store Operations

Effect Edit Mode
141
Effect Edit Mode
The MU100R features a built-in multi-effect processor with 6 independent
digital effects: Reverb, Chorus, Variation, Insertion 1/2 and EQ. The first 5
of these are controlled in the Effect Edit mode.
In this section, only the effect Types and the global parameters common
to all Types are covered. For descriptions and details on the parameters for
each effect Type, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA book-
let.
To enter the Effect Edit mode, press the EFFECT button. The following
menu appears:
Reverb (REV) .............................................................................. 142
Chorus (CHO) ............................................................................ 143
Variation (VAR)........................................................................... 144
Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2) .............................................................. 146
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters ........................................ 147
About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion............... 152

142
Effect Edit Mode
Reverb (REV)
Type
Settings: NO EFFECT, HALL 1 — 2,
ROOM 1 — 3, STAGE 1 —
2, PLATE, WHITE ROOM,
TUNNEL, CANYON, BASE-
MENT
This determines the Reverb Type. Each
Reverb Type has different values for the
rest of the Reverb parameters; for ex-
ample, Basement has a Reverb Time of
0.6 seconds, while Canyon has a Reverb
Time of 12.0 seconds.
NOTE
When “NO EFFECT” is selected, Reverb is
off and none of the other Reverb parameters
are available (with the exception of the Re-
verb Pan parameter).
HINT
Generally when using Reverb, you can sim-
ply select the particular Type needed, and use
it without bothering to adjust the other pa-
rameters. If fine tuning of the Reverb sound
is necessary, delve into the other parameters
as needed.
Reverb Pan (RevPan)
Range: L63 — C — R63
This determines the Pan position of the
Reverb sound, or where it appears in the
stereo image.
For details on the parameters for each
Reverb Type, refer to the separate
SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.
Reverb (REV)
Reverb recreates the sounds of various performance environments by add-
ing an ambient wash of delays or reflections. Several different types of Re-
verb effects are available to simulate the ambience of different sized rooms.
Explanations of the Reverb Type and Reverb Pan parameters are given be-
low. For descriptions and explanations for all other Reverb parameters, refer
to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.

Effect Edit Mode
143
Chorus (CHO)
The Chorus section uses pitch modulation to create a variety of rich, spa-
cious-sounding effects, including Chorus, Flanger, Symphonic and Phaser.
Explanations of the Chorus Type and Chorus Pan parameters are given be-
low. For descriptions and explanations for all other Chorus parameters, refer
to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.
Chorus (CHO)
Type
Settings: NO EFFECT; CHORUS 1 —
4; CELESTE 1 — 4;
FLANGER 1 — 3; SYM-
PHONIC; ENSEMBLE
DETUNE; PHASER 1
This determines the Chorus Type. De-
pending on the Type selected, the specific
parameters and values may differ.
Chorus 1 and 2 are used to subtly enhance
the sound, and generally make it richer,
fatter and warmer. Flanger uses modula-
tion to create an animated, swirling mo-
tion effect, and produces a characteristic
metallic sound. Symphonic also subtly
enhances the sound by making a single
instrument Voice sound like several.
Phaser is similar to Flanger, but with a
stronger and deeper modulation.
NOTE
When NO EFFECT is selected, Chorus is off
and none of the other Chorus parameters are
available (with the exception of the Chorus
Pan and Send Chorus to Reverb parameters).
Chorus Pan (ChoPan)
Range: L63 — C — R63
This determines the Pan position of the
Chorus sound, or where it appears in the
stereo image.
Send Chorus to Reverb (SendCho →
Rev)
Range: 000 — 127
This determines the level of the Chorus
signal sent to and processed by the Re-
verb effect. A setting of 000 results in
none of the Chorus-processed signal go-
ing to the Reverb.
HINT
Setting this to a relatively high level gives you a
more natural sound, since the Chorus-processed
sound is also being processed by the reverb.
More unusual effects can be created by having
a long Reverb and setting this to 0, so that the
Chorus sound is dry (no Reverb) and the origi-
nal sound is “drenched” in Reverb.
For details on the parameters for each
Chorus Type, refer to the separate
SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.

144
Effect Edit Mode
Variation (VAR)
The Variation section provides a wealth of additional effects for processing
the Voices of the MU100R. It features some of the same effects found in the
Reverb, Chorus and Insertion sections. This is not mere redundancy; it al-
lows you to use two types of Reverb, Chorus or other effects on different
Voices. For example, you may want to have the Flanger effect on one Voice
and Phaser on another. Variation also gives you many special effects not
found in the other sections, such as Delay, Gate Reverb, Wah and Pitch
Change.
The Variation section of effects can be applied either to a single selected
Part or to all Parts, depending on the connection setting: Insertion or Sys-
tem. (See About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion on page
152 for more information.)
Explanations of the Variation Type and other common parameters are given
below. For specific descriptions of Variation Types and explanations for all
other Variation parameters, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI
DATA booklet.
Variation (VAR)
Type
Settings: NO EFFECT; WHITE ROOM;
TUNNEL; CANYON; BASE-
MENT; DELAY L,C,R; DELAY
L,R; ECHO; CROSS DELAY;
ER 1 — 2; GATE REVERB;
REVERSE GATE; KARAOKE
1 — 3; CHORUS 1 — 4;
CELESTE 1 — 4; FLANGER
1 — 3; SYMPHONIC; EN-
SEMBLE; DETUNE; AMBI-
ENCE; ROTARY SPEAKER;
2WAY ROTARY SPEAKER;
TREMOLO; AUTO PAN;
PHASER 1 — 2, DISTOR-
TION; COMP+ DISTORTION;
OVER DRIVE; AMP SIMU-
LATOR; 3BAND EQ (MONO);
2BAND EQ (STEREO);
AUTO WAH (LFO); AUTO
WAH+DIST; AUTO
WAH+ODRV; TOUCH WAH
1; TOUCH WAH+DIST;
TOUCH WAH+ ODRV;
TOUCH WAH 2; PITCH
CHANGE 1 — 2; AURAL
EXCITER
®
; COMPRESSOR;
NOISE GATE; VOICE CAN-
CEL; TALK MOD; LO-FI;
DIST+DELAY;
ODRV+DELAY;
CMP+DT+DLY;
CMP+OD+DLY;
WAH+DT+DLY;
WAH+OD+DLY; THRU
NOTE
When NO EFFECT or THRU is selected for
the Type, no Variation effect is applied, and
only the common parameters shown below
are available (with the exception of Dry/Wet).
The NO EFFECT setting cancels the Variation
effect. When the Variation Connection is set
to SYS (System), the sound can be heard with
no effect. When the Variation Connection is
set to INS (Insertion), no sound is output for
the Part.
When set to THRU, the sound of the Part (or
Parts) is output without any Variation effect.
Generally, when Variation Connection is set
to INS (Insertion), you should set the Type to
Thru. When Variation Connection is set to
SYS (System), you should set the Type to NO
EFFECT.

Effect Edit Mode
145
Dry/Wet (Insertion connection)
Range: D63>W — (D=W) — D<W63
Adjusts the level balance of original
sound (dry, or D) and processed sound
(wet, or W). A setting of (D=W) results
in an equal balance of dry and wet sound.
Assignable Controller 1 Variation Con-
trol (AC1VarCtrl) (Insertion connection)
Range: 000 — 127
Determines the amount of effect the As-
signable Controller has on the Variation
effect.
Variation Pan (VarPan) (System
connection)
Range: L63 — C — R63
Determines the pan position of the Varia-
tion effect.
Send Variation to Chorus
(SendVar→Cho) (System connection)
Range: 000 — 127
Determines the amount of Variation ef-
fect sound that is sent to the Chorus ef-
fect.
Send Variation to Reverb
(SendVar→Rev) (System connection)
Range: 000 — 127
Determines the amount of Variation ef-
fect sound that is sent to the Reverb ef-
fect.
Variation Connection (VarConnect)
Settings: INS (Insertion), SYS (System)
Determines how the Variation effect is
connected in the effect chain of the
MU100R. When set to SYS (System),
Variation is applied to all Parts, accord-
ing to the amount of Variation Send set
for each Part. When set to INS (Insertion),
Variation is applied to only the selected
Part, set in Send Variation parameters (see
above).
NOTE
The common parameters above are common
to nearly all the Variation effect types. (Ex-
ceptions are described in the separate
SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.)
Variation (VAR)

146
Effect Edit Mode
Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2)
The Insertion 1 and 2 effects provide additional effects for processing indi-
vidual Parts.
Explanations of the Type, Dry/Wet Balance and Part parameters are given
below. For descriptions and explanations for all other parameters, refer to
the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.
The Insertion effects are set up for Insertion routing and can be applied only
to a single selected Part. Refer to About the Effect Connections — System
and Insertion on page 152 for more information.
Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2)
Type
Settings: THRU; HALL 1 — 2; ROOM
1 — 3; STAGE 1 — 2;
PLATE; DELAY L,C,R;
DELAY L,R; ECHO; CROSS
DELAY; KARAOKE 1 — 3;
CHORUS 1 — 4; CELESTE
1 — 4; FLANGER 1 — 3;
SYMPHONIC; ENSEMBLE
DETUNE; ROTARY
SPEAKER; TREMOLO;
AUTO PAN; PHASER 1;
DISTORTION; OVER
DRIVE; AMP SIMULATOR;
3BAND EQ (MONO);
2BAND EQ (STEREO);
AUTO WAH (LFO); TOUCH
WAH 1 — 2, AURAL EX-
CITER
®
, COMPRESSOR;
NOISE GATE
NOTE
When Thru is selected, no effect is applied,
and none of the parameters are available
(with the exception of the Part parameter).
Dry/Wet Balance
Range: D63>W — (D=W) — D<W63
This determines the balance between the
direct, unprocessed signal (dry) and the pro-
cessed sound (wet). Use this parameter to-
gether with the Output Level parameter
above to obtain the desired overall sound.
Assignable Controller 1 Insertion 1/2
Control (AC1INS1/2Ctrl)
Range: –64 — +63
This determines the degree to which As-
signable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the
MIDI-controllable parametes of the In-
sertion effects. Each of the Insertion ef-
fect types have one parameter which can
be controlled by the AC1. (For details, see
the “Effect Parameter List” of the
“SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA” book-
let.) This parameter is not available in the
performance mode.
Insertion 1, 2 Part (INS 1, 2 Part)
Range: Part 1 — 32, AD 1, AD 2, off
This determines the Part to which the In-
sertion effect is applied. Insertion can be
applied to only one Part at a time.

Effect Edit Mode
147
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters
Path: [EFFECT] button → “PLG” → “PLG100-VH”
These parameters control the Harmony effect. Other Harmony param-
eters not included in this section are the MIDI channel settings for the
harmony and melody, which are set in the Utility mode (see page 171).
For general information on the Harmony effect and how to use it, refer to
the Guided Tour section, page 77.
Type
Settings: THRU, VOCODER HM,
CHORDAL HM, DETUNE HM,
CHROMAT.HM (Chromatic)
This determines the Type of the Harmony
effect (as explained below). For infor-
mation on how each of these Types can
be set, refer to the Mode parameter (page
148), which features different settings de-
pending on the Type. Other Harmony
parameters may or may not be available,
depending on the Type selected here.
Thru
No Harmony effect is applied.
NOTE
When Thru is selected, the only other avail-
able parameter is Insert Part (page 151).
Vocoder
This produces up to three harmony notes
whose pitches correspond to the notes you
play on a connected MIDI keyboard. In
other words, you can sing the melody and
“play” the harmony or harmonies from
the keyboard (or from a sequencer). The
Harmony sound can also be transposed
(see the Mode parameter below).
NOTE
When more than three MIDI notes are received
(or two notes, when the Lead Gender Type param-
eter is set to any setting but “off”), priority is given
first to the most recently played notes. (In other
words, the harmonies of earlier notes are cut off.)
Hint
The Vocoder Type is best suited when:
• You want to determine the precise harmony
notes yourself, including their octave reg-
ister and whether they are above or below
the original melody note.
• You want to use harmony notes and voicings
that fall outside the standard chords avail-
able in the Chordal type (below).
• You can play the harmony part on the key-
board, or have it played on a sequencer.
• You want to precisely control how the har-
mony note or notes change pitch around a
fixed melody pitch.
Chordal
This produces up to three harmony notes
that correspond to the chords you play on
a connected MIDI keyboard (or chords
recorded to a sequencer). For example,
if you play a C major triad on the key-
board and sing C note (and Chordal Mode
is set to “trio”), the resulting harmonies
will be C, E, and G. Thirty-four different
chord types are recognized in this mode
(see list below), giving you an amazingly
full and flexible palette of harmonies,
suitable for nearly any music style. The
number of harmonies produced and their
position above or below the melody is set
in the Mode parameter (page 148).

148
Effect Edit Mode
In general, the Chordal Type is best suited
when you want to simply play the chords
and have the Harmony effect automati-
cally sort out the suitable notes.
Chords Recognized in Chordal Type
Detune
This produces a slightly “detuned” pitch
and mixes it with the input signal for a
rich chorusing effect. The amount of the
detuning is set in the Mode parameter.
MIDI note data from a keyboard or se-
quencer has no effect in this type.
NOTE
When Detune is selected, the Harmony Gen-
der Type and Lead Pitch Correction param-
eters are not available.
Chromatic (CHROMAT.HM)
This produces a harmony at a fixed pitch
interval from the original sound (such as
an octave, or a third). The amount of the
pitch shift is set in the Mode parameter.
MIDI note data from a keyboard or se-
quencer has no effect in this type.
Mode
Settings: (Available settings differ de-
pending on selected Type;
see below.)
For Vocoder Type:
no trans
No transposition. The harmony notes
correspond exactly to the pitch of the in-
coming MIDI notes.
auto trans
Automatic transposition of the harmony
notes. This keeps the harmony notes close
(±600 cents) to the input signal, no mat-
ter which octave the MIDI notes are
played. For example, if your vocal is at a
pitch of C3, playing an E note anywhere
on the connected MIDI keyboard results
in a harmony note of E3.
-3oct trns — +3oct trns
This fixes the octave transposition of the
harmony notes, selectable from 3 octaves
below (-) to 3 octaves above (+).
For Chordal Type:
duet above (Duet Above)
Produces one harmony note, in a pitch
above the lead note.
duet below (Duet Below)
Produces one harmony note, in a pitch
below the lead note.
duet abv+b (Duet Above + Bass)
Produces two harmony notes — one in a
pitch above the lead note, and one an oc-
tave below the chord root harmony. (The
“+b” in the type name stands for “added
bass note.”)
trio above (Trio Above)
Produces two harmony notes, in pitches
above the lead note.
trio a&b (Trio Above & Below)
Produces two harmony notes — one in a
pitch above the lead note, and one below.
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters

Effect Edit Mode
149
trio below (Trio Below)
Produces two harmony notes, in pitches
below the lead note.
trio a&b+b (Trio Above & Below+Bass)
Produces three harmony notes — one in
a pitch above the lead note, and two be-
low — one of them an octave below the
chord root harmony. (The “+b” in the
type name stands for “added bass note.”)
quar above (Quartet Above)
Produces three harmony notes, in pitches
above the lead note.
quar a&b (Quartet Above & Below)
Produces three harmony notes — two in
pitches above the lead note, and one be-
low.
quar below (Quartet Below)
Produces three harmony notes, in pitches
below the lead note.
For Detune Type:
low
Detunes the pitch by ±7 cents (least
amount of detuning).
mid-low
Detunes the pitch by ±11 cents.
mid-high
Detunes the pitch by ±15 cents.
high
Detunes the pitch by ±20 cents (most
amount of detuning).
For Chromatic Type:
oct below
Produces a harmony note an octave be-
low the input note.
3rd below
Produces a major third harmony note in
the octave below the input note. (Har-
mony is transposed eight semitones
down.)
5th below
Produces a perfect fifth harmony note in
the octave below the input note. (Har-
mony is transposed five semitones down.)
unison
Produces a “harmony” note at the same
pitch as the input note. (This can be
clearly distinguished from the original
signal by changing the Harmony Gender;
see below.)
3rd above
Produces a major third harmony note in
the same octave as the input note. (Har-
mony is transposed four semitones up.)
5th above
Produces a perfect fifth harmony note in
the same octave as the input note. (Har-
mony is transposed seven semitones up.)
oct above
Produces a harmony note an octave above
the input note.
Harmony Gender Type (H.GendrTyp)
Settings: off, Auto
This determines the gender of the harmony
notes. When set to “off,” the gender of the
harmony notes does not change (relative to
the actual gender of the singer). When set to
“Auto,” keep in mind that the gender change
effect may vary according to the quality, char-
acter and pitch of the actual voice.
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters

150
Effect Edit Mode
You can control the pitch of the lead voice
separately from the harmonies. One use-
ful application would be to have melody
and harmony data on different tracks/
MIDI channels of sequencer song data —
the melody track would control the pitch
of the lead voice, while the harmony track
would control the harmonies. This would
ensure that all vocal parts stay in tune with
each other and with the song — even if
your actual singing is slightly off pitch!
To control the pitch of the lead voice from
a connected MIDI keyboard or sequencer
(separate from the harmonies), make the
following settings:
Lead Gender Type
— “unis”, “male”, or “fem.”
Pitch Correction
— “on”
Melody Channel (page 171)
— Set to same channel as the MIDI
device. (Match this to the melody
track of the song data.)
Harmony Channel (page 171)
— Set to different value from Melody
Channel. (Match this to the har-
mony track of the song data.)
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters
NOTE
The Harmony Gender Type parameter is not
available when Harmony Type is set to
Detune (page 147).
Lead Gender Type (L.GendrTyp)
Settings: off, unis (unison), male, fem.
(female)
These settings determine whether the gen-
der of the “lead” voice can be changed or
not. It also lets you set the gender. When
this is set to “off,” the gender of the lead
voice cannot be changed. When this is
set to “unis” (unison), the lead voice is
reproduced at the same pitch as the voice;
however, the gender can be changed by
using the Lead Gender Depth parameter
below. The “male” and “fem.” (female)
settings reproduce the voice with the re-
spective male or female vocal qualities.
(To finely adjust the quality of the lead
voice, use the Lead Gender Depth param-
eter below.)
NOTE
When this is set to “unis”, “male” or “fem.”,
up to two-part harmonies are provided.
Using the Lead Voice
To properly use the lead voice, make sure
to set the following parameters:
Lead Gender Type
— “unis,” “male,” or “fem.”
Lead Gender Depth
— Set to desired/appropriate value.
Lead/Harmony Balance
— Set to appropriate value. (For val-
ues at or near the maximum of
“L<H63,” lead may not sound.)

Effect Edit Mode
151
Lead Gender Depth (L.GendrDpt)
Range: -64 — +63
This determines the quality or character of
the lead voice, and depends on the setting
made in Lead Gender Type above. (This
parameter has no effect when Lead Gender
Type is set to “off.”) Extreme negative or
positive values result in pronounced distor-
tion of the voice quality. Also, the effect
may vary according to the quality, charac-
ter and pitch of the actual voice. Experi-
ment with this to find values that sound most
natural (or unnatural, if you prefer).
Lead Pitch Correction (PchCorrect)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether the pitch of the
lead voice is controlled by MIDI note data
or not. When this parameter and Lead
Gender are set to “on,” the pitch of the
lead voice is “corrected” to the pitch of
the received MIDI note on Melody Chan-
nel (page 171).
NOTE
The Pitch Correction parameter is not avail-
able when Harmony Type is set to Detune
(page 147). Also, this parameter has no ef-
fect when Lead Gender Type is set to “off.”
Lead/Harmony Balance (Lead/Harm)
Range: L63>H (maximum lead, mini-
mum harmony) — L=H (equal
level) — L<H63 (maximum
harmony, minimum lead)
This determines the relative balance of the
lead and harmony voices. For most pop
song applications, this should be set to
“L=H” or a slightly higher lead level
(such as “L10>H” or more).
Insert Part (Ins Part)
Settings: 01 — 32, AD01, AD02, off
This determines the Part to which the
Harmony effect is applied. For example,
to apply Harmony to a microphone input
through A/D INPUT 1, set this to “AD01.”
When set to “off,” the Harmony effect is
cancelled.
Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters

152
Effect Edit Mode
About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion
About the Effect Connections
— System and Insertion
The multi-effects of the MU100R provide not only a wide range of sound
processing controls, but also a flexible system for connecting them. Unlike
simple effect routing schemes on conventional sound modules that process
all voices with the same effects, the MU100R allows you to put indepen-
dent, special effects on one or two Parts, as well as use overall effects for
processing all 34 Parts together. For example, you can have a Distortion
effect on a guitar Part and a rotary speaker effect for an organ Part, yet still
use ambient effects such as Reverb and Chorus for processing the overall
mix.
All the effect sections are connected or routed in one of two ways: System
or Insertion. System applies the selected effect to all 34 Parts, while Inser-
tion applies the selected effect to one specific Part. Reverb, Chorus, and EQ
are all System effects, and Insertion 1 and 2, and Harmony are Insertion
effects. The Variation effect section, on the other hand, can be configured for
either System or Insertion routing. (This is done from the Variation Con-
nection parameter; see page 145.) Since System and Insertion are part of the
XG MIDI (Extended General MIDI) format, you can create and play back
song data using the same flexible effect routings on any tone generator or
sound module having the XG mark.
NOTE
The Variation Connection default setting is Insertion.
The illustrations and explanations below cover the System and Insertion con-
nections in greater detail.

Effect Edit Mode
153
When Variation is set to System:
NOTES
• The Parts to which Insertion 1, 2 are applied is determined by the Part parameter in the Insertion section (page 146).
• The Part to which Harmony is applied is determined by the Insert Part parameter in the Harmony Edit section (page 151).
• Even though the System routing applies the selected effect to all Parts, you can control how much the Reverb, Chorus and Variation effects are
applied to any individual Part (with the Reverb Send, Chorus Send and Variation Send parameters in the Single Part controls; see page 97). For
the effects to be properly heard, the Reverb Return, Chorus Return and Variation Return parameters in the All Parts controls must also be set to
appropriate values (see pages 98 — 99).
• The stereo position of the effects is controlled by the Reverb Pan, Chorus Pan and Variation Pan parameters; see pages 142, 143, 145.
• You can set Reverb, Chorus and Variation to be routed in parallel or in serial, and you can determine the amount of Variation effect that is sent
to Chorus and Reverb, as well as the amount of Chorus that is sent to Reverb. This is done with the Send Variation to Chorus (page 145), Send
Variation to Reverb (page 145), and Send Chorus to Reverb (page 133) parameters. When these are all set to 0, all three effects are in parallel
routing. Higher values for each provide varying degrees of serial routing.
About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion
INS2
rev send
cho send
var send
insertion 2 on/off
dry level
VARIATION
REVERB
reverb return
chorus return
variation return
send chorus to reverb
send variation to chorus
send variation to reverb
DRY LINE
PAN
PAN
PAN
reverb pan
chorus pan
variation pan
OUT
Thick line indicates stereo signal.
EQ
Insertion 2 can be
applied to only one
Part at a time.
CHORUS
VARIATION CONNECTION = SYSTEM
insertion 2 part
INS2
rev send
cho send
var send
insertion 2 on/off
dry level
INS2
rev send
cho send
var send
insertion 2 on/off
dry level
INS2
rev send
cho send
var send
insertion 2 on/off
Harmony on/off
Harmony on/off
Harmony on/off
Harmony on/off
PLG
Harmony can be
applied to only one
Part at a time.
Harmony part
PLG
PLG
PLG
dry level
INS1
insertion 1 on/off
part A1
Insertion 1 can be
applied to only one
Part at a time.
insertion 1 part
INS1
insertion 1 on/off
INS1
insertion 1 on/off
INS1
insertion 1 on/off
part A2
part 1
part 32

154
Effect Edit Mode
About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion
When Variation is set to Insertion:
NOTES
• As with System above, the Parts to which Insertion 1, 2 are applied is determined by the Part parameter in the Insertion section (page 146). The
Part to which Harmony is applied is determined by the Insert Part parameter in the Harmony Edit section (page 151). Also, the Part to which
Variation is applied is determined by the Variation Send control in the Single Part controls (page 97).
• As with System above, the effects cannot be properly heard unless the Reverb Send, Chorus Send and Variation Send parameters in the Single
Part controls (page 97) and the Reverb Return and Chorus Return parameters in the All Parts controls are set to appropriate values.
• The stereo position of the effects is controlled by the Reverb Pan and Chorus Pan parameters. (See pages 142, 143.)
• You can set Reverb and Chorus to be routed in parallel or in serial, and you can determine the amount of Chorus that is sent to Reverb. This is
done with the Send Chorus to Reverb parameter (see page 133). When this is set to 0, Reverb and Chorus are in parallel routing. Higher values
for each provide varying degrees of serial routing.
rev send
dry
cho send
rev send
dry
cho send
rev send
dry
cho send
insertion2 part
variation part
part1
REVERB
reverb
pan
send chorus to reverb
part32
DRY LINE
PAN
PAN
reverb
return
chorus
pan
chorus
return
OUT
Thick line indicates stereo signal.
EQ
insertion2 can be applied to
only one Part at a time
CHORUS
Varationcan be applied to
only one Part at a time
insertion1 part
insertion1 can be applied to
only one Part at a time
rev send
cho send
part A1
part A2
INS2
INS2
INS2
INS2
VAR
VAR
VAR
VAR
insertion2
on/off variation on/off
insertion2
on/off variation on/off
insertion2
on/off variation on/off
insertion2
on/off
insertion1
on/off
insertion1
on/off
insertion1
on/off
insertion1
on/off variation on/off
dry
Harmony part
Harmony can be applied to
only one Part at a time
PLG
PLG
PLG
PLG
Harmony
on/off
Harmony
on/off
Harmony
on/off
Harmony
on/off
INS1
INS1
INS1
INS1

Equalizer (EQ) Edit
155
Equalizer (EQ) Edit
The Equalizer (EQ) Edit parameters allow you to adjust the overall
tone of the MU100R sound in five separate frequency bands. EQ pre-
sets are also provided for instantly calling up tone settings specially
suited for different types of music.
0 dB
Fre
q
uenc
y
Low Lo Mid Mid Hi Mid High
To enter the Equalizer Edit mode, press the EQ button.
EQ Type
Settings: Flat, Jazz, Pops, Rock, Con-
cert
EQ Type provides five different preset EQ
settings, specially programmed for spe-
cific types of music. The Flat setting is a
“flat” EQ preset with no change in equal-
ization. Jazz, Pops, Rock and Concert
each have different EQ settings and fre-
quency bands, specially suited for those
types of music.
EQ Frequency Parameters
Thru: 80 Hz, 500 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 4.0
kHz, 8.0 kHz
Jazz: 50 Hz, 125 Hz, 900 Hz, 3.2
kHz, 6.3 kHz
Pops: 125 Hz, 315 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 2.0
kHz, 5.0 kHz
Rock: 125 Hz, 200 Hz, 1.2 kHz, 2.2
kHz, 6.3 kHz
Concert: 80 Hz, 315 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 6.3
kHz, 8.0 kHz
Range: –12 — +12 dB
The remaining EQ parameters let you set
the level of each of the five frequency
ranges: low, low-mid, mid, high-mid and
high. The bars in the display show the EQ
settings as a frequency “curve,” with
peaks indicating level boosts in the fre-
quency range and valleys indicating level
cuts. A setting of 00 dB corresponds to
no level change.
NOTE
Changing the EQ Type automatically restores
the default Frequency Parameter settings and
cancels any Frequency Parameter settings you
have made.

156
Utility Mode
Utility Mode
The Utility mode lets you set functions related to the overall operation of
the MU100R, such as Master Tune, display contrast and playing of the Demo
Song. Included also are utility operations, such as various kinds of data
transfer with an external data storage device, and initializing of the MU100R
settings.
To enter the Utility mode, press the UTIL button. The following menu appears:
System Functions (SYS)............................................................... 157
Dump Out Functions (DUMP).................................................... 161
Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI ................................... 161
Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST ............................ 161
Initialize Functions (INIT)........................................................... 165
Demo Song Play (DEMO) ........................................................... 168
VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) ............... 169
VL Voice System Parameters ............................................... 169
Harmony System Parameters .............................................. 171

Utility Mode
157
System Functions (SYS)
The System functions provide various controls of the overall operation of
the MU100R, such as Master Tune, Mute and A/D Part Lock, some MIDI
receive filters and a display Contrast control.
A/D Part Lock
Settings: off, on
This determines whether or not the cur-
rent parameter values and Variation ef-
fect settings of the A/D Parts are reset
when receiving a GM System On or XG
System On message. If you want to keep
the current parameter values and Varia-
tion settings of the A/D Parts, set Mute
Lock to on. (This parameter has no ef-
fect in the Performance mode.)
Multi Mode Equalizer Lock
(Mlt EQ Lock)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether the Equalizer set-
tings (page 155) are initialized or change in
response to incoming MIDI messages.
When this is set to “on,” the current Equal-
izer settings are maintained, ignoring any
EQ-related messages that are received with
XG System On or GM System On mes-
sages, allowing you to protect your original
Equalizer settings. When set to “off,” the
Equalizer changes according to incoming
XG/GM System On messages. This setting
affects the Multi mode only, and not the Per-
formance mode.
System Functions (SYS)
Master Tune (M.Tune)
Range: –102.4 — +102.3 cents
(approx. +/– 1 semitone)
This determines the overall fine tuning of
the MU100R’s Voices. It also affects the pitch
of the individual drum/percussion sounds of
the drum kits. Master Tune is especially use-
ful for adjusting the pitch of the MU100R
when playing with other instruments. The
actual pitch of each Voice depends also on
the other pitch related parameters: Key (in
Play mode) and Detune (in Edit mode).
NOTE
At around 440 Hz, 1 Hz is approximately
equal to 4 cents.
Mute Lock
Settings: off, on
This determines whether or not the Part Mute
status of the MU100R is reset when receiv-
ing a GM System On or XG System On
message. Generally, this message is automati-
cally transmitted to the MU100R as part of
General MIDI song data. When Mute Lock
is set to off, this resets the Mute status of the
Parts on the MU100R.
If you want to keep
the current Mute settings and disable this
reset, set Mute Lock to on. (For more infor-
mation on the Mute function, see page 85.)

158
Utility Mode
Output Select Lock (OutSel Lock)
Settings: on, off
This determines whether or not the Out-
put Select settings (pages 113, 118) are
reset when receiving a GM System On
or XG System On message. It also de-
termines whether the Output Select set-
ting for a Part can be edited via MIDI or
not. If you want to “lock” the Output Se-
lect settings and keep them from being
changed, set this to “on.”
Receive General MIDI Exclusive
(RcvGMExcl)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether GM System On
or XG System On messages are received
or not. The on setting allows these mes-
sages to be received.
Receive System Exclusive (RcvSysExcl)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether System Exclu-
sive messages are received or not. Sys-
tem Exclusive messages are data specifi-
cally (or “exclusively”) related to the
MU100R. The On setting allows these
messages to be received. This should be
to On when receiving bulk data from a
MIDI data storage device. (See page 18.)
Receive Bank Select (RcvBankSel)
Settings: off, on
This determines whether Bank Select
messages are received or not. Bank Se-
lect messages can be sent from another
MIDI device to change the banks of
Voices on the MU100R. (See page 31.)
The On setting allows Bank Select mes-
sages to be received.
System Functions (SYS)

Utility Mode
159
Tone Generator
Computer and
Software with
multiple-port
capability
MIDI
OUT
Port 1: Channels A1 — A16
Port 2: Channels B1 — B16
Thru Port setting:
3 — 8
POWER
ON/ OFF
MIDI IN
Contrast
Range: 1 — 8
This determines the contrast of the dis-
play. Adjust this as necessary for optimum
visibility. (At extreme settings, the dis-
play may not be readable.)
Dump Interval (DumpIntrval)
Settings: 50, 100, 150, 200, 300
This determines the length of time the
MU100R pauses when sending blocks of
data in the Dump Out functions. If the
receiving device fails to process the data
or displays a “buffer full” type message,
try setting this parameter to a higher value
and send the data again.
Thru Port
Range: 1 — 8
Some MIDI devices and sequencers are
capable of transmitting data over several
MIDI “ports,” effectively breaking the 16-
channel barrier. When this data is received
via the TO HOST terminal on the
MU100R, this parameter determines
which MIDI port’s data will be routed
through the MIDI OUT terminal. This
allows you to connect another multi-
timbral tone generator to the MU100R
and play back data over 48 independent
MIDI channels — 32 on the MU100R and
another 16 on the connected tone genera-
tor.
NOTE
The MU100R can receive Cable messages
(F5) when the TO HOST terminal is con-
nected to the serial terminal of a computer.
On the MU100R, MIDI
receive channels A1 — A16 are controlled
from Port 1, and channels B1 — B16 are con-
trolled from Port 2. If the software you are
using can
address separate MIDI ports, data can be re-
ceived over 32 channels simultaneously, al-
lowing 32 parts to be played with only one
serial cable. By connecting another multi-
timbral tone generator to the MIDI OUT ter-
minal of the MU100R and setting the Thru
Port function to a value other than 1 or 2,
you can play back data over a total of 48 MIDI
channels — 32 on the MU100R and another
16 on the connected tone generator.
System Functions (SYS)

160
Utility Mode
Display Bank Select (DispBankSel)
Settings: 1 (displays only banks with
unique Voices),
2 (displays all banks)
This determines whether the MU100R
displays all Voice banks or not when
changing banks. (For information on
changing banks, see page 28.) When this
is set to “1,” the MU100R conveniently
skips over banks that have the same Voice.
In other words, when you step through
the available banks, the display stops only
on banks for which the Voice is unique or
different (for the selected program num-
ber). If “2” is selected, all banks are dis-
played in succession, regardless of
whether the Voices are the same or not.
The Display Bank Select setting itself
cannot be changed by incoming MIDI
messages.
Voice Map (Map)
Settings: MU basic, MU100Native
This determines the Voice configuration
or assignment of the XG Voice set of the
MU100R. This parameter should be set
to match particular types of song data.
For playback of data recorded on or in-
tended for the MU90R, MU80, and
MU50, set this to “MU basic.” For play-
back of other GM- and XG-compatible
data, as well as the most recent song data
(especially that intended for the
MU100R), this should be set to
“MU100Native.”
NOTES
• Only the Voice map of the basic Voice
bank (MSB = 0, LSB = 0) is affected by this
parameter. The other extended Voice
banks are not affected.
• This setting is not affected by incoming XG
System On or GM System On MIDI mes-
sages.
System Functions (SYS)

Utility Mode
161
Dump Out Functions (DUMP)
The Dump Out functions allow you to save the various settings of the
MU100R (such as settings for Parts, Performances, system, etc.) to a MIDI
sequencer, computer or a MIDI data recorder (such as the Yamaha MDF2
MIDI Data Filer).
The following illustrations show example connections for the Dump Out
functions.
Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI
Bulk Dump data can be sent and received using the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT connections.
MU100R
MIDI Data
Recorder
MIDI IN
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN
MIDI OUT
POWER
ON/ OFF
Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST
Computer
(with sequencer or
MIDI librarian
software)
TO HOST SERIAL PORT
Bulk Dump data can be sent and received using the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT connections.
MU100R
POWER
ON/ OFF
Dump Out Functions (DUMP)
Operation
1 Make sure that the MU100R is properly connected to the device
and that the HOST SELECT switch is properly set.
When using the MIDI terminals, connect the MIDI OUT of the
MU100R to the MIDI IN of the data recorder. (See the illustrations
above.) Also, set the HOST SELECT switch to MIDI.
When using the TO HOST terminal, make sure that the HOST
SELECT switch is set corresponding to the device to be used. (Refer
to page 19 for more on host computer connections.)

162
Utility Mode
2 Press the UTIL button and select “DUMP,” then press the ENTER
button.
3 From the Dump Out menu, select the type of data to be sent: All,
Multi or Performance. Then, press the ENTER button to call up the
selected data dump.
All
This transmits all MU100R data (including Part, Performance,
system, and all parameter values) to the connected device.
Dump Out Functions (DUMP)

Utility Mode
163
Multi
Settings: 32 Parts, 16 Parts, 32 Parts + A/D, 16 Parts + A/D
This transmits the selected MU100R Multi Part data (including
System, Effect and EQ data) to the connected device. (Use the
VALUE -/+ buttons to select the type/amount of data to be
transmitted.)
Performance (PERFORM)
Settings: ALL, I 001 — I 100 (Internal Performance numbers)
This transmits the selected MU100R Performance data to the
connected device. (Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to
select the type/amount of data to be transmitted.)
4 From the “Are you sure?” prompt, press the ENTER button to
execute the operation, or press the EXIT button to cancel it and
return to the Dump Out menu.
A “Transmitting…” message appears in the display during the
operation. When the transmission is completed, the MU100R
returns to the Dump Out menu.
NOTE
If you have more than one MU100R connected in your MIDI system and wish to send
different sets of data to each, you can specify a different Device Number for each. (See page
98.) You should set the Device Number on each MU100R you use, before dumping the data
to a data storage device. Then, when you reload the data to the connected MU100Rs, each
unit will automatically receive only the data that has the corresponding Device Number.
Dump Out Functions (DUMP)

164
Utility Mode
To reload the data from the data recorder back to the MU100R:
Make sure that the devices are properly connected (see the Restoring
Data illustrations on page 18), and execute the appropriate data trans-
fer operation from the data recorder. (Refer to the owner’s manual of
that device for instructions.) The MU100R automatically receives in-
coming bulk data.
Dump Out Functions (DUMP)

Utility Mode
165
Initialize Functions (INIT)
The Initialize functions allow you to restore the factory settings of the
MU100R.
NOTE
Since the Initialize functions replace existing data, you should save any and all
important settings to a MIDI data storage device before using these functions.
(See page 18.)
Operation
1 Press the UTIL button and select “INIT,” then press the
ENTER button.
2 From the Initialize menu, select the type of data to be initialized:
Factory Settings (FactSet), selected Sound Module mode (XGInit,
GM Init, C/MInit, PFMInit) or Drum (DrumInit) Then, press the
ENTER button to call up the selected data dump.
Initialize Functions (INIT)

166
Utility Mode
Factory Settings (FactSet)
This restores the original factory settings of the MU100R.
NOTE
This function replaces internal performance data to the “Internal Performance 2.” To restore
the “Internal Performance 1” (loaded at first), load the data from included floppy disk. (Refer
to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.)
Selected Sound Module Mode:
Extended General MIDI (XGInit)
General MIDI (GM Init)
Computer Music (C/MInit)
Initialize Functions (INIT)

Utility Mode
167
Performance (PFMInit)
One of the four parameters above will be available, depending on
the currently selected Sound Module mode: XG, TG300B, C/M or
PFM. Initializing this parameter restores the original settings for
the selected mode.
NOTES
• For the PFMInit setting, only the currently selected Performance will be initialized.
• For XGInit and GM Init, the initialized settings are the same as when the MU100R is reset
upon receiving an XG System On or GM System On message.
Drum (DrumInit)
Range: DrumS1 — DrumS4
This restores the original drum settings for the selected Drum Setup
S1 — S4. (Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to select the
desired Drum Setup.)
NOTE
This parameter is not available when the MU100R is set to Performance mode.
3 From the “Are you sure?” prompt, press the ENTER button to
execute the operation, or press the EXIT button to cancel it and
return to the previous display.
An “Executing…” message appears in the display during the
operation. When the operation is completed, the MU100R returns
to the Initialize menu.
Initialize Functions (INIT)

168
Utility Mode
Demo Song Play (DEMO)
The Demo Song function in the Utility menu allows you to play the built-in
Demo Song.
Operation
1 Press the UTIL button and select “DEMO,” then press the
ENTER button.
2 Press the ENTER button to start the Demo Song.
The Demo Song starts playing immediately and repeats indefinitely
until stopped (in step 4 below). Playback of the individual Parts of
the song is shown graphically by the “level meter” bars in the
display.
NOTE
During Demo Song playback, no panel controls (with the exception of the EXIT button and
the VOLUME control) can be used.
3 To stop playback of the song, press the EXIT button.
4 To exit from the Demo Song function, press the EXIT button again.
Demo Song Play (DEMO)

Utility Mode
169
VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN)
VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN)
VL Voice System Parameters
Path: [UTIL] button → “PLUGIN” → “PLG100-VL”
These parameters include assignment of the Part for the VL Voice, as
well as other controls that affect overall operation. For more information
on the VL Voices and how to use them, refer to page 62.
Part Assign
Settings:
In XG Mode: 01 - 16, off
In Performance Mode: 01 - 04, off
This determines the Part to which the VL
Voice is assigned. If a Part is not prop-
erly assigned here, none of the VL Voice
banks can be selected for the Part.
NOTE
The VL voices cannot be assinged to several
Parts at one time since the VL tone generator
section is monophonic.
WX Lip Mode
Settings: Norm, Expd
WX-series Wind MIDI Controllers pro-
duce pitch bend data ranging from “-16”
to “+32” in response to lip (reed) pres-
sure. The WX Lip parameter determines
whether these values are used as is
(“Norm”), or expanded to a full “-64”
through “+63” range (“Expd”). This is
also effective for pitch bend data trans-
mitted from devices other than those of
the WX-series.
Details
• The “Expd” setting is recommended when
using a WX controller in the “tight lip”
mode. The “Norm” setting is recommended
when using the WX controller “loose lip”
mode.
• The settings made here are effective only
for the internal VL tone generator.
Breath Mode
Settings: BC/WX, Vel, TchEG
Sets the control source to be used for
“breath” control. This parameter should
be set to “BC/WX” when a breath con-
troller or Yamaha WX-series Wind MIDI
Controller is being used. When “Veloc-
ity” is selected, breath variation is con-
trolled by keyboard initial touch response.
When “Touch EG” is selected, breath
variation is controlled by a combination
of initial keyboard touch response and
aftertouch pressure. Initial key velocity
sets the initial breath level, and aftertouch
pressure determines the shape of the sub-
sequent breath envelope.

170
Utility Mode
Breath Control
Settings: BC, Exp
This determines the MIDI control change
number to be used for breath control of
the VL Voice, when breath controller data
(number 02) is received via MIDI. When
“BC” is selected, control number 02
(breath control) is used. When “Exp” is
selected, control number 11 (expression)
is used.
Breath Curve
Range: -16 — +16
Determines the relationship between
breath controller data (number 02) re-
ceived via MIDI, and the actual amount
of breath variation applied. Negative set-
tings result in a large breath variation with
a relatively small amount of breath pres-
sure applied to the controller, while posi-
tive settings require a greater range of
input breath control values to produce the
same degree of breath variation.
Details
• This is also effective for breath controller
data transmitted from devices other than
those of the WX-series.
• The settings made here are effective only
when “BC/WX” is selected for the Breath
Mode.
VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN)

Utility Mode
171
Harmony System Parameters
Path: [UTIL] button → “PLUGIN” → “PLG100-VH”
These parameters include the MIDI channel settings for the harmony and
melody. For general information on the Harmony effect and how to use
it, refer to the Guided Tour section, page 77.
VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN)
Harmony Channel (Harmony Ch)
Settings: off, 1 - 16
This determines the MIDI channel over
which the Harmony effect is controlled.
For example, when this is set to the same
value as the MIDI transmit channel of a
connected MIDI keyboard and the Vo-
coder or Chordal Harmony Type is se-
lected (page 147), you can use the key-
board to “play” harmonies. (See page 77.)
Melody Channel (Melody Ch)
Settings: off, 1 - 16
This determines the MIDI channel over
which the lead sound of the Harmony ef-
fect is controlled. For example, when this
is set to the same value as the MIDI trans-
mit channel of a connected MIDI key-
board, you can use the keyboard to con-
trol the pitch of the lead sound.

172
Sound Module Mode (MODE)
Sound Module Mode (MODE)
This lets you select the operating mode of the MU100R. Press the
MODE button, then use the SELECT </> buttons to select the de-
sired Sound Module mode: XG (Extended General MIDI), TG300B
(General MIDI), C/M (Computer Music) or PFM (Performance). If
XG, TG300B or C/M are selected, the MU100R automatically sets
itself to the Multi mode. When PFM is selected, the MU100R is in the
Performance mode. (See page 6.)
The bottom right of the display indicates the currently selected Sound
Module mode.
Press the EXIT button (or any one of the other mode select buttons: PLAY,
EDIT, UTIL, EFFECT or EQ) to use the MU100R in the current mode.
NOTES
• When the MU100R is not set to the XG mode and an XG System On message
is received, the MU100R changes to the XG mode after a slight pause of 0.5
seconds.
• When the TG300B or C/M mode is selected, the VL Voices and Harmony
effect cannot be used.
• In the C/M mode, the Voices available in Parts 11 - 16 are different from those
available in Parts 1 - 9. (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.)
• The TG300B mode also has multiple banks. In the C/M mode, there is only
one bank (“Fix” appears at the Bank Number parameter), and for the drum
Part only one drum kit can be selected.
Arrow indicates selected Sound Module mode.
XG
TG300B
C/M
PERFORM

Miscellaneous Functions
173
Miscellaneous Functions
Show Control Change
This function allows you to view the currently used control change number,
its type and its value (in decimal format). It also lets you transmit the dis-
played value with a single button press.
Operation
1 From the Multi Play mode or Performance Play mode, double-
click the ENTER button (press it twice quickly). (The Show Control
Change display appears.)
2 To transmit the currently displayed message, press the ENTER button
again. The message is transmitted via the MIDI or TO HOST
terminals.
3 Press the EXIT button to return to the Play display.
Show Control Change
Number of controller
Type of controller
Current value

174
Miscellaneous Functions
This is convenient for quickly entering desired settings to a sequencer.
Displaying/Sending Voice Bank Settings
The Show Control Change function also allows you to view and send Voice
bank MSB and LSB settings within the XG mode.
To do this:
1) From the Multi Play mode (XG mode), select the desired bank number.
(For information on selecting banks, see page 28.)
2) With the bank number parameter highlighted, double-click the [ENTER]
button.
3) Press the [EXIT] button to return to the Play display.
NOTE
MSB/LSB values are used in conjunction with each other to provide a greater number of
banks than would be possible with the 128-number limit of MIDI's hexadecimal system.
For example, the XG Voices are contained on banks 000 - 127; these banks are selected
over MIDI with the MSB value of 000. MU100 Exclusive Voice banks are at MSB 048.
For more information on MSB and LSB values, see page 30.
Show Control Change

Miscellaneous Functions
175
Show Exclusive
This function allows you to view the current system exclusive message (in
hexadecimal format). It also lets you transmit the displayed value with a
single button press.
Operation
1 Double-click the ENTER button (press it twice quickly). (The Show
Exclusive display appears.)
2 To transmit the currently displayed message, press the ENTER button
again. The message is transmitted via the MIDI or TO HOST
terminals.
3 Press the EXIT button to return to the previous display.
Show Exclusive
System Exclusive message (in hexadecimal format)

178
Appendix
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Even though the MU100R is exceptionally easy to use, it may occasionally
not function as you expect it to. If that happens, check the possible problems
and solutions below before assuming that the instrument is faulty.
Problem
No power.
No sound.
No sound when playing the
MU100R from a computer,
sequencer or external keyboard.
Notes are cut off or omitted.
Reverb, Chorus and/or Variation
effects cannot be heard.
The A/D input sound (mic, guitar,
etc.) cannot be heard.
VL Voice Section/ The VL Voices and/
Harmony Effect or Harmony effect
cannot be used.
Other notes on VL
Voices and
Harmony effect:
Possible Cause and Solution
If you are using an AC adaptor, check that the adaptor is properly plugged into both the
AC outlet and the MU100R (See page 3.)
Check that:
●
The panel volume control is set to an appropriate level.
●
Other volume-related parameters are set to appropriate levels. (See Volume and Ex-
pression in the Single Part controls, page 96, and Master Volume and Master Attenua-
tor in the All Part controls, page 98.)
●
Mute or Solo are not active. (See page 85.) If a Part is being muted, or an empty Part is
being soloed, you may not get any sound.
●
The Variation effect settings are appropriate. No sound will be output at all if Variation
Connection is set to INS (page 145), Variation Send is turned on for the Part (page 97),
and NO EFFECT is selected for the Variation Type (page 144). The easiest solution in
such a case is to turn off Variation Send for the Part.
●
The EG Attack Time (page 103) is appropriately short, for short percussive sounds.
●
The Velocity Sensitivity Offset (page 111) is appropriate.
●
The Note Limit Low and Note Limit High (pages 110, 136) settings are appropriate. If
the former is set higher than the latter, no sound will be output.
●
The Velocity Limit Low and Velocity Limit High (pages 111, 136) settings are appro-
priate. If the former is set too high and the latter too low, no sound may be output.
Check all MIDI connections, making sure that the MIDI OUT of the external device is
connected to the MIDI IN of the MU100R, and that the MIDI IN of the external device is
connected to the MIDI OUT of the MU100R. (See pages 17 – 19.) Or, if you are using the
TO HOST terminal with a computer, make sure that the terminal is properly connected to
the computer and that the HOST SELECT switch is properly set for your particular com-
puter. (See pages 19 – 22.) Also, make sure that you have turned on the connected MIDI
instrument or computer before turning on the MU100R. If you haven’t, simply turning
the MU100R off and back on again may solve the problem.
The maximum polyphony of the MU100R may be exceeded. The MU100R can play no
more than 64 notes at once. (Though 64 notes may seem to be more than enough, you may
run short when playing a connected keyboard along with some densely arranged song data.)
Check all Reverb-, Chorus- and Variation-related controls: Reverb Send, Chorus Send
and Variation Send in Single Part controls (page 97); Reverb Return, Chorus Return and
Variation Return (when Variation Connection is set to SYS) in All Part controls (pages 98
— 99). Also check the individual effect settings; if no Type has been selected, or if the
parameter settings are too low, there may be no effect sound.
Make sure that the appropriate A/D Part (A1 or A2) has been turned on and that the A/D
INPUT control is set to an appropriate level. Also for best results, make sure that the A/D
input type (Mic, Guitar, Keyboard, Audio) is set to match the input you are using.
Check the following points:
●
The VL Voices and Harmony effect can only be used in the XG or Performance modes.
●
The VL Voice must be assigned to a Part in the Part Assign parameter (page 169), and
the Harmony effect must be assigned to a Part in the Insert Part parameter (page 151).
●
The VL Voices can only be used with Parts 1 – 16.
●
When using MIDI, the VL Voices and Harmony effect can only be controlled via the
MIDI-A terminal. When using TO HOST, they can only be controlled via MIDI port 1.
●
The VL Voices and Harmony effect can be used in the Performance mode; however,
the Store operation saves only edits made from the panel controls, and not any of the
“hidden” parameters accessible via MIDI.
●
When controlling certain VL Voice and Harmony effect parameters via MIDI, the value
or setting displayed in the LCD may not change, even though the actual value does.
●
Any edits made to the “hidden” VL Voices/Harmony effect parameters (accessible
only via MIDI) are not saved; turning off the power automatically cancels these set-
tings.
●
When backing up VL Voice and Harmony effect data via MIDI, the time it takes for the
data transfer may be quite long. Be careful not to turn off the power or disconnect the
AC adaptor until the operation is completed.

Appendix
179
Problem
About VL Section Some voices sound
as if they are in the
original octave
even when shifted
down an octave.
Portamento
produces more of a
glissando effect on
some voices.
The filter, EG, and
other parameters
have more effect on
some voices than
others.
Some bowed string
instrument voices
tend to “squeek”.
Pitch bends
produced by a
pitch bend wheel
are not always
accurate.
Some voices don’t
respond as
expected to EG
edits.
The VL section is a
monophonic tone
generator. Why is
the “poly” mode
initialy selected
when the VL-XG
sound module
mode is engaged?
Possible Cause and Solution
This is because Virtual Acoustic synthesis accurately simulates the acoustic behaviour of
a pipe or string. Simply stated, the harmonic balance of the voice when played in the
normal octave is retained even when the voice is shifted down an octave. The change in
timbre can be greater or less, depending on the selected voice.
Trumpets and some other brass instruments tend to exhibit this phenomenon more than
others. In a VA tone generator portamento is produced by lengthening or shortening the
instrument's pipe or string and changing the Embouchure. A trumpet is designed to em-
phasize the “modes” of the pipe(s) to produce notes over a wide range using only three
valves. When portameto is applied to a trumpet voice, the pitch tends to jump from mode
to mode, thus producing the observed glissando effect. The same effect occurs with some
flute voices. Saxophone modes are not nearly as strong as trumpet modes, but some sax
voices do have two definite modes which, when spanned by a portamento slide, can pro-
duce irregularities.
Most voices use the low-pass filter type, but some use the bandpass, high-pass, or band
eliminate types. Some voices use very little filter processing at all. Changing the filter
settings may not produce a particularly noticeable effect. Also the internal Breath Noise,
Throat Formant, Growl, Harmonic Enhancer and Pitch EG parameter settings can have a
significant effect on how much the parameters accessible via the VL section controls
actually affect the sound.
As anyone who has played (or tried to play) a real violin knows, these instruments natu-
rally tend to squeek if not properly controlled. The same occurs with VA synthesis. As
with a real bowed string instrument, bow speed and pressure must be properly controlled
in the VL section to produce the desired sound. Bow speed is usually controlled either via
breath control or an expression pedal. Bow pressure is controlled via control number 13:
“64” is medium pressure, lower values produced reduced bow pressure, and higher values
produce increased bow pressure.
Natural acoustic musical instruments have no “pitch parameter”. Pitch is determined by
the properties of the instrument’s resonant body as well as the condition of the instrument’s
driver. The same applies to Virtual Acoustic Synthesis: in the VL section’s pitch bend is
simulated by manipulating the appropriate pipe/string length and driver characteristics.
As a result, the pitch bend range may not always be “mathematically” accurate.
With reed instruments such as saxophone or clarinet, highly realistic pitch bends are pro-
duced by controlling both pitch and embouchure at the same time. Since the embouchure
component of the pitch bend behaves with characteristics acoustic unpredictability, pre-
cise pitch bends are not always produced.
The effect of editing envelope generator parameters may not always be as expected —
particularly with plucked string instrument voices such as guitar or bass. This is because
the VL section actually simulates the plucking, free oscillation, and muting of the strings
rather than simply using an EG to approximate these events. If the sound of a string voice
decays naturally, for example, setting a long release time will have little or no effect on
the actual sound of the voice. Since the attack and decay portions of the voice also have
natural timbre variations, these can be unnaturally altered by inappropriate EG settings
— which is OK if you’re trying to produce an unnatural effect. Trial and experimentation
and the only sure ways to determine how the EG parameters are going to affect a particu-
lar voice.
This is to provide compatibility between the currrent XG format and future polyphonic
VL-series tone generators. It also provides a certain degree of compatibility to allow
playback of VL-XG song data on existing tone generators which do not feature the VL-
XG extension. Specifically, to switch the VL section to the mono mode a “mono mode”
command (control change no.126, value 0-16) is embedded in the song data which, when
received by a 32-note or 64-note polyphonic XG tone generator, switches the appropriate
parts to the mono mode. The same will apply to future polyphonic VL-series tone genera-
tors, so no changes will be required. The VL section therefore has a “poly” which is
automatically selected when a MIDI “XG on” system exclusive message is received.
Troubleshooting

180
Appendix
Error Messages
Error Messages
Battery Low!
The battery voltage (for internal memory backup) may be too low. Bring the unit to
your local Yamaha dealer or any other authorized Yamaha service personnel.
Illegal Data!
A data error resulted during reception of MIDI messages. Try transmitting the data
again, or turn the MU100R off and back on again.
MIDI Buffer Full!
Too much MIDI data is being received by the MU100R at one time. Reduce the
amount of data being sent to the MU100R.
HOST is OffLine!
This message appears when the host computer is not turned on, the connecting cable
is not properly connected, or the sequencing software is not active.
SysEx Adrs ERROR!
The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the address
of the message and try transmitting again.
SysEx Data ERROR!
The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the data of
the message (as to whether it requires an MSB or LSB header) and try transmitting
again.
SysEx Size ERROR!
The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the size of
the message and try transmitting again.
Check Sum ERROR!
The checksum of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the
checksum of the message and try transmitting again.
This Parameter isn’t Excl Data
The selected parameter has no System Exclusive value and cannot be displayed with
the Show Exclusive function.
No Parameter
The selected parameter for use with the Show Exclusive function does not exist as a
valid parameter.
Rcv CH is OFF!
The selected parameter for use with the Show Exclusive function cannot be con-
verted to a MIDI message value since the Receive Channel for the Part is off. Set the
Receive Channel to an appropriate value.

Appendix
181
Specifications
Tone Generation Method
AWM2 (Advanced Wave Memory 2), Virtual Acoustic Synthesis System (VL)
Maximum Simultaneous Polyphony
64-note + 1-note (VL)
Sound Module Modes
XG (Extended General MIDI), TG300B, C/M, and Performance
Multi-timbral Capacity
32-Part (on 32 MIDI channels; with element reserve priority for later notes and
dynamic Voice allocation)
Internal Voice/Program Structure
Normal Programs
Total Voices......................... 1267 + 256 (VL)
XG mode............................. 1074 + 256 (VL)
TG300B mode .................... 614
C/M mode ........................... 128 (Parts 1 — 9), 64 (Parts 11 — 16)
Drum Programs
Total Programs .................... 46
XG mode............................. 36
TG300B mode .................... 10
C/M mode ........................... 1
Performance Programs
Up to four Voices plus all effect settings can be memorized to a Performance.
Preset Programs .................. 100
User Programs .................... 100
Effects
Six sections of multi-effects: Reverb (12 Types), Chorus (14 Types),
Variation (70 Types), Insertion 1, 2 (43 Types), Harmony (4 Types), Effect and
EQ (4 Types)
Display
Custom back-lit LCD
Specifications

182
Appendix
Controls
VOLUME control; A/D INPUT level control; Mode select buttons: PLAY, UTIL
(UTILITY), MODE, EDIT, EFFECT, EQ; other buttons: MUTE/SOLO, EN-
TER, EXIT, PART -/+, SELECT </>, VALUE -/+; data dial; POWER
button
Jacks and Terminals
Front panel: PHONES jack (1/4"), A/D INPUT 1, 2 jacks (1/4"),
Rear panel: INDIVIDUAL OUTPUT 1, 2 jacks; OUTPUT R, L/MONO jacks
(Right, Left/Mono); DC IN jack; TO HOST terminal; HOST SELECT switch;
MIDI IN A/B, MIDI OUT, and MIDI THRU terminals
Computer/MIDI Interface
Direct connection to host computer port (RS-232C, RS-422) with optional cables
(CCJ-PC1, CCJ-PC1, CCJ-MAC); MIDI terminals allow connection to MIDI
sequencer or MIDI controller
Data Transfer (Baud) Rate
MIDI — 31,250 bps (bits per second)
Mac — 31,250 bps
PC-1 — 31,250 bps
PC-2 — 38,400 bps
Power Supply
Yamaha PA-5B AC Adaptor (included)
Dimensions (W × D × H)
483 × 229 × 44 mm (19" × 9" × 1-3/4")
Weight
2.4 kg (5 lbs., 5 oz.)
Included Accessories
Owner’s Manual, Yamaha PA-5B AC Adaptor
Floppy Disk
* Specifications subject to change without notice.
Specifications

Appendix
183
Glossary
A/D input Abbreviation for analog-to-digital. The A/
D inputs of the MU100R allow you to process ana-
log inputs (such as a microphone, electric guitar,
CD player, or another electronic instrument) with
the digital effects of the MU100R and mix them
with the internal Voices.
Assignable Controller 1 Certain functions on the
MU100R (such as the Filter, Volume or Variation
effect) can be changed in real time by controllers
on a connected MIDI instrument. Assignable Con-
troller 1 lets you determine which controller (for
example: modulation wheel, breath controller, foot
controller, etc.) is used for that purpose.
AWM2 Abbreviation for Advanced Wave Memory 2,
an enhanced version of Yamaha’s original tone gen-
eration system, featuring digital filters for superior
sound.
bank A set of Voices or programs. The MIDI standard
supports up to 128 banks, each of which can con-
tain up to 128 Voices or programs.
edit Editing is the process of changing or adjusting
the settings of the MU100R.
EG Abbreviation for Envelope Generator, a common
control on electronic instruments that affects the
“shape” (or envelope) of the sound in time. The
MU100R provides two types of EGs: one for level
and the other for pitch.
Filter A control for affecting the frequency content of a
sound. Filters are used to selectively cut or boost cer-
tain frequency ranges in the sound — subtly enhanc-
ing the sound, or dramatically changing its character.
On the MU100R, the Filter can be controlled in real
time with the Assignable Controller 1.
General MIDI (GM) An addition to the MIDI stan-
dard which effectively ensures that any General
MIDI-compatible song data can be properly played
back on any General MIDI-compatible tone gen-
erator. The standard specifies that a GM-compat-
ible tone generator must have at least 24-note po-
lyphony, 16-part multi-timbral capacity and 128
standard voices. The MU100R exceeds this with 64-
note polyphony, 32-part multi-timbral capacity and
1523 Voices.
host computer The controlling computer in a com-
puter music system. The host computer is connected
to the MU100R (via the TO HOST or MIDI termi-
nals) and runs the software necessary for recording
and playing back song data, which is reproduced
by the internal sound sources and effects of the
MU100R.
LFO Abbreviation for low frequency oscillator, which
generates a low frequency signal that is used to
modulate certain aspects of the sound, such as pitch
or level. Chorus, Flanger, Tremolo, Vibrato and other
modulation effects use LFOs.
MIDI Acronym for Musical Instrument Digital Inter-
face, a worldwide standard that allows MIDI-com-
patible instruments and devices to communicate
with each other. For the instruments to communi-
cate, they normally must be set to the same MIDI
channel.
modulation wheel A controller found on most MIDI
keyboards which is normally used to control pitch
and other types of modulation. It can be used to
control various aspects of the MU100R sound by
proper setting of the Assignable Controller 1. (See
page 53.)
multi-timbral This refers to the capacity of a tone
generator to produce several different sounds at
once. The MU100R is a 32-Part multi-timbral tone
generator, capable of playing 32 different instrument
Voices at once, each over an independent MIDI
channel.
Mute The Mute function of the MU100R allows you
to silence one Part to hear how all of the other Parts
sound without it.
parameter The word “parameter” refers to any ad-
justable setting of an electronic musical instrument.
For example, the Vibrato function of the MU100R
has three parameters: Rate, Depth, and Delay.
Part The Voices of the MU100R are assigned to sepa-
rate Parts, and up to 32 of these Parts can sound
simultaneously. Parts are analogous to the various
instrumental parts in music: e.g., piano part, guitar
part, etc.
Glossary

184
Appendix
Performance In the MU100R, “Performance” refers
to an operation mode and the programs that are used
in that mode. A Performance can contain up to four
different Parts, all controllable over the same MIDI
channel. The preset Performances of the MU100R
are special multi-Part sound programs designed
particularly for live performance and studio record-
ing purposes.
Pitch Bend A function found on virtually all MIDI
keyboards (usually controlled with a pitch bend
wheel) that allows the pitch to be raised or lowered
continously. The Pitch Bend Control parameter on
the MU100R allows you to set the range over which
the pitch can be changed.
polyphony The number of notes that can be sounded
simultaneously by an electronic instrument. The
MU100R has 64-note polyphony, ensuring that even
the most complex song data will play back com-
pletely and accurately, with no “note robbing.”
port To answer the need for more MIDI channels (the
limit is 16), many MIDI interfaces offer two or more
MIDI ports, each of which can address 16 MIDI
channels. The MU100R is equipped with two inde-
pendent MIDI ports (A and B), providing 32-chan-
nel operation. The two ports are also addressable
via the TO HOST computer interface.
Portamento A function found on early synthesizers
that creates a continuous pitch glide between suc-
cessively played notes. On the MU100R, the time
of the pitch glide can be adjusted.
return Related to effect operation, “return” refers to
the effect-processed signal that is returned to the
overall sound mix. For example, the parameter Re-
verb Return determines the amount of Reverb-pro-
cessed signal that is blended with the overall sound
mix of the MU100R. (“Return” is the companion
function of “send” below.)
send Related to effect operation, “send” refers to the
signal that is sent to an effect for processing. For
example, the parameter Reverb Send determines the
degree to which an individual Part is processed with
the Reverb effect. (“Send” is the companion func-
tion of “return” above.)
sequencer A device used for recording, editing and
playing back of MIDI data. Sequencers are gener-
ally of two types: “dedicated” sequencer units, and
computer-based sequencing software. The MU100R
can be used with either type.
Solo The Solo function of the MU100R allows you to
isolate a single Part, to hear how that Part sounds
by itself.
Sound Module mode The MU100R has four Sound
Module modes, and these determine the basic op-
eration of the unit as a tone generator. Three Multi
modes (XG, TG300B and C/M) and one Perfor-
mance mode (PFM) are available.
tone generator An electronic instrument that func-
tions as a MIDI-controllable sound source. For the
most part, the term “tone generator” refers to those
devices that have no keyboard or other controller,
but are meant to be connected to and played from a
separate keyboard or computer.
Variation In the MU100R, “Variation” refers to the
special section of various effects, including Reverb,
Delay, Chorus, and many others. The Variation ef-
fects total 70, and can be used simultaneously with
the other effect sections of the MU100R: Reverb,
Chorus, Insertion 1, 2 Harmony Effect and EQ.
velocity The speed at which a note is played (for ex-
ample, on a keyboard). Normally, the faster (or
harder) a key is struck, the higher the correspond-
ing note’s velocity — and, hence, the louder the
sound produced. The MU100R features a variety
of velocity-related parameters that provide exten-
sive control over the velocity response of the Voices,
and even allow you to set up sophisticated velocity
splits, in which the Voices change in response to
playing velocity.
Vibrato Vibrato is a quavering, vibrating sound, and
is produced in the MU100R by regularly modulat-
ing the pitch of a Voice. The speed and depth of the
Vibrato can be adjusted, as well as the time it takes
before the Vibrato effect is applied.
Voice The basic sound unit (or sound program) of the
MU100R. There are a total of 1523 Voices avail-
able on the MU100R.
XG-MIDI An abbreviation for Extended General
MIDI, a new standard created by Yamaha which sig-
nificantly improves on the General MIDI standard
by providing a greater variety of high-quality Voices
and enhanced effect operation.
Glossary

Appendix
185
Index
Index
A
A/D input ................................................................87
A/D Part..........................................................87, 133
A/D Part Lock....................................................... 157
Absorption Control Change Number.................... 124
Absorption Control Depth ....................................125
All Part control .........................................35, 98, 128
Alternate Group (Drum Setup) ............................. 117
Assignable Controller 1 ..........................53, 112, 133
Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude
Control.................................................... 113, 133
Assignable Controller 1 Control Change
Number...................................................112, 133
Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control .........112, 133
Assignable Controller 1 Insertion 1/2 Control .....146
Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter
Modulation Depth ..........................................133
Assignable Controller 1 Variation Control ...........145
B
Bank (Performance mode)......................24, 128–129
Bank Number (Multi mode) .............................27, 96
Breath Control ...................................................... 170
Breath Curve.........................................................170
Breath Mode .........................................................169
Breath Noise Control Change Number................ 122
Breath Noise Control Depth .................................122
C
C/M mode ................................................................. 6
Chordal Type ........................................................147
Chorus ..................................................................143
Chorus Pan............................................................ 143
Chorus Return (Multi mode) .................................. 98
Chorus Return (Performance mode).....................128
Chorus Send (Drum Setup) .................................. 116
Chorus Send (Multi mode) .....................................97
Chorus Send (Performance mode)........................ 130
Chorus Type..........................................................143
Chromatic Type ....................................................148
Common parameters.............................................131
computer, connecting cables...................................19
computer, connecting MU100R with .....................19
computer, IBM PC and clones................................21
computer, Macintosh .............................................. 19
connections, audio ..................................................12
connections, MIDI .................................................. 17
Contrast ................................................................159
Copy .....................................................................137
D
Damping Control Change Number.......................124
Damping Control Depth ....................................... 124
Demo song......................................................15, 168
Detune ..........................................................108, 136
Detune Type..........................................................148
Device number........................................................98
Display Bank Select .............................................160
Drum Setup controls............................................. 114
Dry Level ..................................................... 110, 136
Dry/Wet (Variation) ..............................................145
Dry/Wet Balance (Insertion)................................. 146
Dump Interval....................................................... 159
Dump Out functions ............................................. 161
E
Effect Edit mode................................................... 141
effect connections (System and Insertion)............152
EG (Envelope Generator) ............................. 102, 135
EG Attack (Drum Setup) ......................................117
EG Attack Time .................................................... 103
EG Decay 1 (Drum Setup) ...................................117
EG Decay 2 (Drum Setup) ...................................117
EG Decay Time .................................................... 103
EG Release Time .................................................. 104
Element Reserve ...................................................109
Embouchure Control Change Number .................120
Embouchure Control Depth..................................121
EQ Frequency parameters .................................... 155
EQ High Frequency ......................................105, 117
EQ High Gain ...............................................105, 117
EQ Low Frequency.......................................105, 117
EQ Low Gain................................................ 105, 117
EQ Type ................................................................155
Equalizer (EQ)................................ 80, 105, 135, 155
Expression ..............................................................97
F
Filter .............................................................100, 135
Filter EG Depth ....................................................120
G
Growl Control Change Number .......................... 122
Growl Control Depth ............................................123
H
Harmonic Enhancer Control Change Number .....123
Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth ......................124
Harmony Channel.................................................171
Harmony Parameters ............................................147
Harmony Gender Type .........................................149
Harmony Type ......................................................147
HPF Cutoff Frequency (Drum Setup) .................. 116
HPF Cutoff Frequency (Multi mode) ...................101
I
Individual outputs ...............................................3, 83
Initialize functions ................................................165
Insert Part..............................................................151

186
Appendix
Index
Insertion connection .....................................145, 152
Insertion 1, 2 effects .............................................146
Insertion Part ........................................................146
Insertion Type .......................................................146
L
Lead Gender Depth...............................................150
Lead Gender Type ................................................150
Lead Pitch Correction...........................................151
Lead/Harmony Balance ........................................151
Level (Drum Setup) ..............................................115
LPF Cutoff Frequency (Drum Setup) ...................116
LPF Cutoff Frequency (Multi mode)....................101
LPF Resonance (Drum Setup)..............................116
LPF Resonance (Multi mode) ............................. 101
M
Master Attenuator ................................................... 98
Master Tune ..........................................................157
Master Volume ........................................................ 98
Melody Channel ...................................................171
MIDI channel..................................................96, 128
MIDI data flow (diagram) ......................................91
MIDI data storage device ....................................... 18
MIDI devices, connecting to .................................. 17
MIDI keyboard, playing the MU100R with ...........17
MIDI keyboard, selecting Voices with ...................31
MIDI, Receive Channel ..................................96, 128
MIDI, Receive Port................................................. 96
Modulation Wheel —
LFO Filter Modulation Depth ........................133
Modulation Wheel —
LFO Pitch Modulation Depth.................112, 132
Mono/Poly Mode..........................................109, 136
MU100 Exclusive Voice .........................................30
Multi Edit mode....................................................100
Multi mode .............................................................85
Multi Mode Equalizer Lock .................................157
Mute........................................................................85
Mute Lock ............................................................157
N
Note Limit High ...........................................110, 136
Note Limit Low ............................................110, 136
Note Shift (Multi mode) .........................................97
Note Shift (Performance mode)............................130
O
Others parameters .........................................107, 135
Output Select (Drum Setup) .................................118
Output Select (Multi mode)..................................113
Output Select Lock ...............................................158
P
Pan (Drum Setup) .................................................115
Pan (Multi mode)....................................................97
Pan (Performance mode) ...................................... 130
Part Assign ............................................................ 169
Part Mode .............................................................108
Parts, selecting ........................................................ 27
Performance Bank ................................................128
Performance Edit mode ........................................131
Performance mode.......................................... 43, 127
Performance Name ...............................................132
Performance Number............................................128
Performance Pan...................................................128
Performance Part control ...................................... 128
Performance Volume ............................................ 128
Performances, selecting Preset or Internal .............24
Pitch Bend Control ....................................... 111, 133
Pitch Coarse (Drum Setup)...................................115
Pitch EG ...............................................................104
Pitch EG Attack Time ...........................................104
Pitch EG Initial Level ...........................................104
Pitch EG Release Level ........................................ 104
Pitch EG Release Time ......................................... 104
Pitch Fine (Drum Setup).......................................115
Plugin............................................119, 136, 147, 169
Portamento Switch .......................................109, 132
Portamento Time ..........................................109, 132
Pressure Control Change Number ........................120
Pressure Control Depth.........................................120
Program (Voice) Number (Multi mode) .................96
Program (Voice) Number (Performance mode) ...129
R
Recall Function.....................................................140
Receive Bank Select .............................................158
Receive General MIDI Exclusive .........................158
Receive Note Off (Drum Setup) ...........................118
Receive Note On (Drum Setup)............................ 118
Receive System Exclusive ....................................158
Resonance (LPF; Drum Setup).............................116
Resonance (LPF; Multi mode) .............................101
Reverb...................................................................142
Reverb Pan............................................................ 142
Reverb Return (Multi mode) ..................................98
Reverb Return (Performance mode).....................128
Reverb Send (Drum Setup)................................... 115
Reverb Send (Multi mode) .....................................97
Reverb Send (Performance mode)........................130
Reverb Type .......................................................... 142
S
Scream Control Change Number.........................121
Scream Control Depth ..........................................122
Send Chorus to Reverb .........................................133
Send Variation to Chorus ......................................145
Send Variation to Reverb ......................................145
Show Control Change...........................................173
Show Exclusive ....................................................174
Single Part control (Multi mode)............................33
Single Part control (Performance mode) ..............129
Solo.........................................................................85
Sound Module mode ........................................6, 172
Store......................................................................138
System connection................................................153
System functions ..................................................157

Appendix
187
Index
System MIDI Channel .......................................... 128
System Transpose .................................................129
T
TG300B mode .......................................................... 6
Throat Formant Control Change Number ............ 123
Throat Formant Control Depth .............................123
Thru Port...............................................................159
Tonguing Control Change Number ......................121
Tonguing Control Depth ....................................... 121
Transpose................................................................99
U
Utility mode.......................................................... 156
V
Variation ............................................................... 144
Variation Connection ............................................145
Variation Pan ........................................................ 145
Variation Return (Multi mode) ...............................99
Variation Return (Performance mode)..................129
Variation Send (Drum Setup) ...............................116
Variation Send (Multi mode) ..................................97
Variation Send (Performance mode) .................... 130
Variation Type.......................................................144
Velocity LPF Cutoff Frequency............................ 116
Velocity Limit High ......................................111, 136
Velocity Limit Low.......................................111, 136
Velocity Pitch Sensitivity .....................................115
Velocity Sensitivity Depth ............................110, 136
Velocity Sensitivity Offset............................ 111, 136
Vibrato .......................................................... 106, 135
Vibrato Delay........................................................ 106
Vibrato Depth ....................................................... 106
Vibrato Rate ..........................................................106
Virtual Acoustic Synthesis......................................62
VL Voice .................................................................62
VL Voice Part Parameters .....................................119
Vocoder Type ........................................................147
Voice Map.............................................................160
Voices, selecting ..................................................... 26
Volume (Multi mode) ............................................. 96
Volume (Performance mode)........................128, 130
W
WX Lip Mode ......................................................169
X
XG mode ............................................................ 6, 26

For details of products, please contact your nearest Yamaha or the
authorized distributor listed below.
Pour plus de détails sur les produits, veuillez-vous adresser à Yamaha
ou au distributeur le plus proche de vous figurant dans la liste
suivante.
NORTH AMERICA
CANADA
Yamaha Canada Music Ltd.
135 Milner Avenue, Scarborough, Ontario,
M1S 3R1, Canada
Tel: 416-298-1311
U.S.A.
Yamaha Corporation of America
6600 Orangethorpe Ave., Buena Park, Calif. 90620,
U.S.A.
Tel: 714-522-9011
AFRICA
Yamaha Corporation,
International Marketing Division
Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430
Tel: 053-460-2312
MIDDLE EAST
TURKEY/CYPRUS
Yamaha Europa GmbH.
Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen,
F.R. of Germany
Tel: 04101-3030
OTHER COUNTRIES
Yamaha Corporation,
International Marketing Division
Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430
Tel: 053-460-2312
ASIA
HONG KONG
Tom Lee Music Co., Ltd.
11/F., Silvercord Tower 1, 30 Canton Road,
Tsimshatsui, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: 730-1098
INDONESIA
PT. Yamaha Music Indonesia (Distributor)
PT. Nusantik
Gedung Yamaha Music Center, Jalan Jend. Gatot
Subroto Kav. 4, Jakarta 12930, Indonesia
Tel: 21-520-2577
KOREA
Cosmos Corporation
#131-31, Neung-Dong, Sungdong-Ku, Seoul
Korea
Tel: 02-466-0021~5
MALAYSIA
Yamaha Music Malaysia, Sdn., Bhd.
16-28, Jalan SS 2/72, Petaling Jaya, Selangor,
Malaysia
Tel: 3-717-8977
PHILIPPINES
Yupangco Music Corporation
339 Gil J. Puyat Avenue, P.O. Box 885 MCPO,
Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines
Tel: 819-7551
SINGAPORE
Yamaha Music Asia Pte., Ltd.
Blk 17A Toa Payoh #01-190 Lorong 7
Singapore 1231
Tel: 354-0133
TAIWAN
Kung Hsue She Trading Co., Ltd.
No. 322, Section 1, Fu Hsing S. Road,
Taipei 106, Taiwan. R.O.C.
Tel: 02-709-1266
THAILAND
Siam Music Yamaha Co., Ltd.
865 Phornprapha Building, Rama I Road,
Patumwan, Bangkok 10330, Thailand
Tel: 2-215-3443
THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
AND OTHER ASIAN COUNTRIES
Yamaha Corporation,
International Marketing Division
Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430
Tel: 053-460-2317
OCEANIA
AUSTRALIA
Yamaha Music Australia Pty. Ltd.
17-33 Market Street, South Melbourne, Vic. 3205,
Australia
Tel: 3-699-2388
NEW ZEALAND
Music Houses of N.Z. Ltd.
146/148 Captain Springs Road, Te Papapa,
Auckland, New Zealand
Tel: 9-634-0099
COUNTRIES AND TRUST
TERRITORIES IN PACIFIC OCEAN
Yamaha Corporation,
International Marketing Division
Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430
Tel: 053-460-2317
HEAD OFFICE Yamaha Corporation, Electronic Musical Instrument Division
Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430
Tel: 053-460-2445
SY12
EUROPE
THE UNITED KINGDOM
Yamaha-Kemble Music (U.K.) Ltd.
Sherbourne Drive, Tilbrook, Milton Keynes,
MK7 8BL, England
Tel: 01908-366700
IRELAND
Danfay Ltd.
61D, Sallynoggin Road, Dun Laoghaire, Co. Dublin
Tel: 01-2859177
GERMANY/SWITZERLAND
Yamaha Europa GmbH.
Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen,
F.R. of Germany
Tel: 04101-3030
AUSTRIA
Yamaha Music Austria
Schleiergasse 20, A-1100 Wien Austria
Tel: 01-60203900
THE NETHERLANDS
Yamaha Music Nederland
Kanaalweg 18G, 3526KL, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Tel: 030-2828411
BELGIUM
Yamaha Music Belgium
Keiberg Imperiastraat 8, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium
Tel: 02-7258220
FRANCE
Yamaha Musique France,
Division Professionnelle
BP 70-77312 Marne-la-Vallée Cedex 2, France
Tel: 01-64-61-4000
Die Einzelheiten zu Produkten sind bei Ihrer unten aufgeführten
Niederlassung und bei Yamaha Vertragshändlern in den jeweiligen
Bestimmungsländern erhältlich.
Para detalles sobre productos, contacte su tienda Yamaha más cercana
o el distribuidor autorizado que se lista debajo.
MIDDLE & SOUTH AMERICA
MEXICO
Yamaha De Mexico S.A. De C.V.,
Departamento de ventas
Javier Rojo Gomez No.1149, Col. Gpe Del
Moral, Deleg. Iztapalapa, 09300 Mexico, D.F.
Tel: 686-00-33
BRASIL
Yamaha Musical Do Brasil LTDA.
Ave. Reboucas 2636, São Paulo, Brasil
Tel: 011-853-1377
PANAMA
Yamaha De Panama S.A.
Edificio Interseco, Calle Elvira Mendez no.10,
Piso 3, Oficina #105, Ciudad de Panama, Panama
Tel: 507-69-5311
OTHER LATIN AMERICAN COUNTRIES
AND CARIBBEAN COUNTRIES
Yamaha Music Latin America Corp.
6101 Blue Lagoon Drive, Miami, Florida 33126,
U.S.A.
Tel: 305-261-4111
ITALY
Yamaha Musica Italia S.P.A.,
Combo Division
Viale Italia 88, 20020 Lainate (Milano), Italy
Tel: 02-935-771
SPAIN
Yamaha-Hazen Electronica Musical, S.A.
Jorge Juan 30, 28001, Madrid, Spain
Tel: 91-577-7270
PORTUGAL
Valentim de Carvalho CI SA
Estrada de Porto Salvo, Paço de Arcos 2780 Oeiras,
Portugal
Tel: 01-443-3398/4030/1823
GREECE
Philippe Nakas S.A.
Navarinou Street 13, P.Code 10680, Athens, Greece
Tel: 01-364-7111
SWEDEN
Yamaha Scandinavia AB
J. A. Wettergrens Gata 1
Box 30053
S-400 43 Göteborg, Sweden
Tel: 031 89 34 00
DENMARK
YS Copenhagen Liaison Office
Generatorvej 8B
DK-2730 Herlev, Denmark
Tel: 44 92 49 00
FINLAND
Warner Music Finland OY/Fazer Music
Aleksanterinkatu 11, P.O. Box 260
SF-00101 Helsinki, Finland
Tel: 0435 011
NORWAY
Narud Yamaha AS
Grini Næringspark 17
N-1345 Østerås, Norway
Tel: 67 14 47 90
ICELAND
Skifan HF
Skeifan 17 P.O. Box 8120
IS-128 Reykjavik, Iceland
Tel: 525 5000
OTHER EUROPEAN COUNTRIES
Yamaha Europa GmbH.
Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen, F.R. of
Germany
Tel: 04101-3030
Transcripción de documentos
FCC INFORMATION (U.S.A) 1. IMPORTANT NOTICE : DO NOT MODIFY THIS UNIT! This product, when installed as indicated in the instructions contained in this manual, meets FCC requirements. Modifications not expressly approved by Yamaha may void your authority, granted by the FCC, to use the product. 2. IMPORTANT: When connecting this product to accessories and/or another product use only high quality shielded cables. Cable/s supplied with this product MUST be used. Follow all installation instructions. Failure to follow instructions could void your FCC authorization to use this product in the USA. 3. NOTE: This product has been tested and found to comply with the requirements listed in FCC Regulations, Part 15 for Class “B” digital devices. Compliance with these requirements provides a reasonable level of assurance that your use of this product in a residential environment will not result in harmful interference with other electronic devices. This equipment generates/uses radio frequencies and, if not installed and used according to the instructions found in the user’s manual, may cause interference harmful to the operation of other electronic devices. Compliance with FCC regulations does not guarantee that interference will not occur in all installations. If this product is found to be the source of interference, which can be determined by turning the unit “OFF” and “ON”, please try to eliminate the problem by using one of the following measures: Relocate either this product or the device that is being affected by the interference. Utilize power outlets that are on different branch (circuit breaker or fuse) circuits or install AC line filter/s. In the case of radio or TV interference, relocate/reorient the antenna. If the antenna lead-in is 300 ohm ribbon lead, change the lead-in to co-axial type cable. If these corrective measures do not produce satisfactory results, please contact the your local retailer authorized to distribute this type of product. If you can not locate the appropriate retailer, please contact Yamaha Corporation of America, Electronic Service Division, 6600 Orangethorpe Ave, Buena Park, CA 90620 * The above statements apply ONLY to those products distributed by Yamaha Corporation of America or its subsidiaries. NEDERLAND / NETHERLAND • Dit apparaat bevat een lithium batterij voor geheugen back-up. • This apparatus contains a lithium battery for memory back-up. • Raadpleeg uw leverancier over de verwijdering van de batterij op het moment dat u het apparaat ann het einde van de levensduur afdankt of de volgende Yamaha Service Afdeiing: Yamaha Music Nederland Service Afdeiing Kanaalweg 18-G, 3526 KL UTRECHT Tel. 030-2828425 • For the removal of the battery at the moment of the disposal at the end of the service life please consult your retailer or Yamaha Service Center as follows: Yamaha Music Nederland Service Center Address : Kanaalweg 18-G, 3526 KL UTRECHT Tel : 030-2828425 • Gooi de batterij niet weg, maar lever hem in als KCA. • Do not throw away the battery. Instead, hand it in as small chemical waste. 92-BP ADVARSEL! Lithiumbatteri—Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandoren. VARNING Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion. VAROITUS Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti. SPECIAL MESSAGE SECTION This product utilizes batteries or an external power supply (adapter). DO NOT connect this product to any power supply or adapter other than one described in the manual, on the name plate, or specifically recommended by Yamaha. WARNING: Do not place this product in a position where anyone could walk on, trip over, or roll anything over power or connecting cords of any kind. The use of an extension cord is not recommended! If you must use an extension cord, the minimum wire size for a 25' cord (or less ) is 18 AWG. NOTE: The smaller the AWG number, the larger the current handling capacity. For longer extension cords, consult a local electrician. This Product should be used only with the components supplied or; a cart, rack, or stand that is recommended by Yamaha. If a cart, etc., is used, please observe all safety markings and instructions that accompany the accessory product. SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE: The information contained in this manual is believed to be correct at the time of printing. However, Yamaha reserves the right to change or modify any of the specifications without notice or obligation to update existing units. This product, either alone or in combination with an amplifier and headphones or speaker/s, may be capable of producing sound levels that could cause permanent hearing loss. DO NOT operate for long periods of time at a high volume level or at a level that is uncomfortable. If you experience any hearing loss or ringing in the ears, you should consult an audiologist. IMPORTANT: The louder the sound, the shorter the time period before damage occurs. Some Yamaha products may have benches and/or accessory mounting fixtures that are either supplied with the product or as optional accessories. Some of these items are designed to be dealer assembled or installed. Please make sure that benches are stable and any optional fixtures (where applicable) are well secured BEFORE using. Benches supplied by Yamaha are designed for seating only. No other uses are recommended. NOTICE: Service charges incurred due to lack of knowledge relating to how a function or effect works (when the unit is operating as designed) are not covered by the manufacturer’s warranty, and are therefore the owners responsibility. Please study this manual carefully and consult your dealer before requesting service. friendly. We sincerely believe that our products and the production methods used to produce them, meet these goals. In keeping with both the letter and the spirit of the law, we want you to be aware of the following: Battery Notice: This product MAY contain a small nonrechargeable battery which (if applicable) is soldered in place. The average life span of this type of battery is approximately five years. When replacement becomes necessary, contact a qualified service representative to perform the replacement. This Product may also use “household” type batteries. Some of these may be rechargeable. Make sure that the battery being charged is a rechargeable type and that the charger is intended for the battery being charged. When installing batteries, do not mix old batteries with new, or with batteries of a different type. Batteries MUST be installed correctly. Mismatches or incorrect installation may result in overheating and battery case rupture. Warning: Do not attempt to disassemble, or incinerate any battery. Keep all batteries away from children. Dispose of used batteries promptly and as regulated by the laws in your area. Note: Check with any retailer of household type batteries in your area for battery disposal information. Disposal Notice: Should this Product become damaged beyond repair, or for some reason its useful life is considered to be at an end, please observe all local, state, and federal regulations that relate to the disposal of products that contain lead, batteries, plastics, etc. If your dealer is unable to assist you, Please contact Yamaha directly. NAME PLATE LOCATION: The name Plate is located on the top of the product. The model number, power requirements, etc., are located on this plate. (The serial number is located on the rear panel.) You should record the model number, serial number, and the date of purchase in the spaces provided below and retain this manual as a permanent record of your purchase. POWER ON/ Model Serial No. Purchase Date ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES: Yamaha strives to produce products that are both user safe and environmentally PLEASE KEEP THIS MANUAL OFF Welcome to the MU100R Welcome to the MU100R Congratulations and thank you for purchasing the Yamaha MU100R Tone Generator! The MU100R is an advanced tone generator providing an amazing total of 1523 high-quality Voices, full General MIDI compatibility — including Yamaha’s new XG-MIDI (Extended General MIDI) — plus flexible computer interfacing in a compact, easy-to-use rack mount unit. Included in the 1523 Voices are 256 extraordinarily realistic and expressive VL Voices — provided by a separate, yet integrated Virtual Acoustic Synthesis tone generator. With the convenient built-in host computer interface and MIDI terminals, the MU100R is ideal for any computer music system — from connection to a simple laptop to integration in a complete MIDI studio. With its large LCD and the intuitive graphic controls on the display, the MU100R is remarkably easy to use. The MU100R also features completely independent dual MIDI inputs, 32 Part multi-timbral capacity and full 64-note polyphony for playback of even the most sophisticated song data. A special Performance mode gives you flexible four-Voice operation, for live performance applications. Also built into the system are six digital multi-effects and two EQ sections (one per-part, and one overall), which give you enormous versatility in “sweetening” the sound. What’s more, the MU100R provides a host of comprehensive, yet easy-to-use editing tools for getting just the sound you need. The MU100R also has convenient A/D inputs that allow you to connect a microphone, electric guitar or other instrument, and mix those signals with the MU100R’s Voices. A separate Hamony effect section lets you automatically apply two-, three- or four-part harmonies to your A/D input vocals, and have them change as you play different chords on a connected MIDI keyboard. * Company names and product names in this Owner’s Manual are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged. ii Welcome to the MU100R Unpacking Unpacking Your MU100R package should include the items listed below. Make sure that you have them all. Also, write down the serial number of your MU100R in the box below, for future reference. MU100R Serial No.: PA-5B AC Power Adaptor Owner’s Manual Floppy Disk Unpacking iii TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents Welcome to the MU100R ....................................................................................................... ii Unpacking .............................................................................................................................. iii Table of Contents .................................................................................................................. iv How to Use This Manual .................................................................................................... viii PRECAUTIONS .................................................................................................................... ix The Controls of the MU100R ................................................................................................ 1 Front Panel .................................................................................................................... 1 Rear Panel ..................................................................................................................... 3 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do ............................................................... 4 What It Is... ....................................................................................................................... 4 About General MIDI .................................................................................................... 4 About XG-MIDI ........................................................................................................... 5 What It Can Do... ............................................................................................................. 5 Using With MIDI Keyboard ......................................................................................... 5 Using With a Computer or Sequencer .......................................................................... 5 About the Modes of the MU100R ................................................................................... 6 Play Modes and the Part Controls ................................................................................ 7 Part Edit Mode .............................................................................................................. 7 Utility Mode ................................................................................................................. 7 Modes and Function Tree ...................................................................................................... 8 GUIDED TOUR Setting Up Your MU100R .............................................................................................. 12 What You'll Need ........................................................................................................ 12 Making the Connections ............................................................................................. 12 Powering Up .................................................................................................................... 14 Playing the Demo Song .................................................................................................. 15 Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System .......................................................... 17 Connecting to MIDI Devices ..................................................................................... 17 Connecting Directly to a Computer ........................................................................... 19 Macintosh and Compatibles ................................................................................. 19 IBM PC/AT and Compatibles ............................................................................... 21 Selecting and Playing the Performances ...................................................................... 23 Calling Up the Performance Play Mode and Playing the Performances ................... 23 Selecting and Playing Individual Voices ...................................................................... 26 Calling Up the XG Mode ........................................................................................... 26 Selecting Voice Banks and Voices From the Panel .................................................... 27 Selecting Voices From a MIDI Keyboard .................................................................. 31 Editing in the Multi Mode ............................................................................................. 32 Single Part Controls .................................................................................................... 33 Changing the Volume and Pan settings of a Part .................................................. 34 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 35 iv Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Edit Menu Parameters ................................................................................................ 36 Changing the Filter and EG Settings of a Part ..................................................... 36 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 38 Editing Drum Kits — with the Drum Setup Controls ............................................... 39 Making Changes to Individual Drum Sounds — the "Drum" Parameters ........... 40 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 42 Editing in the Performance Mode ................................................................................ 43 All Part Controls ......................................................................................................... 44 Transposing the Overall Key of a Performance ......................................................... 45 Single Part Controls — Selecting Different Voices for the Performance .................. 46 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 47 Edit Menu Parameters — Creating a Two-Voice Layer ............................................. 48 Setting Up a Keyboard Split ....................................................................................... 50 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 51 Using the Assignable Controller in a Performance .................................................... 51 Saving Your Original Performance ............................................................................. 52 Assignable Controller (AC1) ......................................................................................... 53 Controllers and Control Numbers .............................................................................. 53 Control Numbers and the Actual Sound ..................................................................... 54 Assigning the Assignable Controller .......................................................................... 55 Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up ......................................................... 56 Using the Assignable Controller — Some Applications ............................................ 57 Changing the Brightness on a Piano Voice ........................................................... 57 Experssive Volume Control of a Part .................................................................... 59 Expressive Control of Individual Drum Sounds .................................................. 59 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 61 Playing and Editing VL Voices ...................................................................................... 62 About the VL Voice Section ....................................................................................... 62 Virtual Acoustic Synthesis .................................................................................... 63 VA Advantages ................................................................................................ 63 VL Tone Generator Model .............................................................................. 63 Voice Organization ................................................................................................ 67 Selecting VL Voice banks and VL Voices .................................................................. 69 Editing a VL Voice ...................................................................................................... 71 Effects .............................................................................................................................. 73 Using Reverb and Chorus ........................................................................................... 73 Applying Distortion to a Part — Using the Variation Effects .................................... 75 Harmony Effect .............................................................................................................. 77 Using the Harmony Effect .......................................................................................... 77 On Your Own... ................................................................................................ 79 Equalizer (EQ) ................................................................................................................ 80 Adjusting the Tone of a Specific Part — Part EQ ...................................................... 80 Adjusting the Overall Tone — Main EQ .................................................................... 82 Individual Outputs ......................................................................................................... 83 Using the Individual Outputs ..................................................................................... 83 Table of Contents v TABLE OF CONTENTS Mute/Solo ........................................................................................................................ 85 Using Mute/Solo ......................................................................................................... 85 A/D Inputs ....................................................................................................................... 87 Using the A/D Inputs .................................................................................................. 87 Data Flow Block Diagram ............................................................................................. 91 MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables ............................................................................ 92 REFERENCE Multi Mode ...................................................................................................................... 95 Part Controls ............................................................................................................... 95 Single Part Control ................................................................................................ 96 All Part Control ..................................................................................................... 98 Multi Edit Mode ....................................................................................................... 100 Filter (FIL) .......................................................................................................... 100 Envelope Generator (EG) ................................................................................... 102 Equalizer (EQ) .................................................................................................... 105 Vibrato ................................................................................................................. 106 Others .................................................................................................................. 107 Drum Setup Controls .......................................................................................... 114 VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin) ..................................................................... 119 Performance Mode ....................................................................................................... 127 Performance Part Control ......................................................................................... 128 All Part ................................................................................................................ 128 Single Part ........................................................................................................... 129 Performance Edit Mode ............................................................................................ 131 Common .............................................................................................................. 131 Part ...................................................................................................................... 134 Copy and Store Operations ....................................................................................... 137 Copy .................................................................................................................... 137 Store .................................................................................................................... 138 Recall Function ................................................................................................... 140 Effect Edit Mode .......................................................................................................... 141 Reverb (REV) ........................................................................................................... 142 Chorus (CHO) ........................................................................................................... 143 Variation (VAR) ........................................................................................................ 144 Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2) ............................................................................................ 146 Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters .................................................................... 147 About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion .......................................... 152 Equalizer (EQ) Edit ..................................................................................................... 155 vi Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Utility Mode .................................................................................................................. 156 System Functions (SYS) .......................................................................................... 157 Dump Out Functions (DUMP) ................................................................................. 161 Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI ................................................................. 161 Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST .......................................................... 161 Initialize Functions (INIT) ....................................................................................... 165 Demo Song Play (DEMO) ....................................................................................... 168 VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) .......................................... 169 VL Voice System Parameters .............................................................................. 169 Harmony System Parameters .............................................................................. 171 Sound Module Mode (MODE) .................................................................................... 172 Miscellaneous Functions .............................................................................................. 173 Show Control Change ............................................................................................... 173 Show Exclusive ......................................................................................................... 175 APPENDIX Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 178 Error Messages ............................................................................................................. 180 Specifications ................................................................................................................ 181 Glossary ......................................................................................................................... 183 Index .............................................................................................................................. 185 Table of Contents vii How to Use This Manual How to Use This Manual You are probably eager to try out your new MU100R Tone Generator right away and hear what it can do, rather than have to read through a lot of instructions before you can even get a sound out of it. The structure of the manual is very straightforward. You can approach it in a linear manner, reading through from beginning to end, or on an “on-demand” basis, going directly to the information you need as you need it. However, to get the most out of your MU100R, we strongly suggest that you read the following sections in the order given: 1) Precautions This gives you important information on how to care for your new MU100R, how to avoid damaging it, and how to ensure long-term, reliable operation. 2) The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do This briefly provides an overview of the functions and features of the MU100R and offers some important hints on how you can use it effectively. It also provides convenient page references so that you can easily find out about features and functions of interest. 3) The Controls of the MU100R This section introduces you to the panel controls and connectors. 4) Guided Tour This is perhaps the most important and valuable section of the manual. It gets you started using your new MU100R, helping you set up the instrument and play it — and it introduces you to virtually all of the important functions and features. The hands-on experience you gain in this section will help you quickly master the instrument and aid you in navigating the more detailed sections of the manual. 5) Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System; Using the MU100R with a Computer or Sequencer These sections (within the Tutorial) provide all you need to know to effectively integrate the MU100R into your present computer music system. 6) Reference Once you’re familiar with everything above, lightly go over this comprehensive guide to all editing functions. You won’t need (or want) to read everything at once, but it is there for you to refer to when you need information about a certain feature or function. 7) Appendix Use the sections in the Appendix as necessary. For example, the Index will come in handy when you need to quickly find information on a specific topic. Other sections, such as the Glossary, Troubleshooting and Error Messages provide additional useful information. 8) Sound List & MIDI Data booklet This separate booklet features lists of the Performances, Voices, drum sounds, effect types and parameters, as well as details on all relevant MIDI messages and data. viii How to Use This Manual PRECAUTIONS PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE PROCEEDING * Please keep these precautions in a safe place for future reference. WARNING Always follow the basic precautions listed below to avoid the possibility of serious injury or even death from electrical shock, short-circuiting, damages, fire or other hazards. These precautions include, but are not limited to, the following: • Do not open the instrument or attempt to disassemble the internal parts or modify them in any way. The instrument contains no user-serviceable parts. If it should appear to be malfunctioning, discontinue use immediately and have it inspected by qualified Yamaha service personnel. • Do not expose the instrument to rain, use it near water or in damp or wet conditions, or place containers on it containing liquids which might spill into any openings. • If the AC adaptor cord or plug becomes frayed or damaged, or if there is a sudden loss of sound during use of the instrument, or if any unusual smells or smoke should appear to be caused by it, immediately turn off the power switch, disconnect the adaptor plug from the outlet, and have the instrument inspected by qualified Yamaha service personnel. • Use the specified adaptor (PA-5B or an equivalent recommended by Yamaha) only. Using the wrong adaptor can result in damage to the instrument or overheating. • Before cleaning the instrument, always remove the electric plug from the outlet. Never insert or remove an electric plug with wet hands. • Check the electric plug periodically and remove any dirt or dust which may have accumulated on it. CAUTION Always follow the basic precautions listed below to avoid the possibility of physical injury to you or others, or damage to the instrument or other property. These precautions include, but are not limited to, the following: • Do not place the AC adaptor cord near heat sources such as heaters or radiators, and do not excessively bend or otherwise damage the cord, place heavy objects on it, or place it in a position where anyone could walk on, trip over, or roll anything over it. • Do not operate the instrument for a long period of time at a high or uncomfortable volume level, since this can cause permanent hearing loss. If you experience any hearing loss or ringing in the ears, consult a physician. • When removing the electric plug from the instrument or an outlet, always hold the plug itself and not the cord. ■REPLACING THE BACKUP BATTERY • Do not connect the instrument to an electrical outlet using a multipleconnector. Doing so can result in lower sound quality, or possibly cause overheating in the outlet. • Unplug the AC power adaptor when not using the instrument, or during electrical storms. • Before connecting the instrument to other electronic components, turn off the power for all components. Before turning the power on or off for all components, set all volume levels to minimum. • Do not expose the instrument to excessive dust or vibrations, or extreme cold or heat (such as in direct sunlight, near a heater, or in a car during the day) to prevent the possibility of panel disfiguration or damage to the internal components. • Do not use the instrument near other electrical products such as televisions, radios, or speakers, since this might cause interference which can affect proper operation of the other products. • Do not place the instrument in an unstable position where it might accidentally fall over. • Before moving the instrument, remove all connected adaptor and other cables. • When cleaning the instrument, use a soft, dry cloth. Do not use paint thinners, solvents, cleaning fluids, or chemical-impregnated wiping cloths. Also, do not place vinyl or plastic objects on the instrument, since this might discolor the panel or keyboard. • This instrument contains a non rechargeable internal backup battery which permits internal data to remain stored even when the power is off. When the backup battery needs replacing, the message “Battery Low!” will display in the display. When this happens, immediately back up your data (using an external device such as the floppy disk-based Yamaha MIDI Data Filer MDF2), then have qualified Yamaha service personnel replace the backup battery. • Do not attempt to replace the backup battery yourself, in order to prevent the possible serious hazards. Always have qualified Yamaha service personnel replace the backup battery. • Never place the backup battery in a location that a child can reach, since a child might accidentally swallow the battery. If this should happen, consult a physician immediately. ■SAVING USER DATA • Save all data to an external device such as the Yamaha MIDI Data Filer MDF2, in order to help prevent the loss of important data due to a malfunction or user operating error. Yamaha cannot be held responsible for damage caused by improper use or modifications to the instrument, or data that is lost or destroyed. Always turn the power off when the instrument is not in use. • Do not rest your weight on, or place heavy objects on the instrument, and do not use excessive force on the buttons, switches or connectors. PRECAUTIONS ix The Controls of the MU100R The Controls of the MU100R Front Panel 1 2 3 4 5 8 7 9 6 0 1 PHONES jack For connection to a set of stereo headphones (1/4” plug). 2 VOLUME control For adjusting the overall volume of the MU100R. 3 A/D INPUT 1, 2 jacks For connection of a microphone, electric guitar or other electronic instruments (mono 1/4” plugs). 4 A/D INPUT VOLUME control For control of the level of the A/D inputs. 5 PLAY button For entering the Play mode and switching among the different Play displays. (See page 24.) 6 UTIL (UTILITY) button For entering the Utility mode. (See page 15.) 7 MODE button For entering the Sound Module mode. (See page 23.) 8 EDIT button For entering the Edit mode. (See page 36.) 9 EFFECT button For entering the Effect Edit mode. (See page 74.) : EQ button For entering the EQ Edit mode. (See page 82.) The Controls of the MU90R 1 The Controls of the MU100R A D G H POWER ON/ C B OFF E F A MUTE/SOLO button Pressing this alternately mutes or solos the selected Part. (See page 85.) B ENTER button For calling up menu items in the display and for executing certain functions and operations. Double-clicking this (pressing it twice quickly) calls up the Show Exclusive function (see page 175). C EXIT button For leaving various display pages and returning to previous displays. Also for canceling certain functions and operations. D PART -/+ buttons For selecting different Parts. In the Effect Edit mode, these can be used to switch among the different effects. Pressing these together alternately switches between All Part and Single Part control. (See page 48.) E SELECT </> buttons For selecting the various menu items, parameters and controls on the display. F VALUE -/+ buttons For changing the value of a selected parameter or control. Hint You can rapidly move through the values by holding down one of the [VALUE -/+] buttons. You can move even more rapidly by holding down one button and then pressing and holding down the other. For example, to rapidly advance (increase) the value, hold down the [VALUE +] button and simultaneously press and hold down the [VALUE -] button. G Data dial For rapidly adjusting/changing values of the selected function or parameter. Rotate this clockwise to increase the value. H POWER switch Pressing this turns the power on and off. 2 The Controls of the MU90R The Controls of the MU100R Rear Panel 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 MIDI THRU, MIDI OUT and MIDI IN A/B terminals For connection to other MIDI devices, such as a MIDI keyboard, tone generator, sequencer, or to a computer that has a MIDI interface. MIDI IN A and B are independent MIDI ports, allowing full 32-channel MIDI input. MIDI OUT is for data dumps to another MIDI device, while MIDI THRU is for “daisychain” connection of additional MU100Rs or other MIDI instruments. (See page 17 for more information on MIDI connections.) 2 HOST SELECT switch For selecting the type of host computer. (See page 19.) 3 TO HOST terminal For connection to a host computer that does not have a MIDI interface. (See page 19.) 4 DC IN jack For connection to the PA-5B AC power adaptor. 5 OUTPUT R, L/MONO jacks (Right, Left/Mono) For connection to a stereo amplifier/speaker system. When using a mono system, connect it to the L/MONO jack. 6 INDIV. (Individual) OUTPUT 1, 2 jacks For independent output of selected Parts (1/4” jack). Parts selected for output through these jacks are not output through the main OUTPUT or PHONES jacks. (See pages 113 and 118.) The Controls of the MU90R 3 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do What It Is... The MU100R is a full-featured and easy-to-use tone generator, that provides an unprecedented wealth of Voices and expressive sonic control. It features full General MIDI Level 1 compatibility with 128 General MIDI Voices and 9 drum kits. It also provides new XG-MIDI (Extended General MIDI) compatibility, with an huge total of 1074 Voices and 36 drum kits. Moreover, it has an integrated VL tone generator that provides 256 stunning monophonic Voices utilizing Yamaha’s sophisticated Virtual Acoustic Synthesis system. The MU100R has 64-note polyphony and is 32-Part multi-timbral. In other words, the MU100R has 32 different Parts, each with its own Voice, so that up to 32 different Voices can be sounded simultaneously. Since the MU100R features dual MIDI input ports (A and B), 16 Parts can be played from one MIDI port and the remaining 16 from the other port. Additional A/D Parts let you connect up to two external signals — such as a microphone, electric guitar or CD player — and mix them with the MU100R’s Voices. The MU100R also has a TO HOST terminal for easy interfacing with a computer, allowing you to play the Voices using your favorite music software. This is where the advanced multi-timbral capabilities come in, letting you playing sophisticated arrangements using up to 32 different Voices at the same time. Although Voices cannot be directly edited, the various Part controls and Edit mode give you tools for transforming or customizing the sound of the Voices. What’s more, the MU100R has a built-in multi-effect processor, with seven independent digital effect “units” for enhancing the sound. Included in these is a powerful Harmony section that allows you to generate realistic vocal harmonies with your actual voice (using one of the A/D Parts). The MU100R also features a special Performance mode, in which four Parts are played simultaneously over a single MIDI channel. Connected to a MIDI keyboard, this effectively gives you four tone generators in one. The MU100R gives you 100 factory-programmed Preset Performances plus 100 Internal Performance locations for storing your own original Performances. About General MIDI General MIDI is a new addition to the worldwide MIDI standard. MIDI, as you know, stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, and makes it possible for various electronic musical instruments and other devices to “communicate” with each other. For example, by connecting a sequencer to the MU100R’s MIDI IN terminal, you could play back a song on the sequencer using the Voices of the MU100R. 4 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do So, where does General MIDI fit in all of this? One of the most important features of General MIDI is in the standardization of Voices. This means that a song recorded in the General MIDI format can be played back on any General MIDI compatible tone generator and sound just as the composer intended. For example, if there is an alto sax solo in the song, it will be played by an alto sax Voice on the General MIDI tone generator (and not by a tuba or harpsichord!). Since the MU100R is fully compatible with General MIDI, you can take advantage of the vast wealth of musical material recorded in that format. About XG-MIDI The new XG format is an extension of General MIDI, and provides a number of significant improvements and enhancements. XG-compatible song data takes advantage of the extensive MIDI control and built-in effects of the MU100R (and other MU-series instruments). To take greatest advantage of the powerful capabilities of XG-MIDI, we recommend using XG-compatible instruments and software. For example, XGcompatible keyboards such as the Yamaha CBX-K1 keyboard and software give you direct controls for accessing the full expressive potential of the MU100R’s XG Voices and the XG-related parameters. What It Can Do... Here are a few ideas on how you can use the MU100R. The list below is not comprehensive, but is meant to be a general guide to the possibilities and provide a starting point or springboard for your own creative ideas and explorations. Using With MIDI Keyboard Use the MU100R as supplementary tone generator with your MIDI keyboard and play the Voices of both instruments in a layer together. Or, use the convenient Performance mode, and play four Voices on the MU100R at once. You can split the four Voices across the keyboard, playing each from a different register. Or you can create sophisticated velocity splits, in which a different Voice is heard depending on how strongly you play the keyboard. Or use keyboard and velocity splits together for even greater flexibility. Using With a Computer or Sequencer Home Studio Setup The MU100R integrates instantly and easily into any existing setup. If you have a MIDI keyboard, computer and sequencing software, the MU100R with its highquality Voices and multi-timbral capabilities can expand your home studio system. The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do 5 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do Carry It With You If you have a laptop computer (and sequencing software), simply connect the MU100R, plug in some headphones and you’ve got a complete, high-powered music making system that’s ready to go wherever you go. Use it for composing, arranging, practicing or making/playing demos for your band. Use It on a Gig Similarly, you can connect a laptop or a MIDI data filer and playback song data with the MU100R’s Voices. Plug a microphone into one of the A/D inputs and a guitar into the other, and you can mix your own live performance with the sequencer tracks. What’s more, you can produce automatic vocal harmonies with the Harmony effect — controlled either from a keyboard or directly from one of the sequencer tracks! Multimedia Since it’s compatible with General MIDI and XG, the MU100R is a natural for multimedia applications. Bring it with you to a presentation — since the computer interface is built-in to the MU100R, it hooks up instantly and easily to the computer’s serial port or printer port, without the need for any other equipment. About the Modes of the MU100R The MU100R has two main operating modes: Multi and Performance. In Multi mode, the MU100R is a 32-Part multi-timbral tone generator; in Performance mode, the MU100R effectively functions as four tone generators controlled over a single MIDI channel. Which mode the MU100R is in depends on the selected Sound Module mode. If XG, TG300B or C/M are selected, the MU100R automatically sets itself to the Multi mode. When PFM is selected, the MU100R is in the Performance mode. (For information on selecting the Sound Module mode, see page 172.) Each mode provides compatibility with different music software and hardware. XG: This stands for Extended General MIDI and provides the full potential of the MU100R, giving you access to the 1074 XG Voices plus the VL Voices. TG300B: This mode provides compatibility with the GM-B mode of the TG300 Tone Generator. C/M: This mode provides compatibility with most computer music software not supported by the other two Multi modes. PFM: This mode (Performance) lets you play four Voices simultaneously over a single MIDI channel. (For more information on using the Performance mode, see page 43.) 6 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do The bottom right of the display indicates the currently selected Sound Module mode. XG TG300B C/M PERFORM Selected Sound Module mode. NOTE When set to the TG300B mode, the MU100R may not be able to play TG300-specific song data with complete accuracy. However, MIDI data designed for other computer music tone generators is compatible with the MU100R. Play Modes and the Part Controls Once the operating mode of the MU100R is set (Multi or Performance), there are two main ways you can use the MU100R: playing and editing. In the Play modes, you play the Voices; in the various Edit modes, you change their settings. Within the Play modes are the Part controls. These let you make basic settings for the Parts. The Single Part controls allow you to make independent settings for each Part, while the All Part controls allow you to change the overall settings of all Parts. (See pages 96 and 98 for more information.) The MU100R has several different Edit modes, each with various menus and operations: Part Edit Mode The Part Edit mode allows you to change certain settings for each individual Part, such as those of the Filter, EG (Envelope Generator), and many other settings. The internal Voices can be sounded during editing, allowing you to hear the effects of your edits. Utility Mode The Utility mode lets you set functions related to the overall operation of the MU100R, such as Master Tune, display Contrast and reception of certain MIDI messages that affect the entire instrument. Included also are miscellaneous operations, such as sending bulk data to a data storage device, initializing of the MU100R settings, and playing the special Demo song. The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do 7 Modes and Function Tree Modes and Function Tree [PLAY] Multi Play Mode ( When the sound module mode is “XG”, “TG300B”, or “C/M”) [SELECT </>] Multi Part Control P. 95 P. 96 [PART++-] [SELECT </>] Multi All Part Control [EDIT] [PLAY] P. 98 Multi Part Edit Mode Performance Play Mode P. 100 [SELECT <] Filter Edit [ENTER] P. 100 [SELECT </>] EG Edit [ENTER] P. 102 [SELECT </>] EQ Edit (Only when Normal or VL Part is selected.) [ENTER] P. 105 [SELECT </>] Drum Setup Edit P. 114 (Only when Drum Part is selected.) [ENTER] [SELECT </>] Vibrato Edit [ENTER] P. 106 [SELECT </>] Others Edit [ENTER] P. 107 [SELECT >] Plugin Edit (Only when VL Part is selected.) [ENTER] P. 119 ( When the sound module mode is ”PFM”) [SELECT </>] Performance Control P. 127 P. 128 [PART++-] [SELECT </>] Performance Part Control [EDIT] 8 P. 129 Performance Edit Mode P. 131 [SELECT <] Common Edit [ENTER] P. 131 [SELECT </>] Part Edit [ENTER] P. 134 [SELECT <] Filter Edit [ENTER] P. 135 [SELECT </>] EG Edit [ENTER] P. 135 [SELECT </>] EQ Edit [ENTER] P. 135 [SELECT </>] Vibrato Edit [ENTER] P. 135 [SELECT </>] Others Edit [ENTER] P. 135 [SELECT >] Plugin Edit (Only when VL Part is selected.) [ENTER] P. 136 [SELECT </>] Copy [ENTER] P. 137 [SELECT </>] Store [ENTER] P. 138 [SELECT >] Recall [ENTER] P. 140 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do Modes and Function Tree [UTIL] [MODE] [EFFECT] [EQ] P. 156 Utility Mode [SELECT <] System Setup [ENTER] P. 157 [SELECT </>] Dump Out [ENTER] P. 161 [SELECT </>] Initialize [ENTER] P. 165 [SELECT </>] Demo Song Play [ENTER] P. 168 [SELECT >] Plugin [ENTER] P. 169 Sound Module Mode P. 172 [SELECT <] or [VALUE-] XG P. 172 [SELECT </>] or [VALUE+/-] TG300 P. 172 [SELECT </>] or [VALUE+/-] C/M P. 172 [SELECT >] or [VALUE+] PFM P. 172 Effect Mode P. 141 [SELECT <] Reverb Edit [ENTER] P. 142 [SELECT </>] Chorus Edit [ENTER] P. 143 [SELECT </>] Variation Edit [ENTER] P. 144 [SELECT </>] Insertion 1 Edit [ENTER] P. 146 [SELECT </>] Insertion 2 Edit [ENTER] P. 146 [SELECT >] Plugin Edit [ENTER] P. 147 Equalizer Mode P. 155 : Mode : Submode Push on the SELECT buttons either < or > for SELECT < / >. Push on the PART + and - simultaneously for PART ++ -. The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do 9 10 The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do G UIDED T OUR When using your MU100R for the first time, read through this short section of the manual. It guides you step-by-step in using many of the basic operations: setting the instrument up, connecting it properly to other equipment, and — most importantly — playing it. It also introduces you to most of the other, advanced features and operations of the instrument — enabling you to quickly and effectively get the most out of your new MU100R. Setting Up Your MU100R Setting Up Your MU100R In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Connect the MU100R in the most basic setup — with a MIDI keyboard and an external amplifier/speaker system. Other setup examples are covered in later sections; for example, setting up for use with a computer is on page 19. Once you’ve set up the MU100R, we urge you to play the Demo song (page 15) and hear what the instrument is capable of. What You’ll Need ☛ The MU100R and the included PA-5B power adaptor. ☛ A MIDI keyboard, electronic piano, or any instrument that can output MIDI data. ☛ An amplifier/speaker system, preferably stereo. Alternately, you can use a set of stereo headphones. ☛ Audio connecting cables. ☛ A MIDI cable. Making the Connections CAUTION! Before making any connections, turn all related equipment off, and make sure the MU100R power adaptor is not connected to an electrical outlet. Operation 1 Connect the MIDI cable. Connect the MIDI OUT terminal of the MIDI keyboard to the MIDI IN-A of the MU100R (as shown in the illustration). 2 Connect the audio cables. Connect the R and L/MONO OUTPUT jacks of the MU100R to the appropriate inputs on the amplifier speaker system (as shown in the illustration). •If the amplifier has only one input, use the L/MONO jack on the MU100R. If you are using stereo headphones, connect them to the front panel PHONES jack. 12 Guided Tour Setting Up Your MU100R 3 Set the HOST SELECT switch. Set this rear panel switch to MIDI (see illustration). 4 Connect the AC power adaptor. Plug the DC output cable of the PA-5B into the DC IN terminal on the rear panel, then plug the adaptor into an appropriate electrical outlet. •Wrap the DC output cable of the adaptor around the cable clip (as shown below) to prevent accidental unplugging of the cable during operation. CAUTION! • Do not attempt to use an AC adaptor other than the PA-5B. The use of an incompatible adaptor may result in irreparable damage to the MU100R, and even pose a serious shock hazard. • Be sure to disconnect the power adaptor from the outlet when the MU100R is not in use. Amplifier Speaker System L/MONO R Power Adaptor DC IN MIDI IN-A POWER MIDI CABLE ON/ OFF PHONES MIDI OUT IN MIDI OUT DC IN POWER ON OFF CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST PITCH CONTROL CHANGE 1 MODULATION DEPTH 2 BREATH CONTROL 4 FOOT CONTROL 5 PORTAMENTO TIME 6 DATA ENTRY 7 MAIN VOLUME 8 BALANCE CONTROL 10 PANPOT ASSIGNABLE SEQUENCER SHIFT STOP CONTINUE START PROGRAM TEMPO BANK SELECT PROGRAM CHANGE 11 EXPRESSION 64 HOLD1(DAMPER) 65 PORTAMENTO 66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD) 67 SOFT PEDAL 69 HOLD2 (FREEZE) 71 HARMONIC CONTENT 72 RELEASE TIME RESET GM ON SOUND OFF 73 ATTACK TIME 74 BRIGHTNESS 84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL 91 REVERB DEPTH 92 TREMOLO DEPTH 93 CHORUS DEPTH 94 VARIATION DEPTH 95 PHASER DEPTH SYSTEM XG ON MERGE ON/OFF MIDI CH FIXED VELOCITY WHEEL ASSIGN RPN CONTROLLER NRPN OTHERS 142 CHANNEL PRESSURE 143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE 144 MASTER VOLUME 145 MASTER BALANCE 146 MASTER TUNING 147 VELOCITY 148 TEMPO 134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE 135 DRUM PITCH COARSE 136 DRUM PITCH FINE 137 DRUM LEVEL 138 DRUM PAN 139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH 140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH 141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH 126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 127 FILTER RESONANCE 128 EG ATTACK TIME 129 EG DECAY TIME 130 EG RELEASE TIME 131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE 133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE (RPN) 120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY 121 FINE TUNING 122 COARSE TUNING (NRPN) 123 VIBRATO RATE 124 VIBRATO DEPTH 125 VIBRATO DELAY MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1 TRANSPOSE DRUM NUMBER ENTER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0 HEXA DECIMAL DECIMAL OCTAVE OCTAVE SHIFT OCTAVE RESET MIDI Keyboard Now that you’ve set up the MU100R, we urge you to go on to the next section, turn on the instrument, and play the Demo song (page 15) to hear what the instrument is capable of. If you need information on setting up the MU100R for a different type of system, refer to “Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System” on page 17. Guided Tour 13 Powering Up Powering Up Admittedly this is a simple operation, but you should be careful to follow the instructions below to avoid possible damage to your equipment and speakers. Operation 1 Turn on the power of your MIDI keyboard. 2 Turn on the power of the MU100R. Press the POWER switch. After the animated greeting display finishes, the following display appears: 3 Turn down all volume controls. This includes the MU100R and any connected equipment. 4 Turn on the amplifier/speaker system. 5 Set the volume controls. First, set the volume control on the MU100R to about the midway position, then set the volume on the amplifier to a suitable level. Powering Down When you turn the power off, make sure to do it in the following order: 1) Amplifier/speaker system 2) MU100R 3) Other connected equipment (MIDI keyboard, etc.) This prevents possible damage to the speakers. 14 Guided Tour Playing the Demo Song Playing the Demo Song Now that you’ve set everything up properly, try playing the built-in Demo song. This showcases the high-quality Voices and the AWM2 tone generation system of the MU100R. It also is an excellent demonstration of the 32part multi-timbral capacity and the various expressive controls and effects that can be used simultaneously. Most importantly, the Demo song will give you an idea of how powerful the MU100R can be in your own MIDI/computer music setup. Operation 1 Press the [UTIL] button. 2 Select and open the DEMO menu. Use the [SELECT -/>] buttons to select “DEMO” (the menu icon flashes), then press the [ENTER] button. 3 Start the Demo song. Press the [ENTER] button. The Demo Song starts playing immediately and repeats indefinitely until stopped (in step 4 below). Playback of the individual Parts of the song is shown graphically by the “level meter” bars in the display. NOTE During Demo Song playback, none of the panel controls (with the exception of the [EXIT] button and the VOLUME control) can be used. Guided Tour 15 Playing the Demo Song 4 Stop playback of the song. Press the [EXIT] button. 5 Exit from the Demo Song function. Press the [EXIT] button again — twice to return to the Play mode. (Or you can simply press the [PLAY] button.) 16 Guided Tour Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System As you learned in the section The MU100R — What It Is and What It Can Do on page 4, the MU100R can be integrated into a variety of setups. It would be impossible to cover all connection possibilities in a short manual as this; however, the section below will help in quickly setting up the MU100R and using it in your system. Connecting to MIDI Devices The MU100R is equipped with MIDI IN, OUT, and THRU terminals, allowing you to use it in any MIDI system. Moreover, the two MIDI IN terminals are independent 16-channel ports, effectively giving you two tone generators in one. Here are some common connection examples using the built-in MIDI interface. Refer to the example that most closely matches your setup, then read the Operation steps at the end of this section. • MIDI keyboard In this setup, you can play the sounds of the MU100R from the connected keyboard. MIDI CABLE MIDI OUT IN MIDI OUT DC IN POWER ON OFF CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST PITCH CONTROL CHANGE 1 MODULATION DEPTH 2 BREATH CONTROL 4 FOOT CONTROL 5 PORTAMENTO TIME 6 DATA ENTRY 7 MAIN VOLUME 8 BALANCE CONTROL 10 PANPOT ASSIGNABLE SEQUENCER SHIFT STOP CONTINUE START PROGRAM TEMPO BANK PROGRAM SELECT CHANGE 11 EXPRESSION 64 HOLD1(DAMPER) 65 PORTAMENTO 66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD) 67 SOFT PEDAL 69 HOLD2 (FREEZE) 71 HARMONIC CONTENT 72 RELEASE TIME RESET GM ON SOUND OFF SYSTEM XG ON MERGE ON/OFF MIDI CH FIXED VELOCITY 73 ATTACK TIME 74 BRIGHTNESS 84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL 91 REVERB DEPTH 92 TREMOLO DEPTH 93 CHORUS DEPTH 94 VARIATION DEPTH 95 PHASER DEPTH (RPN) 120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY 121 FINE TUNING 122 COARSE TUNING (NRPN) 123 VIBRATO RATE 124 VIBRATO DEPTH 125 VIBRATO DELAY WHEEL ASSIGN RPN CONTROLLER NRPN OTHERS 142 CHANNEL PRESSURE 143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE 144 MASTER VOLUME 145 MASTER BALANCE 146 MASTER TUNING 147 VELOCITY 148 TEMPO 134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE 135 DRUM PITCH COARSE 136 DRUM PITCH FINE 137 DRUM LEVEL 138 DRUM PAN 139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH 140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH 141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH 126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 127 FILTER RESONANCE 128 EG ATTACK TIME 129 EG DECAY TIME 130 EG RELEASE TIME 131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE 133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1 TRANSPOSE ENTER DRUM NUMBER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0 HEXA DECIMAL DECIMAL OCTAVE OCTAVE SHIFT OCTAVE RESET MIDI Keyboard MIDI IN-A or B • Hardware sequencer In this setup, a hardware sequencer (such as the Yamaha QY700) is used. The main advantage of such a setup is its portability. MIDI CABLE MIDI OUT L/MONO OUTPUT R IN A FOOT SW IN B OUT A MIDI OUT B IN A IN B MUSIC SEQUENCER PITCH OUT A OUT B MIDI ASSIGNABLE SONG PATTERN UTILITY VOICE EFFECT DISK MAX VOLUME SHIFT REC PLAY A OCT UP OCT DOWN ON BASS F# B Gb G# A F4 TRACK DOWN TRACK UP MUTE SOLO REST TIE C A# Bb Ab C# ) E Db D# F Eb F5 ! M F ? N G B C F6 SHIFT # 7( 5) b 7( 5) G # 7( 9) b 7( 9) H -1 EXIT % Q S # O A P B D E +1 NO YES a I 7sus4 b 7( 13) 7(13) J sus4 m7(11) # 7( 11) 3 7 8 9 4 5 6 1 2 3 0 - DEL SPACE OCT DOWN OCT UP 3 c C _ & R D S add9 M SECTION F3 JOB LOC 2 c _ L E F2 EDIT LOC 1 ( D ORG BASS K F1 CONTRAST SHIFT CAPS F G T / V U W X Y M7(9) 6(9) 7(9) add9 m7 (9) mM7 M7 6 7 m m7 m6 Z dim m7( b 5) aug H MIDI IN-A Guided Tour 17 Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System • MIDI data storage device This setup is used for backing up your important data — including original Performances you’ve created, as well as settings you’ve changed in the Part Edit, Effect, EQ, or Utility modes. In this example, a Yamaha MDF2 MIDI Data Filer is used. To back up data, connect the MIDI IN of the MDF2 to the MIDI OUT of the MU100R. To restore the data to the MU100R, connect the MIDI OUT of the MDF2 to the MIDI IN of the MU100R. Refer to the owner’s manual of the MDF2 (or your particular data storage device) for specific operating instructions in receiving or sending data. MIDI CABLE MIDI IN MDF2 MIDI OUT With the MDF2, you can also play compatible song data on the MU100R directly from the MDF2 itself, without the need of a sequencer. In this case, the MIDI OUT of the MDF2 should be connected to the MIDI IN of the MU100R. • Computer equipped with a MIDI interface In this setup, you can control the MU100R from a computer (using sequencing or other song playback software). In a variation on this, you can connect the computer to MIDI-A and a keyboard to MIDI-B. This allows you to play parts live over sequencer playback — even if the sequencer uses all 16 MIDI channels. MIDI OUT MIDI CABLE Computer MIDI IN-A 18 Guided Tour Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System Operation 1 Set the HOST SELECT switch to MIDI. 2 Connect the MU100R to the appropriate MIDI device. Refer to the illustrations above. Use a standard MIDI cable (see page 92). 3 Turn on the the connected device, then the MU100R. 4 If you are using a computer, start up your music software, and set up the appropriate options on the software for operation with the MU100R. Connecting Directly to a Computer The MU100R features a built-in host computer interface, allowing you to directly connect it to your computer — eliminating the need of installing a special MIDI interface to your computer. The MU100R can be used with the following computers: Apple Macintosh and compatibles, IBM PC/AT and compatibles. If your computer has a MIDI interface you may want to connect the MU100R to it, rather than using the host computer interface on the MU100R. (See the section “Connecting to MIDI Devices” on page 17.) Depending on the computer or interface used, set the HOST SELECT switch to the appropriate setting: MIDI, PC-1, PC-2 (IBM and compatibles), or Mac (Macintosh and compaibles). For information on the types of cables that can be used for connection, see the section “MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables” on page 92. Macintosh and Compatibles Follow these instructions if you have an Apple Macintosh not equipped with an external MIDI interface. Connect the TO HOST terminal on the MU100R to the Modem or Printer port on the Macintosh. Modem or Printer Port Macintosh Guided Tour 19 Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System Operation 1 Set the HOST SELECT switch to Mac. 2 Connect the MU100R to the host computer. Refer to the illustration above. Use a standard Macintosh cable (8-pin Mini DIN on both ends; see page 92). 3 Turn on the the host computer, then the MU100R. 4 Start up your music software. If necessary, set up the appropriate options on the software for operation with the MU100R. The relevant settings may be found in menu(s) called “Studio Setup,” “System Setup,” or “MIDI Setup.” In this menu, you should be able to set separate MIDI outputs to access the two MIDI ports on the MU100R. For example, the device for MIDI OUT 1 should be set to “Yamaha MU100” (or “MU80,” if “MU100” is not available). Other options you may have to set include: MIDI Interface Type g Standard MIDI Interface MIDI Time Piece g On (for controlling all 32 Parts of the MU100R) Clock g 1 MHz (The specific menu/parameter names may differ depending on your particular music software. For detailed instructions, refer to the owner’s manual or on-line help of the software.) Hint If you have a second multi-timbral tone generator (such as the MU50), you can connect it to the MIDI OUT terminal of the MU100R and have three independent MIDI ports (for 48-channel operation). The software settings above apply here as well: Set the device for MIDI OUT 3 to “Yamaha MU50” (or similar). (For more information, see page 159.) 20 Guided Tour Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System IBM PC/AT and Compatibles Follow these instructions if you have an IBM PC/AT or compatible computer not equipped with an external MIDI interface. Connect the TO HOST terminal on the MU100R to one of the computer’s serial ports, COM 1 or COM 2. Serial Port IBM PC/AT and Compatible The instructions below assume you are running Windows95 on your PC. For using the TO HOST connection with other software and operating systems, consult your Yamaha dealer. If your computer and music software cannot recognize the TO HOST connection, you can still use the MU100R by installing a MIDI interface (internal card or external) to the computer. Operation 1 Install the included driver software. For Windows95 Install the included Yamaha CBX Driver for Windows95. The driver software is on a floppy disk included with the MU100R. Make sure to thoroughly read the “A:\MIDIDRV\README_E.TXT” on the disk. This contains essential information on installing and setting up the driver to your computer. For Windows3.1 Install the included Yamaha CBX Driver for Windows3.1. The driver software is on a floppy disk included with the MU100R. Make sure to thoroughly read the “A:\IBMPC\ CBXT3.WRI” on the disk. This contains essential information on installing and setting up the driver to your computer. 2 Set the HOST SELECT switch to PC-2. 3 Connect the MU100R to the host computer. Refer to the illustration above. Use a standard computer cable (8-pin Mini DIN to 9-pin D-SUB; see page 92). 4 Turn on the the host computer, then the MU100R. Guided Tour 21 Setting Up the MU100R in Your Music System 5 Start up your music software. If necessary, set up the appropriate options on the software for operation with the MU100R. The relevant settings may be found in menu(s) called “Studio Setup,” “System Setup,” or “MIDI Setup.” In this menu, you should be able to set separate MIDI outputs to access the two MIDI ports on the MU100R. For example, MIDI OUT 1 should be set to “Yamaha CBX A Driver” (or “Windows MIDI, Output 1”). Similarly, MIDI OUT 2 should be set to “Yamaha CBX B Driver” (or “Windows MIDI, Output 2”). (The specific menu/parameter names may differ depending on your particular music software. For detailed instructions, refer to the owner’s manual or on-line help of the software.) Hint If you have a second multi-timbral tone generator (such as the MU50), you can connect it to the MIDI OUT terminal of the MU100R and have three independent MIDI ports (for 48-channel operation). The software settings above apply here as well: Set MIDI OUT 3 should be set to “Yamaha CBX C Driver” (or “Windows MIDI, Output 3”). (For more information, see page 159.) Once you’ve set up the MU100R in your system, check that the MU100R is properly receiving data. 22 Guided Tour Selecting and Playing the Performances Selecting and Playing the Performances As pointed out on page 43, the Performances of the MU100R let you play four Voices together over one MIDI channel. These specially programmed Performances (100 Preset and 100 Internal) take full advantage of the MU100R dynamic Voices and flexible editing functions — giving you exceptionally powerful and expressive sounds for live performance situations. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Call up the Performance mode. © Select and play Performances. Calling Up the Performance Play Mode and Playing the Performances Operation 1 Press the [MODE] button. 2 Select “PFM” (PERFORMANCE) in the display. Use the [SELECT -/>] buttons, [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. XG TG300B C/M PERFORM Indicates Performance mode. The Performance mode setting is also shown by the arrow at the bottom right of the display. NOTE For more information on the sound module modes, see page 6. Guided Tour 23 Selecting and Playing the Performances 3 Press the [PLAY] button to go to the Performance Play mode. You can press the [EXIT] button for this as well. “All” and keyboard player icon indicate All Part display of Performance Play mode. If the All Part display above (with the keyboard player icon) is not shown, press both [PART-/+] buttons simultaneously. 4 Select the desired bank of Performances — Preset or Internal. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Bank parameter, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons to select the desired bank, Preset (Pre) or Internal (Int). • Preset bank The upper body of the keyboard player icon is black, indicating the Preset bank. • Internal bank The upper body of the keyboard player icon is white, indicating the Internal bank. 24 Guided Tour Selecting and Playing the Performances 5 Select the desired Performance. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Program Number parameter, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to select the desired Performance number. Performance number 6 Play the connected MIDI keyboard. Make sure that your keyboard is transmitting over MIDI channel 1. (Refer to the owner’s manual of that instrument if necessary.) If you’ve carefully followed all instructions up to now, the “level meter” bars in the display should move — and you should be able to hear the sound of the MU100R as you play. The “level meter” bars indicate the “level” (velocity) of the incoming MIDI data. These numbers indicate the four Parts of the Performance. Go on to select other Performances in the same bank and play those as well. To try out Performances in the other bank, return to step #4 above. Guided Tour 25 Selecting and Playing Individual Voices Selecting and Playing Individual Voices The MU100R has a stunningly huge variety of Voices — a total of 1267. In this section, you’ll select and play Voices in the XG mode, which features 1074 different Voices. The MU100R also features a built-in VL tone generator that provides 256 Voices using the sophisticated Virtual Acoustic Synthesis system (page 63). In this section, you’ll learn how to: © © © © Call up the XG mode. Select Voice banks and Voices from the panel controls. Change the Play mode display to suit your preference. Select and play Voices from a MIDI keyboard. Calling Up the XG Mode Operation 1 Press the [MODE] button. 2 Select “XG” in the display. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. XG TG300B C/M PERFORM Indicates XG mode. The XG mode setting is also shown by the arrow at the bottom right of the display. 3 Press the [PLAY] button to go to the Play mode. You can press the [EXIT] button for this as well. 26 Guided Tour Selecting and Playing Individual Voices About the Modes — Multi and Performance The MU100R has two main operating modes: Multi and Performance. You used the Performance mode earlier when playing Performances — playing four Voices over one MIDI channel. The Multi mode is primarily used in sequencer and computer music applications, since it allows you to play all 32 Parts independently over different MIDI channels. Which mode the MU100R is set to depends on the selected Sound Module mode. The XG, TG300B and C/M settings are all Multi mode. When PFM is selected, the MU100R is in the Performance mode. Selecting Voice Banks and Voices From the Panel Operation 1 Select a Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Depending on the selected Part, one of the displays below will appear: • For Parts 1 – 16 and the A/D Parts: • For Parts 17 – 32: For this example, select Part 1. Press the appropriate button until “01” appears in the PART section of the display. Guided Tour 27 Selecting and Playing Individual Voices 2 Select the bank number. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the bank number parameter (as shown below). Instrument icon. Arrow at top left of icon indicates bank number is selected. Bank number. Dark arrow indicates bank number is selected. Program number. 3 Change the bank number. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Notice that the bank numbers “jump” as they are selected — the MU100R skips bank numbers that have the same Voice as bank “000.” In the XG mode, several banks of Voices are available. Each bank contains up to 128 different Voices, for a total of 1074 Voices. 4 Select the program (Voice) number. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program number parameter (as shown below). 28 Guided Tour Selecting and Playing Individual Voices Bank number. Instrument icon, indicating the type of Voice. Arrow at top right of icon indicates program number is selected. Program number. Dark arrow indicates program number is selected. 5 Change the program number. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. In the example display below, Voice number 25 has been selected. 6 Play the Voice. Play this new Voice from the connected MIDI keyboard. (Make sure that the keyboard is transmitting on channel 1.) If you’ve carefully followed all instructions up to now, the “level meter” of the Part should move — and you should be able to hear the sound of the MU100R as you play. Try selecting other Voice banks and Voices and play them as well. Each Voice bank contains some different Voices, some of which are variations, some unique. Details • The MU100R’s Voices and program numbers follow the GM (General MIDI) format. This means that you can select a Voice type by its number, then select Voice variations by bank. For example, all the nylon guitar Voices are at program number 25. • In the XG mode, the Voices are conveniently organized in the banks according to their type. For example, Voices having stereo variations or brighter variations are found in the “Stereo” and “Bright” banks, respectively. (See the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) • Banks MSB 48, 46 and above feature Voices that are not simply variations, but use different instrument samples. (See the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) Guided Tour 29 Selecting and Playing Individual Voices • Notice that as you increase the bank number, at some point beyond the XG Voice banks (above bank 127) the bank number returns to “000” and the following icon appears in the display: Banks showing this icon are MU100 Exclusive Voice banks, and are different than the same numbered XG Voice banks. (See the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) • VL Voice banks may also be selected if VL Voice selection for the Part has been enabled. (See page 69.) • Though the MU100R skips over bank numbers with identical Voices (see step #3 above), it can be set to not skip bank numbers, if desired. (See page 160: Utility mode/System/Display Bank Select.) Changing the Play Mode Display The MU100R lets you view the Parts in three ways, depending on your preference. Press the [PLAY] button repeatedly. Each press of the [PLAY] button switches among the three displays below. 1) Full level meters This shows the level meters at their maximum height, but only displays half of the Parts. 2) All Parts, with half level meters This displays all Parts, but the level meters are at half the height. 3) All Parts, with full level meters This displays all Parts with the level meters at maximum height. However, the Voice name and number are not displayed. 30 Guided Tour Selecting and Playing Individual Voices Selecting Voices From a MIDI Keyboard You can also select Voices remotely from a connected MIDI keyboard. Though the actual operation may differ depending on the keyboard used, the general procedure is the same. These instructions also apply to use with a computer. (Refer to the owner’s manual of your specific instrument or software for detailed instructions.) Operation 1 Make the necessary settings on the keyboard. Make sure that the keyboard is set to transmit over the desired MIDI channel (the same as that of the selected Part), and that it is set up to send Program Change messages. 2 Select a program number on the keyboard. The Voice number and name on the MU100R will change, and will be the same number as the program number you selected on your keyboard. Details • Depending on what keyboard you are using to control the MU100R, you may need to be careful in selecting program numbers. The MU100R’s program numbers start at “001,” but some keyboards have different numbering systems. For example, some start at “0” — which means that selecting “25” on the keyboard will select Voice 026 on the MU100R. • Part 10 is reserved for playing drum “kits.” This is the default factory setting for all of the Multi modes (XG, TG300B, and C/M). For more information on drum Parts, see page 39. Guided Tour 31 Editing in the Multi Mode Editing in the Multi Mode This section takes you step-by-step through an example editing session in the Multi mode. The operations and techniques you learn here enable you to perform any editing operation in the Multi mode. There are two separate sections of the Multi mode that are devoted to editing: the Single/All Part controls, and the Edit menus. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Select a Part for editing. © Use the Single Part controls — to change the MIDI channel of a Part, and change its Volume and Pan settings. © Use the Edit menu parameters — to change the filter and EG (Envelope Generator) settings of a Part. © Use the Drum Setup controls — to edit change the Part settings for a drum kit. Hints • Editing Parts, not Voices It is important to remember that in editing you are not changing the Voice itself, but rather the Part the Voice is assigned to. This means that when you change the Voice of the Part, the edited settings apply to the new voice, whether they’re appropriate or not. You can use this to your advantage by recording all Multi settings to your sequencer, before the actual song data. This lets you instantly reconfigure the MU100R and all its settings for each song. • Saving your edits Keep in mind that any edits you make in the Multi mode are automatically saved as the power on defaults. In other words, the next time you turn on the power, the previous condition of all Parts is automatically recalled. If you want to save one “set” of edits (for example, for use with a specific song) before creating another set, you must first save the current setup to a sequencer or MIDI data filer. (For details, see page 161.) 32 Guided Tour Editing in the Multi Mode Single Part Controls You can make changes to each individual Part by using the Single Part controls. These are displayed in the Multi Play mode, and give you at-a-glance confirmation and control of the important basic settings of the selected Part. If the Multi mode was active when you last turned the power off, the next time you turn the power on, the Single Part controls are automatically called up. Let’s take a look at the Play display again: Voice name, bank number and program number. PART MIDI BANK/PGM# VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY Note Shift (key transpose). Variation Send. Chorus Send. Reverb Send. Pan (stereo position). MIDI receive channel. Expression. Volume. Part number. (Change this with the [PART -/+] buttons.) Each of these settings are made independently for each Part. For example, each Part could have a different Volume setting, or a different Pan setting. Try going through the brief sections below and making some changes in the Part controls yourself. Guided Tour 33 Editing in the Multi Mode Changing the Volume and Pan settings of a Part Here, we’ll change the Volume and Pan settings of one Part’s Voice. Operation 1 Select the desired Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons to select Part 1. 2 Select the desired control. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Volume control. Current Volume setting. 3 Change the setting. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial, and play the keyboard as you edit so you can hear the change in the sound. Now, let’s change the Pan setting for the Part: 4 Select the desired control. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Pan control. Current Pan setting. 5 Change the setting. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to change the setting, and play the keyboard again as you make changes. 6 Return to “home base.” Pressing the [EXIT] button from any of the Single Part controls automatically returns to the Voice name/program number display. This is a convenient way to instantly return to “home base” from a “distant” control. 34 Guided Tour Editing in the Multi Mode On Your Own... If you want to, try making changes to some of the other Part controls. The procedure is the same: 1) 2) 3) 4) Select a Part with the [PART -/+] buttons. Select a control for editing with the [SELECT </>] buttons. Change the setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to “home base” — Voice name and number. Hint • You can easily edit the same control for different Parts. To do this, simply remain at the selected control and use the [PART -/+] buttons to change the Part to be edited. • Setting different Parts to the same MIDI channel is a way to build “fat,” richly textured sounds — like the four-Voice sounds created in the Performance mode. The advantage to this method here is that you are not limited to four Voices. The disadvantage is that you can only create and use one of these “monster” sounds at a time. (However, you can store/load your Multi mode settings to/from a computer or data filer; see page 17.) To do this: 1) Select the desired Part (by using the [PART -/+] buttons). 2) Select the Receive Channel (“Rcv CH”) control (by using the [SELECT </>] buttons). 3) Set the Receive Channel value (by using the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). 4) With the Receive Channel still selected, select a different Part (with the [PART /+] buttons), and set it to the same value as the other Part. 5) Repeat step #4 above for as many other Parts as desired. For example, if you’ve set both Parts 1 and 2 to MIDI channel 1, both of their “level meters” should move together as you play. And, if the two Parts are set to different Voices, you should hear two different Voices sound at the same time. (For instructions on changing the Voice for a Part, refer back to “Selecting and Playing Individual Voices” on page 26.) For more information on the specific Part controls, see page 96. All Part controls The instructions in this section show you how to change the settings for individual Parts; these are the Single Part controls. The All Part controls, on the other hand, let you change certain global settings affecting all the Parts. To select the All Part controls, simultaneously press both [PART -/+] buttons. (For more information on the All Part controls, see page 98.) Guided Tour 35 Editing in the Multi Mode Edit Menu Parameters The Edit menu parameters provide more detailed and advanced controls over the Parts. These are powerful tools that let you subtly enhance or fine-tune the sound of a Voice — or radically change its character for some wild and unique sounds. Changing the Filter and EG Settings of a Part Operation 1 Select the desired Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Also, for the sake of these instructions, select the “SquareLd” Voice, #081. (See page 27.) 2 Call up the Edit menu. Press the [EDIT] button. 3 Select “FILTER” in the display. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. The Edit menu has five items: FILTER, EG (Envelope Generator), EQ (Equalizer), VIBRATO, and OTHERS. The “flag” next to the item flashes when selected. Details • When a drum Part is selected, the EQ menu item is replaced by “DRUM.” (See page 114 for information on editing drum Parts.) • When a VL Voice Part is selected, the “PLUGIN” menu item also appears in the display. 4 Call up the Filter parameters. Press the [ENTER] button. 36 Guided Tour Editing in the Multi Mode 5 Select the “LPF Cutoff” parameter. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. Selected Part The bars graphically indicate paflashes. rameter values for each Part. Indicates additional parameters Indicates no other parameters are available (to the right). are available (to the left). 6 Adjust the value while listening to the sound. Hold down a note on the connected keyboard and turn the data dial to adjust the value, swinging between the maximum (+63) and minimum (-64) values. Notice how the timbre of the sound changes. Before going to the next step, set LPF Cutoff to “+63.” 7 Select “LPF Reso” and change the value. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. Then, do the same as you did in the last step, holding a note and changing the value with the data dial. Hint • Try holding notes or chords in different octaves of the keyboard as you adjust the parameters, since the Filter effects depend on the pitch or frequency of the sound. Details • The effect of the Filter parameters also differs depending on the selected Voice. (For more information on the Filter parameters, see page 100.) Now, let’s change one of the EG parameters: 8 Go back to the Edit menu. Press the [EXIT] button. 9 Select and call up “EG.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “EG,” then press the [ENTER] button. ; Select the “Attack Time” parameter. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. Guided Tour 37 Editing in the Multi Mode a Adjust the value while listening to the sound. Try setting this to around “+30” and play the keyboard. Notice how the attack of the sound has become slower. b Select and adjust the “Release Time” parameter. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then set this to around “+50.” Play some notes on the keyboard and release them. Notice how the sound sustains after you release each key. Details • The effect of the EG parameters differs depending on the selected Voice. (For more information on the EG parameters, see page 102.) On Your Own... While you’re at it, try making changes to some of the other Edit parameters. The procedure is the same: 1) Select the desired Part with the [PART -/+] buttons. 2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button. 3) Select the desired menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press [ENTER]. 4) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 5) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu. Hint You can select different Parts (by using the [PART -/+] buttons) at any point in the editing session, no matter which Edit menu or parameter is selected. This lets you quickly shuttle among the various parts and effectively edit the desired parameters. The selected Part is always indicated at the bottom left of the display. For more information on the specific Edit parameters, see page 100. 38 Guided Tour Editing in the Multi Mode Editing Drum Kits — with the Drum Setup Controls The Drum Setup controls provide a comprehensive set of tools for controlling and changing the drum kit Voices. Many of these parameters can be set individually for each sound in a Drum Part. Up to four of your original editing setups can be permanently stored. Unless you’ve set them otherwise, Parts 10 and 26 are automatically set to play a Drum Part and the MIDI channel for both is set to 10. (General MIDI song data is standardized for playing drum/percussion sounds over channel 10.) For the sake of these instructions, we’ll simply select Part 10 and edit the existing Drum Part. However, you can set up additional Drum Parts on any of the Part numbers; refer to the box section below. Remember that once a Part is assigned a Drum Part, different drum kit Voices can be selected. (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) Assigning a Drum Part This operation allows you to assign a Drum Part to any of the Part numbers — letting you use two or more different drum kits within the same song. 1. Select the desired Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons. 2. Call up the Edit menu. Press the [EDIT] button. 3. Select and call up the OTHERS menu. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER]. 4. Select the Part Mode parameter. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons. 5. Set the parameter to “drumS1.” Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. As long as you select one of the “drum sets” (drumS1 – drumS4), any edits you make will automatically be saved to the selected set. Details • The “normal” setting is for normal Voices; the “drum” setting selects the Drum Part, but cannot be edited. (For more information on the Part Mode, see page 108.) 6. Press the [EXIT] button. Press it once to return to the Edit menus, twice to return to the Play display. Guided Tour 39 Editing in the Multi Mode Making Changes to Individual Drum Sounds — the “Drum” Parameters The Drum parameters provide extraordinary flexibility, since they allow you to make independent settings for the individual drum/percussion sounds in a Drum Part. We’ll explore a couple of the possiblilities here: Operation 1 Select “DRUM” from the Edit menus (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and press [ENTER]. 2 Select “E3: Conga L.” Play E3 on the connected MIDI keyboard, or use the [PART -/ +] buttons to select “E3.” Details • In the Drum parameters you cannot use the [PART -/+] buttons to select a Part; they are reserved for selecting notes/sounds only. 3 Select the Pitch Coarse parameter, and set it to “-22.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. This setting creates a deep log drum sound. 4 Select the Velocity Pitch Sensitivity parameter (VelPchSens), and set it to “+12.” Again use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Play the key softly to strongly and notice how the pitch changes according to key velocity. 40 Guided Tour Editing in the Multi Mode 5 Select “F#3: Timbale L.” Play F#3 on the connected keyboard, or use the [PART -/+] buttons to select “F#3.” 6 Select the LPF Cutoff parameter, and set it to –40. 7 Select the LPF Resonance (LPF Reso) parameter, and set it to +63. 8 Select the Velocity LPF Sensitivity parameter (VelLPFSens), and set it to +16. Play the key softly to strongly and notice how key velocity changes the timbre of the sound for a “wah-wah” effect. More Drum Editing Try some of the other parameters in the edit menus (FILTER, EG, VIBRATO, OTHERS) on your own and hear how they affect the drum sounds. Keep in mind that these are applied to the entire Part, and cannot be set individually for each sound. As a springboard for further exploration, try editing the following parameters in the OTHERS menu: 1. With a drum Part selected, call up the OTHERS parameters. Press [EDIT], select “OTHERS,” then press [ENTER]. 2. Select “PitBndCtrl” and set the value to +24. Play with the pitch bend wheel on the connected keyboard while playing different keys. 3. Select “MW LFOPMod” and set the value to 090. Play with the modulation wheel on the connected keyboard while playing different keys. Select and change other parameters in the same way. NOTE Some of the parameters (such as Release Time in the EG menu) may not have any affect on the drum sounds at all. Also, the effect of a parameter may differ depending on the specific drum sound. (For more information on editing Drum Parts, see page 114.) Guided Tour 41 Editing in the Multi Mode On Your Own... 1) Select a Drum Part with the [PART -/+] buttons. 2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button. 3) Select the “DRUM” menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press [ENTER]. 4) Select the desired drum sound, either by playing the corresponding key of the MIDI keyboard or by using the [PART -/+] buttons. 5) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 6) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu. Hint Use of a connected MIDI keyboard is an exceptionally fast and convenient way to edit Drum Parts. It not only lets you quickly shuttle among the various sounds while editing, it also lets you hear the sound being edited and see the sound name. For more information on the specific Drum parameters, see page 114. 42 Guided Tour Editing in the Performance Mode Editing in the Performance Mode The Performance mode is an exceptionally powerful and flexible mode that allows you to combine four different Voices (including both A/D inputs) and play them from a single MIDI channel. The potential applications of the Performance mode are enormous, and we’ll touch on some of the main ones here. As the name suggests, the Performance mode is primarily intended for live performance situations. The four Voices can be played altogether in a huge, “fat” layer, or can be split across the keyboard in different zones, or can be switched according to key velocity. A total of 200 Performances are available: 100 Preset, which are reserved for only factory settings, and 100 Internal, to which you can save your own original Performances. This section takes you step-by-step through an example editing session in the Performance mode. The operations and techniques you learn here enable you to perform any editing operation in the Performance mode. As with the Multi mode, the Performance mode has two separate sections that are devoted to editing: the Single/All Part controls, and the Edit menus. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Use the All Part controls — to transpose the overall key of a Performance. © Use the Single Part controls — to select different Voices for the Performance. © Use the Edit menu parameters to create a “fat” two-Voice sound. © Use the Mute/Solo button for effective editing. © Set up a keyboard split — with individual Voices playable from different sections of the keyboard. © Set up a Performance for “playing” filter sweeps with the modulation wheel on your keyboard. © Save your original Performance. Guided Tour 43 Editing in the Performance Mode All Part Controls You can make changes to the overall Performance by using the All Part controls. These are displayed in the Performance Play mode, and give you at-aglance confirmation and control of some important basic settings of the selected Performance. In the Performance mode, the All Part controls are automatically called up whenever you turn the power on or select the Performance mode. Let’s take a look at the All Part Performance Play display: Performance name, bank (Preset or Internal), and program number. PART MIDI BANK/PGM# VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY System Transpose (key transpose setting for entire Performance). Variation Return. Chorus Return. Reverb Return. Performance Pan (stereo position of entire Performance). Expression (not available; always set to maximum). Performance Volume. System Channel (MIDI receive channel for entire Performance). Indicates All Part control. For more information on the All Part controls, see page 128. 44 Guided Tour Editing in the Performance Mode Transposing the Overall Key of a Performance In this example, you’ll change the System Transpose setting for the “Rich Piano” Performance. This All Part control is useful for instantly changing the key to match the range of a vocalist, or for ease in playing difficult keys. Operation 1 Select the “Rich Piano” Performance. First select the Preset bank (“Pre”), then select Performance number 002 (“Stereo Grand”). (For instructions on selecting Performances, see steps #4 and #5 on page 24.) 2 Select the System Transpose control. Use the [SELECT >] buttons to move the cursor arrow to the appropriate control. (“SysTran” appears in the display.) Current System transpose setting (in semitones). 3 Change the System Transpose setting as desired. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. (The “+00” setting is normal; ±“12” is up/down one octave.) Play the connected keyboard and try other transpose settings as you play. Guided Tour 45 Editing in the Performance Mode Single Part Controls — Selecting Different Voices for the Performance In this next section, you’ll use the Single Part controls to change the Voice settings of the Performance. Operation 1 Call up the Single Part controls. Simultaneously press both [PART -/+] buttons. Indicates active Part(s) of the Performance. PART MIDI Performance name, bank (Preset or Internal), and program number. BANK/PGM# VOL EXP PAN REV CHO VAR KEY Note Shift (key transpose setting for selected Part). Variation Send. Chorus Send. Reverb Send. Part Pan (stereo position of selected Part). Expression (not available; always set to maximum). Part Volume. (Not available in Single Part.) Selected Part number. (Change this with the [PART -/+] buttons.) For more information on the Single Part controls, see page 129. 2 Select the desired Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Keep in mind that you should select only from the active Parts — the ones with a dark bar in the display. Other Parts can be selected and changed; however, they will not sound in the Performance. 3 Select the desired bank and Voice. Do this in the same way as you did in the Multi mode. (See steps #2 and #3 on page 28.) 46 Guided Tour Editing in the Performance Mode Details • Drum Parts are not available in the Performance mode. However, percussive Voices (numbers 113 – 120) can be selected. When editing a Performance: • Decide how many Parts you want. When creating a Performance, choose a preset that uses the same number of Parts (Voices) you intend to use. (You can easily tell how many Parts a Performance has by looking at the “level meters”; a dark bar appears above the Part numbers that are active.) Two active Parts • Start with a similar sound. When editing, it’s a good idea to start with a sound that’s relatively similar to the one you intend to create. For example, if you want to create an soft, ethereal strings pad, you probably wouldn’t start with a brash preset such as “Dance Chord”! This is not a hard and fast rule, however, since each preset is only a basic “template” over which you can easily change Voices and create a completely different sound. On Your Own... If you want to, try making changes to some of the other Part controls. The procedure is the same: 1) Select a Part with the [PART -/+] buttons. 2) Select a control for editing with the [SELECT </>] buttons. 3) Change the setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons. 4) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to “home base.” (When editing in Single Part, pressing once returns to Voice name and number; pressing once again returns to All Part.) For more information on the specific Part controls, see page 96. Guided Tour 47 Editing in the Performance Mode Edit Menu Parameters — Creating a Two-Voice Layer Editing a Performance is almost identical to editing Parts in the Multi mode. The Edit menu tree is slightly different, and certain parameters are different as well. (For a full list and description of Performance Edit parameters, see page 131.) In the following instructions, you’ll use the Edit menu parameters to create a two-Voice Performance and “fatten” the sound using Detune. Operation 1 Select the desired Performance. For this example, select the Preset bank, then Performance number 027, “Jump-off.” 2 Select Part 1. Call up the Single Part controls (simultaneously press both [PART -/+] buttons), then select Part 1. 3 Solo the selected Part. Press the [MUTE/SOLO] button twice (or repeatedly until the display below appears) to solo the selected Part. Dark bar indicates Part 1 is being soloed. Using Mute/Solo for effective editing: The [MUTE/SOLO] button is a convenient tool, especially in editing Performances. Make sure that the Single Part controls are selected, then use the button to switch among the following three conditions. (In All Part, the [MUTE/ SOLO] button simply mutes/un-mutes all Parts.) Mute: Lets you hear what the other Parts of the Performance sound like, minus the selected Part. Solo: Lets you hear what the selected Part sounds like by itself. Normal: Lets you hear all Parts together. Use this function regularly as you edit the sound. While you’re editing, you should solo the Part, so you can clearly hear the changes. Make sure to frequently use Normal (all Parts on), so you can hear the total effect of your edits. For more on Mute/Solo, see page 85. 48 Guided Tour Editing in the Performance Mode 4 Select Part 1 and select a new Voice for it: “HeavySyn” (082). 5 Select Part 2 and select the “HeavySyn” Voice for it as well. 6 Select the “OTHERS” parameters. Press the [EDIT] button. From the first Edit menu, select and call up “PART,” then select and call up “OTHERS.” First Edit menu. Second Edit menu. 7 Select and set the Detune parameter for Part 2. Use the [SELECT <] buttons to select the parameter, then the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. With Part 2 selected, increase this to “+2.2.” 8 Set the Detune parameter for Part 1. Keep the display at the Detune parameter and select Part 1. Decrease this setting to “–2.2.” This produces a “fat” layered sound. You can check how much this changes the sound by exiting to the Single Part display and using [MUTE/SOLO] button to listen to the Parts by themselves and together. Now, try changing some other parameters. 9 Exit to the second Edit menu and call up the “VIBRATO” parameters. Press the [EXIT] button once, then select and call up the “VIBRATO” parameters. Guided Tour 49 Editing in the Performance Mode ; Change the Vibrato Rate, Depth, and Delay settings. Select one of the Parts and set the Vibrato parameters as follows: Rate: +15 Depth: +04 Delay: +15 This produces a delayed vibrato for Part 1; in other words, the vibrato effect starts after the keys have been held for a while. Notes played staccato have no vibrato. a Exit back to the Single Part control display. Press the [PLAY] button. Setting Up a Keyboard Split In the following steps, you’ll assign two different Parts to separate sections of the keyboard. Operation 1 Select Part 2 and select a new Voice for it: “NewAgePd” (089). From the Single Part display, use [PART -/+] buttons to select Part 2. Then select Voice 089 in the normal way. (Keep Part 1’s Voice set to “HeavySyn,” 082, as set in step #4 of “Creating a Two-Voice Layer” above.) 2 Change the Note Limit High setting for Part 1. The Note Limit parameters determines the range of notes over which the Part will sound. To set this: 1) In Edit menu select and call up the “PART” menu, then do the same with the “OTHERS” menu. 2) Select Part 1. 3) Select and change the “NoteLimitH” setting to “B2.” (Leave the “NoteLimitL” setting unchanged.) 3 Change the Note Limit Low setting for Part 2. 1) Select Part 2. 2) Select and change the “NoteLimitL” setting to “C3.” (Leave the “NoteLimitH” setting unchanged.) Playing notes below middle C on the keyboard plays the synth bass sound, while notes above middle C play the “New Age” pad. Hint • You may want to raise the octave setting of Part 1. To do this, exit to Single Part, select Part 1, then use the [SELECT >] buttons to select the Note Shift control. For a higher “HeavySyn” Voice, set this to “+00.”) 50 Guided Tour Editing in the Performance Mode If you wish to save this newly created Performance, refer to “Saving Your Original Performance” on page 52. On Your Own... While you’re at it, try making changes to some of the other Edit (part) parameters. The procedure is the same: 1) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button. 2) Select “PART” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER]. 3) Select the desired menu with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press [ENTER]. 4) Select the desired Part with the [PART -/+] buttons. 5) Select the desired parameter with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 6) Use the [EXIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu. Using the Assignable Controller in a Performance In this section, you’ll set up a Performance in which the modulation wheel on your connected keyboard can be used to “play” dynamic filter sweeps. This is done with the Assignable Controller functions. Here, we’ll simply show you what steps to follow; for more detailed information on the Assignable Controller and using it in the Multi mode, refer to page 59. Operation 1 Select the “Dark Pad” Performance (Preset #025). 2 Select and call up “COM” (Common) from the first Edit menu. 3 From the Common menu, select the “AC1 CC No.” parameter and set it to “01.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 4 Select the “AC1FilCtrl” parameter and set it to “+63.” 5 Select Part 1 and change some of its Filter settings. The Filter settings determine how the Part responds to the “AC1FilCtrl” setting above. To set these: 1) In Edit menu select and call up the “PART” menu, then do the same with the “FILTER” menu. Guided Tour 51 Editing in the Performance Mode 2) Select Part 1. 3) Select and change these parameters: LPF Cutoff: –64 LPF Reso: +50 Provided your connected keyboard has a modulation wheel (most do), and all other settings are appropriate, you can create wide, dynamic filter sweeps by holding notes and moving the modulation wheel. Saving Your Original Performance Once you’ve edited a Performance, you can give it a different name and save it for future recall. The MU100R has 100 Internal memory locations for your original Performances. For instructions on naming a newly created Performance, see page 132. Operation 1 Press the [EDIT] button. 2 Select “STORE.” Either Preset or Internal Performances can be edited, but they can only be saved to the Internal bank. 3 Select a different Internal number, if desired. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 4 Press the [ENTER] button to save the Performance, or press the [EXIT] button to cancel. Saving the new Performance will erase the old one. You can restore the factory-programmed Internal Performances from included floppy disk. 52 Guided Tour Assignable Controller (AC1) Assignable Controller (AC1) The Assignable Controller (AC1) is one of the more powerful features of the MU100R — it gives you extraordinarily flexible and expressive real-time control over the Voices. In this section, you’ll: © Learn about MIDI controllers and control numbers, and how they can affect the Voices. © Set up your system for using the Assignable Controller. © Try out some specific controller application examples, such as: * Varying degrees of brightness on a Part * Filter sweep and “wah” effects * “Expression pedal” control of volume * Variable filter control of specific drum sounds Hint A good way to introduce yourself to some of the Assignable Controller applications is to explore the Performances — many of them feature Assignable Controller settings that let you change some aspect of the sound (usually with the modulation wheel on the connected keyboard). (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet, and select/play Performances that mention “MW” in the “Description” section of the lists.) Controllers and Control Numbers In the MIDI world, “controllers” are used to change some aspect of the sound. In this section, we’ll work with “continuous” controllers — so named because they let you add musical, expressive effects that change smoothly over time (such as crescendos and decrescendos). The illustration below shows some continuous controllers you’re likely to see on a MIDI keyboard. Breath controller Data entry slider Foot controller Modulation wheel MIDI Keyboard Volume pedal NOTE Your own MIDI instrument may not have all the controllers shown in the illustration. Guided Tour 53 Assignable Controller (AC1) The actual, physical means of controlling (such as foot pedals, modulation wheels, etc. on a connected keyboard) are generally assigned to specific “virtual” control numbers. A few examples of these include the modulation wheel (at control number 1), foot controller (control number 4), and volume pedal (control number 7).* “Virtual” controller: control number 7 (MIDI Volume) MIDI OUT IN MIDI OUT DC IN POWER ON OFF CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST PITCH CONTROL CHANGE 1 MODULATION DEPTH 2 BREATH CONTROL 4 FOOT CONTROL 5 PORTAMENTO TIME 6 DATA ENTRY 7 MAIN VOLUME 8 BALANCE CONTROL 10 PANPOT ASSIGNABLE SEQUENCER SHIFT STOP CONTINUE START PROGRAM TEMPO BANK PROGRAM SELECT CHANGE 11 EXPRESSION 64 HOLD1(DAMPER) 65 PORTAMENTO 66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD) 67 SOFT PEDAL 69 HOLD2 (FREEZE) 71 HARMONIC CONTENT 72 RELEASE TIME RESET GM ON XG ON SOUND OFF 73 ATTACK TIME 74 BRIGHTNESS 84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL 91 REVERB DEPTH 92 TREMOLO DEPTH 93 CHORUS DEPTH 94 VARIATION DEPTH 95 PHASER DEPTH SYSTEM MERGE ON/OFF MIDI CH (RPN) 120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY 121 FINE TUNING 122 COARSE TUNING (NRPN) 123 VIBRATO RATE 124 VIBRATO DEPTH 125 VIBRATO DELAY WHEEL ASSIGN FIXED VELOCITY RPN CONTROLLER NRPN OTHERS 142 CHANNEL PRESSURE 143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE 144 MASTER VOLUME 145 MASTER BALANCE 146 MASTER TUNING 147 VELOCITY 148 TEMPO 134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE 135 DRUM PITCH COARSE 136 DRUM PITCH FINE 137 DRUM LEVEL 138 DRUM PAN 139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH 140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH 141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH 126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 127 FILTER RESONANCE 128 EG ATTACK TIME 129 EG DECAY TIME 130 EG RELEASE TIME 131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE 133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1 TRANSPOSE ENTER DRUM NUMBER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0 HEXA DECIMAL DECIMAL OCTAVE Physical controller (volume pedal) OCTAVE SHIFT OCTAVE RESET MIDI Keyboard * On some instruments, the control number for the physical controllers is fixed; some instruments allow you to assign a different control number to the existing control. (Refer to the owner’s manual of your instrument for details. Also for more on control numbers, see the list on page 126 of this manual, and the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) Control Numbers and the Actual Sound The control numbers described above are in turn assigned to some specific aspect of the sound on the connected tone generator (for example, to volume, pitch modulation, dry/wet balance of an effect, etc.). As you might expect, control number 7 (Volume) affects the volume of the connected tone generator. MIDI OUT IN MIDI OUT DC IN POWER ON MIDI IN OFF CONTROLLER NUMBER LIST PITCH CONTROL CHANGE 1 MODULATION DEPTH 2 BREATH CONTROL 4 FOOT CONTROL 5 PORTAMENTO TIME 6 DATA ENTRY 7 MAIN VOLUME 8 BALANCE CONTROL 10 PANPOT ASSIGNABLE 11 EXPRESSION 64 HOLD1(DAMPER) 65 PORTAMENTO 66 SOSTENUTO(CHORD HOLD) 67 SOFT PEDAL 69 HOLD2 (FREEZE) 71 HARMONIC CONTENT 72 RELEASE TIME 73 ATTACK TIME 74 BRIGHTNESS 84 PORTAMENTO CONTROL 91 REVERB DEPTH 92 TREMOLO DEPTH 93 CHORUS DEPTH 94 VARIATION DEPTH 95 PHASER DEPTH (RPN) 120 PITCH BEND SENSITIVITY 121 FINE TUNING 122 COARSE TUNING (NRPN) 123 VIBRATO RATE 124 VIBRATO DEPTH 125 VIBRATO DELAY OTHERS 142 CHANNEL PRESSURE 143 POLYPHONIC KEY PRESSURE 144 MASTER VOLUME 145 MASTER BALANCE 146 MASTER TUNING 147 VELOCITY 148 TEMPO 134 DRUM EG DECAY RATE 135 DRUM PITCH COARSE 136 DRUM PITCH FINE 137 DRUM LEVEL 138 DRUM PAN 139 DRUM REVERB DEPTH 140 DRUM CHORUS DEPTH 141 DRUM VARIATION DEPTH 126 FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 127 FILTER RESONANCE 128 EG ATTACK TIME 129 EG DECAY TIME 130 EG RELEASE TIME 131 DRUM FILTER CUTOFF FREQUENCY 132 DRUM FILTER RESONANCE 133 DRUM EG ATTACK RATE POWER MIDI KEYBOARD CBX-K1 ON/ SEQUENCER SHIFT STOP CONTINUE START PROGRAM TEMPO BANK PROGRAM SELECT CHANGE RESET GM ON SOUND OFF SYSTEM XG ON MERGE ON/OFF MIDI CH FIXED VELOCITY WHEEL ASSIGN RPN CONTROLLER NRPN TRANSPOSE DRUM NUMBER OFF ENTER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0 HEXA DECIMAL DECIMAL MU100R OCTAVE OCTAVE SHIFT OCTAVE RESET MIDI Keyboard In this example, the foot controller of a keyboard controls the volume on the MU100R. 54 Guided Tour Assignable Controller (AC1) Assigning the Assignable Controller The Assignable Controller on the MU100R lets you specify the control number to be used and determine which aspect or aspects of the sound will be affected. It also lets you set the degree to which the controller affects the sound. Physical Controllers Modulation wheel, Controllers Parameters Filter Control Amplitude (level) Control Variation Effect Control Insertion 1 Effect Control Insertion 2 Effect Control Foot controller, (In Performance mode:) Filter Control Amplitude Control LFO Filter Modulation Depth Breath controller, etc. The best way to understand all this is to go through some actual examples, so go on to the next section and set up your system: Guided Tour 55 Assignable Controller (AC1) Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up Operation 1 Set up the MIDI keyboard or instrument. Connect the foot controller to the appropriate jack, and make sure that the instrument is set to transmit over MIDI channel 1. (If your instrument doesn’t have a foot controller, use another controller as described in the next step.) PHONES L/MONO R DC IN POWER OUTPUT FOOT FOOT FOOT VOLUME CONTROLLER SWITCH TO HOST HOST SELECT IN OUT THRU MIDI ARPEGGIATOR TEMPO TYPE P BEND RANGE MULTI ATTACK RELEASE ASSIGN 1/DATA ARPEGGIO HOLD STORE UTILITY SHIFT + PART/LAYER/ OCTAVE 2 MW/FC PRESET + 1 PROGRAM FILTER SCENE PITCH CUTOFF RESONANCE YZ' 7 8 MNO PQR 4 5 DEF GHI 1 2 ABC USER PRESET USER ARPEGGIATOR LEVEL CUTOFF REV TYPE FMOD CHO TYPE FC CUTOFF NOTE EFECT VARI TYPE LIMIT LOW REL TIME AMOD PMOD FMOD DCY LEVEL REL TIME INIT LEVEL PAN REV SEND ATK TIME EFFECT CHO SEND ATK LEVEL VOLUME VEL FIX TRANS CH RCV CH LIMIT LOW LIMIT HIGH ATK TIME 9 DCY TIME DEPTH PERFORM NAME ASSIGN1 PARAM COMMON ASSIGN2 DATA PARAM LFO FEG 6 VARI VARI PARAM DATA PORTA SWITCH TIME VARI EF VEL OFFSET LIMIT HIGH DCY LEVEL DCY TIME PROGRAM AEG *& STU WAVE SPEED PHASE INIT PEG VARI SEND DCY REL TIME TIME FILTER CUTOFF REZ LAYER REL LEVEL POLY/ MONO JKL DEMO 3 SPACE 0 PERFORM SUB DIVIDE MW FMOD PMOD TUNE DETUNE ATK TIME BANK NOTE SFT VWX PERFORMANCE AMP EG VOLUME PERFORMANCE MULTI STORE UTILITY ENTER NO/ QUICK PC YES ASSIGN 2 MASTER TUNE SYSTEM VEL KBD CURVE TRANS MIDI DEVICE NO LOCAL BULK DUMP ASSIGN CTRL NO UTILITY MODULATION CS1X 2 Select the desired Part. From the Multi Play mode, use the [PART -/+] buttons. For the sake of these instructions, select Part 1. 3 Call up and set the Assignable Controller number. The control number of your instrument’s controller must match the Assignable Controller control number. In this example and all the following instructions in this section, we’ll use the foot controller. Since the foot controller is control number 4, the Assignable Controller must be set to “04.” To do this: 1) Press the [EDIT] button. 2) Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “OTHERS,” then press [ENTER]. 3) Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select “AC1 CC No.” 4) Set the value to “04” with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. If you don’t have a foot controller, you can use another controller, such as the modulation wheel (01) or volume pedal (07) — making sure that the Assignable Controller number matches. Keep in mind that this setting applies only to the selected Part. Other Parts can have separate control number settings. 56 Guided Tour Assignable Controller (AC1) Modulation Wheel The modulation wheel is the most common controller, and can be found on nearly every MIDI keyboard. It is usually used to produce LFO effects (regular wavering of the sound, like vibrato and tremolo). Since it is so common, the MU100R features various parameters that are reserved strictly for modulation wheel control. In the Multi mode, the modulation wheel can control Pitch LFO. The Performance mode features both Pitch LFO and Filter LFO. For more information on these parameters, see page 132. Using the Assignable Controller — Some Applications Changing the Brightness on a Piano Voice Though you can use the Equalizer (page 80) to adjust the brightness of a Part’s Voice, you may find it convenient to be able to change the character of the sound “on the fly,” as you play. This uses the AC1 Filter Control parameter. Try this with the Grand Piano Voice (001:GrandP #). Operation 1 Call up the Edit menu. From the Multi Play mode, press the [EDIT] button. 2 Select and call up “OTHERS.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER]. 3 Select “AC1FilCtrl” and set it to “+63.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Filter Control parameter, then set the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Playing the Part at the minimum pedal position results in mellow “lounge” piano sound; maximum position results in a bright “rock’n’roll” piano. Minimum position — mellow sound. Maximum position — bright sound. Guided Tour 57 Assignable Controller (AC1) 4 Try the setting on other Voices. Exit to the Multi Play mode display (press the [PLAY] button) and select other Voices, trying out the new setting, and moving the foot controller up and down as you play. Try out some of these Voices, and notice how the sound changes: SynBass2 (040), Saw Ld (082), Warm Pad (090) — for a “wah” filter sweep effect. SynVoice (055), NewAgePd (089) — for gradually fading in a breathy sound. For details on the AC1 Filter Control parameter, see page 112. Details • Keep in mind that the degree and character of the AC1 Filter Control depends also on the Filter parameter settings for the Part (see page 112). Some Voices may not change at all unless these parameters are set appropriately. However, all of the example Voices above should clearly change in response to AC1 (if the Filter parameters are all at their default setting of 00). Resetting the parameter values The simple operation below lets you instantly restore the factory preset values. Since it automatically cancels any edits you’ve made, you should use it with care. 1. Press the [MODE] button. 2. Select a different mode, then re-select the original one. For example, if you were editing in the XG mode, use the [SELECT </>] buttons to move the cursor to “TG300,” then back to “XG.” Doing this automatically resets all Part settings to the factory-programmed condition and cancels any edits you made in the Multi mode (including whatever Voices you selected). 58 Guided Tour Assignable Controller (AC1) Expressive Volume Control of a Part This example shows you how to use the foot controller as an expression pedal. This may come in handy when use of MIDI Volume (#7) or Expression (#11) is unavailable. Operation 1 Select the desired Part and Voice. Keep the settings you made to Part 1 (in the last example), and select a new Part/Voice for this example. From the Multi Play mode, select Part 2 with the [PART -/+] buttons. (This should be set to MIDI channel 2; set the MIDI channel on the connected keyboard accordingly.) A good Voice for this application would be PercOrg# (018); select this with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 2 Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part. Set this to “04.” (Refer to step #3 in “Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up” above.) 3 From the “OTHERS” parameters, select “AC1AmpCtrl” and set it to “+63.” Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the Amplitude (level) Control parameter, then set the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Now, play the organ sound and use the foot controller to play expressive volume swells. For details on the AC1 Amplitude Control parameter, see page 113. Expressive Control of Individual Drum Sounds In this example, the foot controller is used to produce expressive timbre changes and filter sweeps on selected drum sounds, using the Filter Control parameter. Operation 1 Select a Drum Part. Select Part 10 with the [PART -/+] buttons, and make sure that the connected keyboard is set to transmit over MIDI channel 10. 2 Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part. Set this to “04.” (Refer to step #3 in “Using the Assignable Controller — Setting Up” above.) Guided Tour 59 Assignable Controller (AC1) 3 Set the AC1 Filter Control to “+63.” Since you’ve called up the “OTHERS” parameters in the previous step, select “AC1FilCtrl” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and set it to “+63” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). 4 Select the “DRUM” parameters. Call up the Edit menu, then select “DRUM” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and press [ENTER]. 5 Select “A3: Cabasa.” Play A3 on the connected keyboard, or use the [PART -/+] buttons to select “A3.” 6 Set some of the filter parameters for the Cabasa sound. Select using [SELECT </>] button and set the two parameters below as indicated: LPF Cutoff: –40 LPF Reso: +60 Now, play the sound and move the foot controller as you play. Notice how this gives you dynamic, expressive control over the timbre of the selected sound — without affecting the other sounds of the drum kit. Hints • Since virtually all sequencers record controller data as well as note data, you can record these expressive sound changes into your song tracks — either while you record the notes themselves, or separately for a previously recorded track. • The negative values of the AC1 parameters let you control the sound by moving the controller in the opposite direction. For example, moving the foot controller to the minimum position produces the greatest change in the sound. An application of this might be to create a pedal-controlled crossfade between two Parts. To do this: 1) Set two Parts to the same MIDI channel. (See page 96.) 2) Set each Part to a different Voice. 3) Set the “AC1AmpCtrl” parameter for one Part to “–64,” and the same parameter for the other Part to “+64.” • The Assignable Controller can also be used to control one parameter of a selected effect. 60 Guided Tour Assignable Controller (AC1) On Your Own... While you’re at it, try making some of your own settings. The procedure is the same: 1) Select the desired Part and Voice. 2) Call up the Edit menus by pressing the [EDIT] button. 3) Select “OTHERS” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, then press [ENTER]. 4) Set the Assignable Controller number for the Part. 5) Select the appropriate parameters with the [SELECT </>] buttons. • If you are using the AC1 Filter Control, make sure to appropriately set other filter settings (in “FILTER” parameters, page 100, and/or “DRUM” parameters, page 114). • Select the AC1 parameters in the “OTHERS” parameters. (In the Performance mode, these are in the “COMMON” parameters; see page 133.) • If you are using a Drum Part, select the desired drum sound, either by playing the corresponding key or by using the [PART -/+] buttons. 6) Change the value, with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 7) Use the [EDIT] button as needed to return to the Edit menu. Guided Tour 61 Playing and Editing VL Voices Playing and Editing VL Voices The VL section of the MU100R is a tone generator incorporating Yamaha’s revolutionary “Virtual Acoustic Synthesis” tone generation system. Based on sophisticated computer physical modeling technology, Virtual Acoustic Synthesis produces sound that is more realistic, more expressive, and more musical than any other system to date. The VL section is a monophonic* tone generator, with its own set of separate controls, yet is completely integrated with the other Parts of the MU100R. VL Voices can be used only in the XG and Performance modes, and only one Part can be used to play a VL Voice at a time. For more details on VL Voices, see “About the VL Voice Section,” below. * A “monophonic” tone generator plays only one note at a time. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Learn about the VL. © Select VL Voice banks and VL Voices. © Edit VL Voices. About the VL Voice Section Main Features • Allows you to play back song data which has been programmed with the VL-XG Voice data. • Allows you to simulate the sound of acoustic musical instruments by editing the VL parameters directly from the MU100R (page 119). • Allows you to play VL Voices with a WX11 Wind MIDI Controller (via BT7) connected by MIDI to the MU100R. VL Voice Edit • Editing VL-XG Voices If you want to edit the existing MIDI files using VL Voices from the VL tone generator section, you’ll need to use an external sequencer which is capable of editing system exclusive messages and transmitting the parameter changes to the VL tone generator section. See MIDI Data Format for more information on system exclusive messages. 62 Guided Tour Playing and Editing VL Voices Virtual Acoustic Synthesis Unlike previous tone generation systems which use oscillators, function generators, preset waveforms or samples to produce sound, Yamaha Virtual Acoustic (“VA”) Synthesis applies sophisticated computer-based “physical modeling” technology to musical sound synthesis. In the same way that computer “models” are used to simulate weather systems or the flight characteristics of aircraft in the design stage, the VL tone generator section simulates the very complex vibrations, resonances, reflections and other acoustic phenomena that occur in a real wind or string instrument. VA Advantages The VL tone generator section offers many advantages in terms of musical performance. Not just in terms of sound, but also in terms of the “behavior” that makes acoustic instruments so … well, musical! Yamaha Virtual Acoustic Synthesis is simply the most musical tone generation system ever created. • The VL tone generator section sounds better, has more depth, and is more realistic in the musical sense than any other tone generation system. • Simply playing a note in the same way does not always produce precisely the same sound. The instrument is responsive and “alive”. • Note-to-note transitions have the same continuity exhibited by acoustic instruments. What goes on in between the notes is just as important musically as the notes themselves. • It has extraordinary expressive capability. Rather than simply controlling parameters like volume or pitch, you can control characteristics such as breath and reed pressure with appropriate complex effects on the timbre of the sound. VL Tone Generator Model The overall VL Tone Generator model or “algorithm” consists of three main blocks: the instrument, controllers, and modifiers. In schematic form these blocks are arranged as follows: Controllers (also envelopes) Instrument Modifiers Guided Tour Sound out 63 Playing and Editing VL Voices The Instrument The key block in this algorithm is the instrument, since it is here that the fundamental tone or “timbre” of the sound is defined. The instrument model consists primarily of a driver — the reed/mouthpiece, lip/mouthpiece, or bow/string system — and a resonant system corresponding to the tube and air column or string. In all these instruments pressure applied here (the driving point) causes vibration which results in sound. Reed vibration Lip vibration Air vibration String vibration One of the remarkable features of the Virtual Acoustic Synthesis system is that just about any driver can be used with any type of pipe or string. Drivers Pipes/String NOTES • The sound thus produced is amplified and sustained by the body of the instrument. • The pitch of the sound is determined by the length of the air column or string, and the timbre is a complex product of the driving source (reed, lip, air, string), the shape of the resonant cavity, the materials from which the instrument is made, etc. 64 Guided Tour Playing and Editing VL Voices The Controllers The input to an acoustic wind instrument comes from the player’s lungs, trachea, oral cavity, and lips. In a string instrument it comes from the player’s arm movement, transmitted to the string via a bow. These elements actually form an important part of the sound generating system and, in the VL tone generator section, are included in the controllers block. The player also influences the sound of the instrument by playing the keys, tone holes, or frets, and this aspect of control constitutes another part of the controllers block. These and other control parameters provided by the VL tone generator section are listed in the illustration below. In essence, the controller parameters determine how the instrument “plays”. All of these parameters can be assigned to any external controller that can be used with the VL tone generator section: breath controller, foot controller, modulation wheel, etc. The pressure parameter, for example, will normally be assigned to a breath controller so the player can control the dynamics of the instrument by varying the breath pressure applied to the controller — a natural, instinctive way to play wind-instrument Voices. At the same time the growl and throat parameters might also be assigned to the breath controller in order to achieve life-like response and effects. Embouchure The tightness of the lips against the reed or against each other, or the force of the bow against the string. Throat Controls the characteristics of the “player’s” throat or bowing arm. Pressure The amount of breath pressure applied to the reed or mouthpiece, or bow velocity applied to the string. Tonguing Simulates the half-tonguing technique used by saxophone players by changing the “slit” of the reed. Growl A periodic pressure (bow velocity) modulation which produces the “growl” effect often heard in wind instruments. Pitch Changes the length of the air column or string, and thereby the pitch of the sound. Scream Drives the entire system into chaotic oscillation, creating effects that can only be achieved with physical modelling technology. Damping & Absorption Simulate the effects of air friction in the pipe or on the string, and of highfrequency losses at the end of the pipe or string. Guided Tour 65 Playing and Editing VL Voices The Modifiers The modifiers block consists of 4 sections as shown in the diagram. Although these may appear to be simple effects, they are actually intimately related to the VL’s sound-producing model and have a significant effect on the sound. Harmonic Enhancer The Harmonic Enhancer determines the harmonic structure of the sound to the extent that it can produce radical timbral variations within an instrument “family” (e.g., saxophones). Dynamic Filter This section is similar to the dynamic filters found in many conventional synthesizers, with high-pass, bandpass, band elimination, and low-pass modes. Some filter parameters are available via the VL tone generator section controls. Harmonic Enhancer Dynamic Filter Frequency Equalizer Resonator Frequency Equalizer This is a 5-band parametric equalizer with frequency, Q (bandwidth), and level control. The equalizer also has pre-EQ high- and low-pass filters as well as key scaling capability for precise response control throughout the instrument’s range. Resonator The Resonator uses simulated “resonator” pipes or strings and delays to produce a “woody” resonance effect — although it has little or no effect on some Voices. The Resonator is employed as one of the preset Voice parameters. 66 Guided Tour Playing and Editing VL Voices Voice Organization The VL Voices have each program number and are organized into 13 banks. Refer to the Voice list in the “SoundList & MIDI Data” booklet. • Banks 112 through 119: VL-XG Banks (Bank Select MSB: 81 or 97) The Voices from the PRESET 1 and PRESET 2 banks are assigned to MIDI banks and program change numbers conforming to the Yamaha XG format. IMPORTANT Since the VL tone generator section does not have a full set of XG-compatible Voices, however, some Voice numbers will be skipped (e.g., 22, 23, 25, 27, etc.). If the truncated number is designated, no sound will be produced (when Bank Select MSB is 81) or the XG Voice in the bank 1 will sound instead (when Bank Select MSB is 97). • Bank 000: PRESET 1 The PRESET 1 bank contains 128 preset Voices which have been created primarily to be played via a keyboard. • Bank 001: PRESET 2 The PRESET 2 bank contains 128 preset Voices which have been created to provide maximum expressive capability when played with a breath controller or a WX-series Wind MIDI Controller. • Bank 002: CUSTOM The CUSTOM bank has 6 memory locations (program numbers 001 - 006) in which you can load the Voices created by the Yamaha VL70-m. The loaded Voices cannot be backed up. When the MU100R is turned on, the Voices are reset to their defaults, the sound-effect type Voices from the PRESET banks. • Bank 003: INTERNAL The internal Voices of the VL70-m can be received and loaded (bulk data). The Internal bank has 64 memory locations in which Voices you have edited can temporarily be stored. The loaded Voices cannot be backed up. When the MU100R is turned on, the Voices are reset to their defaults, the Voices from the Preset banks, set up to be played via a WX-series Wind MIDI Controller. IMPORTANT The edited Voices cannot be stored in the Internal Voice bank. If you want to keep your edited Voice, save it as a part of the song data using the sequencing software which is capable of editing and transmitting system exclusive messages. Guided Tour 67 Playing and Editing VL Voices NOTE • If you save the MU100R Performance mixed and layered with a VL Voice, the VL Voice number and its VL parameter setting edited on the MU100R panel will be stored. • Note that the “program numbers” here are 001~128 and the “MIDI program change numbers” are 000~127. When selecting Voices (programs) using an external MIDI device, subtract a value of “1” from the “program number” to match the “MIDI program change numbers.” Selecting Banks • Use the MIDI bank MSB (control number 00) and LSB (control number 32) numbers listed at right to select VL banks from an external MIDI device. BANK BANK 112 BANK 113 BANK 114 BANK 115 BANK 116 BANK 117 BANK 118 BANK 119 PRESET 1 PRESET 2 CUSTOM INTERNAL 68 MSB 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 97 or 81 33 33 33 33 Guided Tour LSB 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 0 1 2 3 Playing and Editing VL Voices Selecting VL Voice banks and VL Voices The VL Voices can be selected in the much the same way as the XG Voices. Selecting VL Voices from an External Device If you want to control the MU100R including the VL tone generator section by using sequencing software and/or use the tone generator without panel buttons (e.g., sound card), you’ll need to transmit the MIDI messages such as XG System On, Bank Select MSB/LSB and program change to the MU100R by using the sequencing software which is capable of editing and transmitting system exclusive messages. Refer to the MIDI Data Format in the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet. Operation 1 Make sure that the XG or Performance mode is selected. For information on selecting the Sound Module mode, see page 172. 2 Assign one of the Parts for playing VL Voices. Only one Part can be used for the VL Voices, and this must be properly assigned. To do this: 1) Press the [UTIL] button. 2) Select “PLUGIN” (with the [SELECT >] button) and press the [ENTER] button. 3) Select “PLG100-VL” (VL Voices) with the [SELECT <] button, and press [ENTER] again. 4) Select the Part Assign parameter (with the [SELECT <] button). 5) Set the desired Part number (01– 16 for XG, 01 – 04 for Performance) with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. Guided Tour 69 Playing and Editing VL Voices 3 Return to the Play mode, and select the approriate Part. Press the [PLAY] button, then use the [PART -/+] buttons to select the same Part as you assigned in step #2 above. 4 Select one of the VL bank numbers. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the bank number parameter, then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to select one of the VL Voice banks. (The VL Voice banks follow the “SFX” bank. For this example, select VL bank 000.) VL Voice icon. Bank number. Program number. 5 Select the desired Voice. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program number parameter, then use the[VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to select one of the VL Voices. 6 Play the Voice. Play this new Voice from the connected MIDI keyboard. Go on to select other VL Voices in this bank, and from other banks as well. For details on the available VL Voice banks, see page 68. 70 Guided Tour Playing and Editing VL Voices Editing a VL Voice This section shows you the basic steps in editing VL Voices. The VL parameters here are completely different from those of the normal Voices, the ones you edited on page 36. (For more information on the VL Edit parameters, see page 119.) Keep in mind that in editing the VL Voices, you are not changing the Voice itself, but rather the Part the Voice is assigned to. This means that when you select a different VL Voice for the Part, the edited settings apply to the new Voice, whether they’re appropriate or not. You can use this to your advantage by recording all VL Part settings to your sequencer, before the actual song data. This ensures that the VL Part will play exactly as intended for each song. Also remember that any edits you make to the VL Part are automatically saved as the power on defaults. In other words, the next time you turn on the power, the previous condition of the VL Part is automatically recalled. If you want to save one “set” of edits (for example, for use with a specific song) before creating another set, you must first save the current setup to a sequencer or MIDI data filer. (For details, see page 18.) NOTE The VL Edit parameters are not available for the normal Voices or Drum Voices. Operation 1 Select the VL Part. In order to edit the VL Voice, you must first select the Part to which the VL Voice has been assigned. Also make sure that a VL Voice has been selected for the Part. (See “Selecting VL Voice banks and VL Voices” above.) 2 Call up the Edit menu. Press the [EDIT] button. 3 Call up the VL Edit menu. Use the [SELECT >] button to select “PLUGIN” in the display, then press [ENTER]. Guided Tour 71 Playing and Editing VL Voices 4 Select the desired parameter. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter for editing. For complete descriptions and details of all VL Edit parameters, see page 119. 5 Change the parameter value or setting. Use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to change the value or setting. 6 Return to the Play mode after finishing editing. Press the [PLAY] button to return to the Play mode. NOTE There are additional VL-related parameters in the Utility mode. For more information on these parameters, refer to page 169. To call up these parameters: 1. Press the [UTIL] button. 2. Use the [SELECT >] button to select “PLUGIN,” then press [ENTER]. 3. If it isn’t already selected, select “PLG100-VL” with the [SELECT <] button, then press [ENTER]. 4. Select and edit the parameters in the normal way, using the [SELECT </>] buttons, then the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 72 Guided Tour Effects Effects To complement the huge variety of Voices and the 32-Part multi-timbral capacity, the MU100R features a built-in multi-effect processor with seven independent digital effects: Reverb, Chorus, Variation, Insertion 1 and 2, Harmony, and EQ. (In this section, we’ll examine the first five; Harmony and EQ are covered on pages 77 and 80, respectively.) These high-quality effects provide an enormous amount of sound processing power and flexibility. Combine these with the Part controls in the Multi mode, and you have a “virtual” 34-channel mixer at your disposal, with per-channel EQ, master EQ, and six effect sends — complete with six independent effect units! The following instructions assume that the XG mode is selected (page 26). However, using effects in the Performance mode and the other modes is done in virtually the same way. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Set the Reverb Type and adjust the amount applied to a Part. © Set the Chorus Type and adjust the amount applied to a Part. © Use the Variation effects to apply distortion to a Part. Using Reverb and Chorus Judicious use of Reverb creates a sense of space and enhances the realism of the Voices. The selected Reverb Type is applied to all Parts; however, the amount of Reverb for each Part can be adjusted. This lets you add special textures to the mix of a song, such as “drenching” one Part in Reverb while another Part is kept “dry.” The Chorus effect section features a variety of pitch modulation effects. These let you subtly enhance or “fatten” the sound, or completely transform the sound in wild and unique ways. As with Reverb, only one Chorus Type can be used for all Parts; however, the amount of Chorus for each Part can be adjusted. Guided Tour 73 Effects Operation 1 First, set the Send and Return controls to appropriate levels. Before you actually change the Reverb or Chorus settings, you should set the Send and Return controls, in order to properly hear the effect and the changes you make. To do this: 1) Select the desired Part from the Multi Play mode Single Part display. (Use the [PART -/+] buttons.) 2) Select “RevSend” (Reverb Send) or “ChoSend” (Chorus Send) with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and set it to “40” or higher. 3) Select the All Part display (by pressing both [PART -/+] buttons). 4) Select “RevRtn” (Reverb Return) or “ChoRth” (Chorus Return) with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and set it to “60” or higher. 2 Call up the Effect Edit mode. Press the [EFFECT] button. 3 Select and call up the desired effet section. Select “REV” (Reverb) or “CHO” (Chorus) with the [SELECT </ >] buttons. 4 Select and change the Type parameter. Use the [SELECT <] button to select “Type,” then change the setting with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 5 Edit other parameters as desired. Once you’ve selected a Reverb or Chorus Type, you can adjust the other parameters. For Reverb, try changing the Reverb Time and HPF Cutoff and listen to how the changes affect the Reverb sound. For Chorus, the parameters differ depending on the selected Chorus Type. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then adjust the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. For a list of Reverb Types and other information on Reverb, see page 142. For a list of the available parameters for each Reverb Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet. For a list of Chorus Types and other information on Chorus, see page 143. For a list of the available parameters for each Chorus Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet. 74 Guided Tour Effects Applying Distortion to a Part — Using the Variation Effects The Variation effect section provides a wealth of additional effects. With a total of 70 different Types, it features some of the same effects found in the Reverb, Chorus and Insertion sections. This is not mere redundancy; it allows you to use two Types of Reverb or Chorus on different Voices. For example, you may want to have a Symphonic effect on one Voice and Phaser on another. Variation also gives you many special effects not found in the Reverb and Chorus sections, such as Delay, Gate Reverb, Wah and Pitch Change. The Variation effect can be applied either to all Parts (as with Reverb and Chorus), or to a single selected Part (as described below). Operation 1 Set Variation Connection to “INS” (Insertion). To use Variation with a single Part, the Variation Connection parameter should be set to Insertion. To do this: 1) Press the [EFFECT] button. 2) Select “VAR” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and press [ENTER]. 3) Select “VarConnect” (with the [SELECT >] button), and change the setting to “INS” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). 2 Select the desired Part and set its Variation Send control to “on.” To do this: 1) Return to the Multi Play mode Single Part display (press the [PLAY] button), then select the desired Part (with the [PART -/+] buttons). 2) Select “VarSend” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons), and set it to “on” (with the [VALUE-/+] buttons or data dial). 3 Return to the Variation parameters, select the Distortion Type, and make other necessary settings. To do this: 1) Press the [EFFECT] button. 2) Select “VAR” (with the [SELECT -/+] buttons) and press [ENTER]. 3) Select “Type” (with the [SELECT <] button), and change the setting to “DISTORTION” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). Guided Tour 75 Effects 4) If you cannot hear the Distortion effect clearly, select the “Dry/Wet” parameter (with the [SELECT </>] buttons) and adjust it (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial) until the sound is appropriate. 5) Using the same method (as in step #4), select and adjust other important Distortion parameters as needed, such as “Drive” and “OutputLvl” (Output Level). Now, play the Part and hear how Distortion affects the sound. Select other Types and play with them as well. The Variation parameters differ depending on the selected Variation Type. For a list of Variation Types and other information on Variation, see page 144. For a list of the available parameters for each Variation Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet. Details • When Variation is set for use with a single Part (Insertion), only Variation Send is available. (The Dry/Wet parameter in Variation Edit effectively performs the same function as Variation Return in this case; see page 145.) Also, Variation Send can be set to “on” for only one Part. • When Variation is set for use with all Parts (System), both Variation Send and Return must be set to appropriate values. (The operation is the same as step #1 in “Using Reverb” and “Using Chorus” above.) For more information, refer to “About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion” on page 152. Insertion 1 and 2 Effect Sections The Insertion 1 and 2 sections provide additional signal processing power. Each of the Insertion sections can be applied to a single selected Part, and each features 43 effect Types. For a list of Insertion Types and other information on Insertion, see page 146. For a list of the available parameters for each Insertion Type, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet. 76 Guided Tour Harmony Effect Harmony Effect This sophisticated effect takes the sound of your voice (via a microphone and one of the A/D inputs) and reproduces it as a harmony vocal, providing up to four-part harmonies (including your original voice). You can pre-program the pitch interval of the harmony, or you can “play” the harmony from your connected MIDI keyboard (or sequencer), and even have the harmony interval change, depending on the chord you play. As long as your own voice is in pitch and you play the appropriate chords, the MU100R ensures that the harmony “voices” will be enharmonically correct and stay in pitch with the chord changes of the song. Though the Harmony effect can be applied to any Part, it is designed primarily to be used with vocal input. It also includes a “gender changer” effect that turns a male voice into a female voice (or vice versa), and a vibrato effect that automatically adds a warm, natural vibrato to your voice. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Set up your system and the MU100R for the Harmony effect. © Select a Harmony Type and Mode. © “Play” vocal harmonies from a connected MIDI keyboard, to match the melody you sing. Using the Harmony Effect Operation 1 Set up the MIDI keyboard. Connect a MIDI keyboard (as described on page 17) and set the MIDI transmit channel to 1. Hint • Alternately, you could set up a sequencer in this step and use the sequencer’s song data to control the Harmony effect and determine specific harmony notes. In this way, when you play back the song and sing along with it, all the appropriate backing harmonies will be produced automatically. 2 Connect a microphone to the MU100R and set up the A/D Part. Connect a microphone to the A/D INPUT 1 jack, select Part “A1,” then select the “Mic” preset (bank #000, program #002). (Refer to the section “Using the A/D Inputs” on page 87, for detailed instructions.) Guided Tour 77 Harmony Effect 3 Call up the Harmony System menu (in the Utility mode). To do this: 1) Press the [UTIL] button. 2) Select “PLUGIN” with the [SELECT </>] buttons, and press the [ENTER] button. 3) Select “PLG100-VH” (Harmony) with the [SELECT >] button, and press the [ENTER] button. 4 Set the Harmony Channel to 1. Use the [SELECT <] button to select “Harmony Ch” (Harmony Channel), then set the parameter to “01” to match it with the transmit channel of the connected MIDI keyboard. 5 Call up the Harmony Edit menu. To do this: 1) Press the [EFFECT] button. 2) Select “PLG” (with the [SELECT >] button) and press the [ENTER] button. 3) At the “PLG100-VH” (Harmony) menu, press [ENTER] again. 6 Set the Harmony Insert Part to the corresponding A/D Part. Use the [SELECT >] button to select “Ins Part” (Insert Part), then set the parameter to “AD01”. 78 Guided Tour Harmony Effect 7 Set the Harmony Type to Chordal. Select “Type” (with the [SELECT <] button), then set the parameter to “CHORDAL HM” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). When set to Chordal, chords you play on the connected MIDI keyboard determine the notes of the Harmony effect. (For more information on Chordal and the other Types, see page 147.) 8 Set the Harmony Mode to “trio above”. Select “Mode” (with the [SELECT </>] buttons), then set the parameter to “trio above” (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). 9 Sing into the microphone and play chords on the MIDI keyboard. The Harmony function recognizes thirty-four different chord types. Chords can be played at any register on the keyboard and result in the same harmonies. Experiment with different chord types (major, minor, seventh, etc.) and hear how the harmonies change — even while holding the same pitch with your voice. Hints • Keep in mind that you don’t need to hold the chord down — simply play it once at the point you want the harmony to change, then release it and continue singing until the next chord change. • If another Part is set to MIDI channel 1, you’ll hear its Voice playing the chord. To keep this Voice from sounding, use the [MUTE/SOLO] button to mute the part, or turn its Volume setting down. On Your Own... Here is a summary of the steps you should follow when using the Harmony effect: 1) Set up one of the A/D input Parts, and select one of the presets. Do this if you want to apply Harmony to an external source (such as a microphone or guitar). (See page 87.) 2) Set the Harmony Channel to match the transmit channel of a connected MIDI keyboard. Do this if you want to control the Harmony effect via MIDI. Path: UTILITY g “PLUGIN” g “PLG100-VH” g “Harmony Ch” 3) Set the Insert Part to the corresponding Part. For the A/D inputs, this would be set to “AD01” or “AD02.” Path: EFFECT g “PLG” g “PLG100-VH”g “Ins Part” 4) Make other appropriate settings in the “PLG100-VH” menu (called up in step #3 above). Most important of these are Harmony Type, Harmony Mode, and Lead/Harmony Balance. (See page 147.) Guided Tour 79 Equalizer (EQ) Equalizer (EQ) The MU100R features an extensive set of equalization controls that give you comprehensive control over the tone quality — both of individual Parts and over the entire instrument sound. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Use the Part EQ edit parameters to adjust the tone of a specific Part. © Use the main EQ to adjust the overall tone of the MU100R. Adjusting the Tone of a Specific Part — Part EQ The Part EQ parameters give you two-band (low and high frequencies) control over the sound of individual Parts. These can be used in both the Multi mode and the Performance mode. NOTE When a Drum Part is selected, the EQ menu is not available. However, the same EQ parameters can be adjusted for each individual drum sound in the “DRUM” menu. (See page 117.) Operation 1 Select the desired Part. From the Multi mode Single Part display, use the [PART -/+] buttons to select the desired Part (excepting Drum Parts). 2 Call up the EQ parameters. Press the [EDIT] button, then select “EQ” (with the [SELECT </ >] buttons) and press the [ENTER] button. 3 Select the general frequency range — low or high. In this example, we’ll boost the bass of the Part, so select “Low Freq” (Low Frequency) with the [SELECT </>] buttons. 80 Guided Tour Equalizer (EQ) 4 Set the specific frequency to be adjusted. For this example, set the Low Frequency value to “315” (Hz). 5 Select the Low Gain parameter and adjust the value. For this example, set the Low Gain value to “+35.” Play the Voice (especially in the lower octaves) and hear how the sound has changed. NOTE Depending on the Voice selected for the Part (and depending in which octave you play the Voice), you may or may not hear very much change in the sound at certain frequencies. If you want, try adjusting the High Frequency/Gain parameters as well. EQ in the Performance Mode The EQ settings of individual Parts in the Performance mode can be adjusted in the same way: 1) Select a Part (in the Single Part controls). 2) Press the [EDIT] button. 3) Select “PART”, then press the [ENTER] button. 4) Select “EQ”, then press the [ENTER] button, and edit the parameters as shown in steps #3 – #5 above. Guided Tour 81 Equalizer (EQ) Adjusting the Overall Tone — Main EQ The main EQ section gives you five-band control (at specific frequencies) over the entire sound of the MU100R. Special presets are also available for instantly changing the tone to suit different types of music. Operation 1 Call up the “EQ TYPE” parameter and select the desired EQ preset. First press the [EQ] button, then use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter. Then use the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial to select the desired preset. 2 If desired, change the values of the five different bands. Use the [SELECT </>] buttons to select the parameter, then change the value with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. 1) The graphic EQ display shows the EQ curve. 2) The EQ icon’s sliders indicate current settings and move as the value is adjusted. The changes you make to a selected EQ preset are maintained even when the power is turned off. However, selecting another preset automatically cancels your original settings. For more information on the Equalizer effects, see page 155. Also, refer to the Multi Mode Equalizer Lock parameter (page 158). 82 Guided Tour Individual Outputs Individual Outputs This convenient feature allows you to send the output of a selected Part or Parts to the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. For Drum Parts, you can even select specific drum sounds to be output through these jacks. In general, the extensive built-in effects and other Part controls of the MU100R provide all you need for processing and mixing complex multiPart songs. However, there may be times (in studio recording, for instance) when you want to “sweeten” or process a certain Voice or sound with a favorite outboard effect unit, or record a Part to a separate track of a tape recorder. The individual outputs are designed just for these kinds of applications. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Set up the MU100R so that two Parts are independently routed to the two INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. Using the Individual Outputs Operation 1 Make the necessary audio connections. In the example illustration below, the INDIV. OUTPUT 1 jack is connected to the input of an effect unit. The output of the effect unit is then connected to a channel on a mixing console, along with the main OUTPUT jacks of the MU100R. Effect unit (1) Out (2) In MU100R (4) OUTPUT L and R (3) INDIV. OUTPUT Mixing Console In a variation of this, INDIV. OUTPUT 1 could be connected directly to a separate input channel on the mixing console, then processed with an outboard effect using the send/return connections on the mixer. Hint If you don’t have an external mixer yet want to use the individual output and an external effect to process a Part, you can do so and return the output from the effect device back into the MU100R via one of the A/D inputs. (For information on using the A/D inputs, see page 87.) Guided Tour 83 Individual Outputs 2 Select the desired Part. From the Multi mode Single Part display, use the [PART -/+] buttons to select the desired Part for using with the individual output. 3 Set the Output Select parameter to the desired setting. Here, we’ll set the selected Part to output from the INDIV. OUTPUT 1 jack. To do this: 1) Press the [EDIT] button. 2) Select “OTHERS” with the [SELECT >] button, and press the [ENTER] button. 3) Select “OutPtSel” (Output Select) with the [SELECT >] button. 4) Set the parameter to “ind1” with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial. The selected Part will now be output only through the INDIV. OUTPUT 1 jack. (Output through the main OUTPUT jacks and PHONES jack is cancelled.) To select another Part for individual output, repeat steps #2 and #3 above. You can set additional Parts to be output through the same jack, or select “ind2” to output a Part or Parts through INDIV. OUTPUT 2. For more information on the individual outputs, refer to the Output Select parameter (page 113) and the Output Select Lock parameter (page 158). Routing Drum Sounds to the Individual Outputs Individual drum sounds can also be routed to the individual outputs. To do this: 1) Select a Drum Part. 2) Press the [EDIT] button. 3) Select “DRUM,” and press the [ENTER] button. 4) Select the desired drum sound (either from the connected MIDI keyboard or with the [PART -/+] buttons). 5) Call up the Output Select parameter (with the [SELECT >] button) and make the desired setting (with the [VALUE -/+] buttons or data dial). For more information on using Drum Parts with the individual outputs, refer to the Output Select parameter (page 118). 84 Guided Tour Mute/Solo Mute/Solo The MU100R has convenient Mute and Solo functions for selectively muting or soloing any of the 32 normal Parts and the A1 and A2 A/D Parts. This is especially useful when playing back several Parts from a connected computer or sequencer. Mute lets you silence one Part to hear how all of the other Parts sound without it. Solo lets you isolate a single Part, to hear how that Part sounds by itself. In the Performance mode, Mute and Solo are especially effective tools that help you as you edit the Parts, since they allow you to better hear how the changes you make affect specific Voices as well as the overall sound of the Performance. Using Mute/Solo Operation 1 Select the desired Part. Make sure the Single Part mode is active (see page 108), then use the [PART -/+] buttons to select the Part. Selected Part number. 2 Press the [MUTE/SOLO] button. While playing the keyboard (or during playback of a song from a sequencer), press the [MUTE] button. Each press cycles through the three functions: Mute, Solo and Normal operation. The selected Part is muted, while all other Parts sound normally. Guided Tour 85 Mute/Solo The selected Part is soloed, while all other Parts are muted. All Parts sound normally. 86 Guided Tour A/D Inputs A/D Inputs The MU100R features a special A/D (Analog-to-Digital) input function that allows you to connect up to two different external signals (microphone, electric guitar, CD player, etc.), mix those signals with the MU100R’s Voices. A/ D input is perfect for singing along with your keyboard performance, since it allows you to blend the two signals without the need for an external mixer. Or you can use it to sing or play guitar over backing tracks played from a MIDI sequencer. There are two A/D Parts (A1 and A2) and they can be manipulated in much the same way as the other parts — for example, they can have independent Volume, Pan, and effect send settings. What’s more, you can control certain parameters automatically via a connected MIDI sequencer. (See page 17.) The two A/D Parts include several specially programmed presets, complete with proper gain settings and suitable effects — using the built-in effects of the MU100R. In this section, you’ll learn how to: © Set up the MU100R for using the A/D inputs. © Call up the A/D input presets. Using the A/D Inputs Operation 1 Turn down the A/D INPUT VOLUME control on the front panel. CAUTION! Before connecting an external input, always turn the VOLUME control down. 2 Connect the microphone or instrument to one of the A/D INPUT jacks. For this example, connect to the A/D INPUT 1 jack. (Depending on the equipment being used, appropriate conversion adaptors may be necessary; the A/D INPUT jacks accept 1/4” phone plugs.) Guided Tour 87 A/D Inputs 3 Select the corresponding Part. Use the [PART -/+] buttons. Since you connected to the A/D INPUT 1 jack above, select Part A1 in this step. 4 Select the appropriate bank of presets. Do this in the normal way, using the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the bank number parameter, then using the [VALUE /+] buttons to change the bank. The selected bank determines the type of input and sets the appropriate gain level. Each bank/type is indicated by an icon in the LCD: Bank 000 For input of a microphone (or other mic level instruments). 88 Guided Tour A/D Inputs Bank 001 For input of an electric or electric/acoustic guitar (or other mic level instruments). Bank 002 For input of a keyboard (or other line level instruments, such as tone generators, rhythm machines, etc.). Bank 003 For input of audio equipment (such as CD players, cassette decks, etc.). Bank 018 For input of a stereo keyboard (or other stereo signals from line level instruments, such as tone generators, rhythm machines, etc.). Guided Tour 89 A/D Inputs Bank 019 For input of stereo audio equipment (such as CD players, cassette decks, etc.). CAUTION! Do not use line level signals (such as from keyboards, etc.) with the mic level banks. The signal may be too high, resulting in damage to the MU100R. 5 Select the desired preset. Do this in the normal way (as you selected Voices), using the [SELECT </>] buttons to highlight the program number parameter, then using the [VALUE -/+] buttons to select the preset. The available presets have been specially programmed to suit the type of input selected. For example, presets for Mic input include Karaoke and Vocal; Guitar input presets include Tube, Stack and Phaser. Explore some of these settings on your own with a microphone and different instruments. (For a list of all available A/D input presets, refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) 6 Turn up the level. If the connected source has a volume control, first set it to an appropriate level, then slowly bring up the A/D INPUT VOLUME control on the MU100R while playing the instrument (or singing into the microphone), until the level is appropriate. 90 Guided Tour Data Flow Block Diagram Data Flow Block Diagram When HOST SELECT switch is set to MIDI (31,250 bps): TO HOST IN-B IN-A OUT THRU Sound Module B1~16CH Sound Module A1~16CH When HOST SELECT switch is set to PC-1/MAC (31,250 bps) or PC-2 (38,400 bps): TO HOST IN-B IN-A OUT THRU Sound Module B1~16CH Sound Module A1~16CH Guided Tour 91 MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables MIDI/Computer Connecting Cables MIDI Standard MIDI cable. Maximum length 15 meters. DIN 5-PIN 4 2 (GND) 5 4 2 5 DIN 5-PIN Mac Apple Macintosh Peripheral cable (M0197). Maximum length 2 meters. MINI DIN 8-PIN 2 (HSK i) 1 (HSK o) 5 (RxD –) 4 (GND) 3 (TxD –) 8 (RxD +) 7 (GP i) 6 (TxD +) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MINI DIN 8-PIN PC-1 8-pin MINI DIN to D-SUB 25-pin cable. If your PC-1 type computer has a 9-pin serial port, use the PC-2 type cable. Maximum length 1.8 meters. MINI DIN 8-PIN 5 (CTS) 4 (RTS) 3 (RxD) 7 (GND) 1 2 3 4 8 5 D-SUB 25-PIN 2 (TxD) PC-2 8-pin MINI DIN to D-SUB 9-pin cable. Maximum length 1.8 meters. MINI DIN 8-PIN 8 (CTS) 7 (RTS) 2 (RxD) 5 (GND) 1 2 3 4 8 5 D-SUB 9-PIN 3 (TxD) This concludes your basic tour of the important functions of the MU100R. To find out more about how to best use your MU100R, look through the Reference section that follows and try out some of the functions and operations that interest you. 92 Guided Tour R EFERENCE The Reference section of this manual covers in detail all of the functions of the MU100R. Refer to it when you need information about a specific function, feature or operation. Part Controls Multi Mode In the Multi mode, the MU100R performs as a multi-timbral tone generator capable of playing up to 32 Parts simultaneously, over 32 MIDI channels. Normally, the MU100R should be set to Multi mode when using it with a sequencer and General MIDI song data. There are three Multi modes: XG, TG300B and C/M. (For information on selecting these, see pages 6 and 172.) Part Controls ................................................................................ 95 Single Part Control ................................................................ 96 All Part Control ..................................................................... 98 Multi Edit Mode .......................................................................... 100 Filter (FIL) ........................................................................... 100 Envelope Generator (EG) .................................................... 102 Equalizer (EQ)..................................................................... 105 Vibrato ............................................................................... 106 Others ................................................................................ 107 Drum Setup Controls ...........................................................114 VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin) ........................................119 Part Controls The Part controls in the Play mode give you tools for adjusting the basic sound and settings for each Part. The MU100R lets you adjust the various settings for each Part individually (Single Part control) or together (All Part control). Each of these types is explained in greater detail below. NOTE In the Multi mode, no settings can be permanently saved to the internal memory of the MU100R. However, you can use the Dump Out function to save Multi settings to a MIDI data storage device. (See page 18.) Multi Mode 95 Part Controls Single Part Control The Single Part controls include: MIDI Receive Channel, Bank Number, Program Number, Volume, Expression, Pan, Reverb Send, Chorus Send, Variation Send and Note Shift. For basic information on using the Single Part control, see page 33. MIDI Receive Port/Channel Settings: A1 — A16, B1 — B16, OFF This determines the bank number of the selected Part’s Voice. (Refer to the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) This determines the MIDI IN port (A or B) and the receive channel (1 — 16) for the selected Part. For more information on selecting banks, see page 28 and Display Bank Select parameter, page 160. Bank Number Settings: A1 (A/D Input part): 000 — 003, 018, 019 A2 (A/D Input part): 000 — 003 Normal part: XG: 000, 001, 003, 006, 008, 012, 014, 016 — 022, 024 — 029, 032 — 043, 045, 048, 052 — 054, 064 — 088, 096 — 101, 126, 127 [icon-MU100] 000, 008, 016, 024, 048, 056, 064, 072, 080, 088, 096, 104, 120 [icon-SFX] SFX [icon-VL] 000 — 003, 112 — 119 TG300B: 000, 001 — 011, 016 — 019, 024 — 026, 032, 033, 040, 126, 127 C/M: Fixed (only one bank) Drum part: XG: 126, 127 TG300B: 000 C/M: Fixed (only one bank) Program (Voice) Number Settings: A1 (A/D Input part): 001 — 013 A2 (A/D Input part): 001 — 005 Normal part: 001 — 128 This determines the Voice for the selected Part. (Refer to the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) Volume Range: 000 — 127 This determines the Volume setting for the selected Part’s Voice. 96 Multi Mode Part Controls Expression (Expresn) Range: Chorus Send (ChoSend) 000 — 127 Range: This determines the Expression setting for the selected Part’s Voice. This determines the level of the selected Part’s Voice that is sent to the Chorus effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” Voice sound (no Chorus effect). Pan Settings: 000 — 127 Rnd (Random), L63 — C — R63 NOTE Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 143.) Variation Send (VarSend) Settings: This determines the stereo position of the selected Part’s Voice. A setting of “Rnd” (Random) randomly assigns the Voice to a pan position. This is useful when you want to have different Voices sound from different random parts of the stereo image. (The Random setting does not affect the A/D input Parts and VL Voice Parts.) This determines whether the selected Part’s Voice is sent to the Variation effect or not. A setting of “off” or “000” results in no Variation effect being applied to the Voice. Reverb Send (RevSend) Range: off, on (when Variation Connection is set to INS); 000 — 127 (when Variation Connection is set to SYS) 000 — 127 Note Shift (NoteSft) Range: –24 — +24 semitones This determines the level of the selected Part’s Voice that is sent to the Reverb effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” Voice sound. NOTE Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 142.) Multi Mode This determines the key transposition setting for the Part’s Voice. 97 Part Controls All Part Control The All Part controls include: Device Number, Master Volume, Master Attenuator, Reverb Return, Chorus Return, Variation Return and Transpose. Keep in mind that these controls affect all Parts equally, and either add to or subtract from their individual values. For example, if Note Shift on one Part is set to –12, and Transpose (in All Part) is set to +12, that Part’s pitch value will actually be 0 or normal. For basic information on using the All Part controls, see page 35. Device Number (DevNo.) Settings: Master Attenuator (M.Attn) 1 — 16, all Range: This determines the Device Number for the MU100R, a kind of MIDI “identification” number to distinguish between multiple units. For example, if you are using more than one MU100R, set a different Device Number for each. This setting only applies to the data dump features. (See page 161.) If you have only one MU100R, set this to “all.” 000 (maximum volume) — 127 (minimum volume) This determines the level of all Parts, but functions as an attenuator; the greater the value, the lower the volume. This is useful when you are playing several songs and want to keep their overall level consistent. Reverb Return (RevRtn) Range: 000 — 127 Master Volume (M.Volum) Range: 000 — 127 This determines the amount of Reverb return in the overall mix. This determines the overall Volume of the Parts. Chorus Return (ChoRtn) Range: 000 — 127 This determines the amount of Chorus return in the overall mix. 98 Multi Mode Part Controls Variation Return (VarRtn) Range: 000 — 127 This determines the amount of Variation return in the overall mix. Variation Return is only available when the Variation Connection parameter is set to SYS. (See page 145.) Transpose (Trans) Range: –24 — +24 semitones This determines the overall Transpose setting of the Parts. Multi Mode 99 Multi Edit Mode Multi Edit Mode The Multi Edit mode features various parameters for controlling the Filter, the EG (Envelope Generator), the EQ, and Vibrato. It also features a variety of other miscellaneous controls grouped in the Others parameters. When a Drum Part is selected, Drum-related parameters are also available. When the VL Voices are assigned to the selected Part, the VL Edit parameters (“PLUGIN”) are also available (page 119). For basic information on using the Multi Edit mode, see page 36. NOTE When a VL Voice is selected, the following Multi Edit parameters are not available: HPF Cutoff — in Filter menu Low Frequency and High Frequency — in EQ Menu (However, both Gain parameters are effective.) Element Reserve, Velocity Limit Low and Velocity Limit High — in Others menu Filter (FIL) Path: [EDIT] button → “FILTER” (“FIL” when a VL Part is selected.) Filter —————————————————————————— ● LPF Cutoff Frequency ● LPF Resonance ● HPF Cutoff Frequency The MU100R features a digital filter that can be used to change the timbre of the Voices. The filter is affected (together with the level) by the EG (Envelope Generator), which allows you to change the timbre over time as well. (See EG, page 102.) 100 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff) Range: HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff) –64 — +63 Range: This determines the cutoff frequency of the low pass filter (LPF). The LPF filters out frequencies higher than the cutoff point and “passes” the lower frequencies. Lower cutoff values create a deeper, more rounded tone, while higher values create a brighter tone. This determines the cutoff frequency of the high pass filter (HPF). The HPF filters out frequencies lower than the cutoff point and “passes” the higher frequencies. Lower cutoff values preserve the fundamental and lower overtones of the sound, while higher values create a thinner, brighter tone. Level Level These frequencies are “cut” or filtered out. These frequencies are “passed” or let through. –64 — +63 These frequencies are “passed” or let through. These frequencies are “cut” or filtered out. Frequency LPF Cutoff Frequency setting Frequency HPF Cutoff Frequency setting LPF Resonance (LPF Reso) Range: –64 — +63 This determines the amount of filter resonance or emphasis of the LPF Cutoff Frequency above. Higher values make the filter effect more pronounced and stronger, creating a resonant peak around the cutoff frequency. Level Resonance Frequency LPF Cutoff Frequency setting Multi Mode 101 Multi Edit Mode Envelope Generator (EG) Path: [EDIT] button → “EG” EG (Envelope Generator) ————————————————— Level/Filter EG Parameters ..................................... 103 ● EG Attack Time ● EG Decay Time ● EG Release Time Pitch EG Parameters .............................................. 103 ● Pitch EG Initial Level ● Pitch EG Attack Time ● Pitch EG Release Level ● Pitch EG Release Time The EG parameters allow you to shape the sound of a Part’s Voice — or, in other words, set how the level and timbre of the Voice changes over time. This section also includes independent Pitch Envelope Generator (PEG) parameters for controlling how the pitch of a Part’s Voice changes over time. The relationship of the main EG parameters — Attack, Decay and Release — are shown in the illustration below. These parameters not only affect the sound level, but also the timbre (with the Filter parameters; see page 100). 1) Short Attack, Decay, Release times: Level Attack Decay Max. Level Release Attack Decay Release Max. Min. Key is pressed 2) Long Attack, Decay, Release times: Time Key is released Min. Key is pressed Time Key is released Even though the key is held for the same length of time in both examples, the sound of the second example slowly reaches full volume and decays over a longer time. It also sustains longer after the key is released. Keep in mind that the EG parameters affect each other, and are affected by how long a note is held. For example, if Decay is set to a low value and the note is held for a long time, you may not be able to hear changes made to the Release parameter. 102 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode Level/Filter EG Parameters Pitch EG Parameters EG Attack Time Range: The Pitch EG parameters determine how the pitch of a Part’s Voice changes over time. This lets you produce subtle or pronounced pitch changes as a note is played. In the example Pitch EG settings below, a played note is gradually bent up to its normal pitch, and kept there as the note is held. When the note is released, the pitch rapidly climbs up. –64 — +63 This determines the Attack Time of the EG, or how long it takes for the sound to reach full volume when a note is played. For the Filter, this determines how long it takes for the sound to be affected by the maximum Filter values. Pitch High Normal EG Decay Time Range: Low –64 — +63 Time Key is released This determines the Decay Time of the EG, or how rapidly the sound dies out as a note is held. For the Filter, this determines how long it takes for the Filter effect to die out. NOTE The Pitch EG parameters may have little or no effect, depending on the particular Voice used and the settings made to the main EG parameters. Pitch EG Initial Level (PEGInitLvl) Range: –64 — +63 EG Release Time Range: –64 — +63 This determines the initial pitch of the Part’s Voice, when the note is first played. A setting of 00 corresponds to normal pitch. This determines the Release Time of the EG, or how long the sound sustains after a note is released. For the Filter, this determines how long the Filter effect continues after a note is released. Multi Mode 103 Multi Edit Mode Pitch EG Attack Time (PEGAtakTime) Range: –64 — +63 This determines the Attack Time of the Pitch EG, or how long it takes for the pitch to return to normal (from the pitch value set in Initial Level above). Pitch EG Release Level (PEGReleLvel) Range: –64 — +63 This determines the final pitch of the Part’s Voice, or the pitch that is reached after the note is released. A setting of 00 corresponds to normal pitch. NOTE The Pitch EG Release Level and Time parameters may have no effect if the Voice itself does not sustain after the note is released. (Short percussive Voices may fall into this category.) Also make sure that the main EG Release Time is set to an appropriate value so that the sound sustains. Pitch EG Release Time (PEGReleTime) Range: –64 — +63 This determines the Release Time of the Pitch EG, or how long it takes for the pitch to change to the pitch value set in Release Level above. 104 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode Equalizer (EQ) Path: [EDIT] button → “EQ” EQ (Equalizer) —————————————————————— ● EQ Low Frequency ● EQ Low Gain ● EQ High Frequency ● EQ High Gain The EQ parameters let you adjust and set the tonal quality of a Part’s Voice, such as boosting the bass sound, or making it brighter. This is a two-band equalizer with wide frequency variation for each band, and is independent of the overall EQ controls (see page 155). EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq) Range: EQ High Frequency (High Freq) 32 Hz — 2.0 kHz Range: This determines the frequency which is boosted or cut (in the Low Gain parameter below) for each Part. EQ Low Gain Range: 500 Hz — 16 kHz This determines the frequency which is boosted or cut (in the High Gain parameter below) for each Part. EQ High Gain –64 — +00 — +63 Range: This determines the level of the selected frequency (in Low Freq above). Positive values boost the level of the selected frequency and negative values attenuate it. Multi Mode –64 — +00 — +63 This determines the level of the selected frequency (in High Freq above). Positive values boost the level of the selected frequency and negative values attenuate it. 105 Multi Edit Mode Vibrato Path: [EDIT] button → “VIBRATO” (“VIB” When a VL Part is selected) Vibrato ————————————————————————— ● Vibrato Rate ● Vibrato Depth ● Vibrato Delay Vibrato produces a quavering, vibrating sound in the Part’s Voice, by regularly modulating the pitch. You can control the speed and depth of the Vibrato, as well as the time it takes before the Vibrato effect is applied. Vibrato Rate Range: Vibrato Delay –64 — +63 Range: This determines the speed of the Vibrato effect. Higher values result in a faster Vibrato sound. Vibrato Depth Range: –64 — +63 This determines the depth of the Vibrato effect. Higher values result in a stronger, more pronounced Vibrato sound. 106 Multi Mode –64 — +63 This determines the delay in the onset of the Vibrato effect. Delay is effective especially on stringed instrument Voices. For example, violin players often use delayed vibrato, especially while playing long notes. The Delay parameter is useful in recreating this effect, producing a more natural, lifelike sound. Higher values result in a longer Delay time. Multi Edit Mode Others Path: [EDIT] button → “OTHERS” Others ————————————————————————— Detune .................................................................. 108 ● Detune Assignment Parameters .......................................... 108 ● Part Mode ● Mono/Poly Mode Portamento Parameters .......................................... 109 ● Portamento Switch ● Portamento Time Element ................................................................. 109 ● Element Reserve Note Limit Parameters ........................................... 110 ● Note Limit Low ● Note Limit High Dry Level ............................................................... 110 ● Dry Level (VarConnect=SYS) Velocity Sensitivity Parameters .............................. 110 ● Velocity Sensitivity Depth ● Velocity Sensitivity Offset Velocity Limit Parameters ...................................... 111 ● Velocity Limit Low ● Velocity Limit High Pitch Bend, Modulation Wheel, Assignable Controller ............................................ 111 ● Pitch Bend Control ● MW LFO Pitch Modulation Depth ● AC1 Control Change Number ● AC1 Filter Control ● AC1 Amplitude Control Output Assignment ................................................ 113 ● Output select The Others section of parameters contains miscellaneous controls, including those related to tuning, Part Mode, velocity, portamento, note range, etc. Multi Mode 107 Multi Edit Mode Detune (See page 114.) The drum and drumS1 — S4 settings are not available in the Performance mode (all Parts are fixed to “normal”). The Part Mode settings differ depending on the Sound Module mode selected, as described below. Detune Range: –12.8 — +12.7 This determines the fine tuning of the Part’s Voice. HINT Detune could be used to slightly detune a Voice compared to the tuning of the rest of the Voices for a richer sound. It could also be used to detune two different Voices being played in unison. For example if two different Parts are set to the same MIDI channel (see page 96) and same Voice, a naturally thick chorusing effect can be obtained by slightly detuning each Voice in opposite directions here. Assignment Parameters Part Mode Settings: normal, drum, drumS1 — S4 (When Sound Module mode is set to C/M, both Parts 10 and 26 are set to drumS1.) Height of bars indicates selected Part Mode setting for each Part. (A single bar indicates “normal” setting.) This determines the mode for the Part. A setting of normal allows selection of the normal instrument Voices. (See the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) The drum setting allows selection of the drum kits. (See the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) The drumS1 — S4 settings are locations for storing specially programmed drum setups. These setups can be edited by using the Drum Setup controls in the Multi Edit mode. 108 Multi Mode For XG (Extended General MIDI) mode: All settings described above are available. When normal is selected, any of the basic or the extended set of Voices can be used for the Part. For TG300B mode: The settings normal and drumS1 — S4 are available; drum cannot be selected. When normal is selected, either the basic or the extended set of Voices (for the TG300B mode) can be used for the Part. For C/M mode: The Part Mode settings are fixed in this mode and cannot be changed: Parts 10 and 26 are set to drumS1, and all other Parts are set to normal. The MIDI Receive Channel setting for Parts 1 and 17 is set to off. The 128 Voices of C/M Type 1 can be used for Parts 1 — 9 and 17 — 25; the 64 Voices of C/M Type 2 can be used for Parts 11 — 16 and 27 — 32. For PFM (Performance) mode: All four Parts are set to normal; none of the drum settings are available. Any of the basic or the extended set of Voices can be used for each Part. NOTE When two or more different Parts are set to the same editable drum setup (drumS1 — S4), any edits made to that drum setup automatically affect all those Parts. For example, when two Parts are set to drumS1, any changes made to drumS1 affect both Parts. Multi Edit Mode Mono/Poly Mode Settings: Portamento Time (PortametTm) mono, poly Range: 000 — 127 Height of bars indicates selected Mono/Poly Mode setting for each Part. (A single bar indicates “mono” setting, while full height indicates “poly”.) This determines whether the Part’s Voice is played monophonically (only one note at a time) or polyphonically (up to 64 notes at a time). This parameter is not available when the Part Mode is set to Drum. This determines the time of the Portamento effect, or how long it takes to glide the pitch from one note to the next. Higher values result in a longer pitch glide time. (This parameter is not available for Drum Parts.) Element Element Reserve (ElemReserv) Range: Portamento Parameters 00 — 64 Portamento is a function that creates a smooth pitch glide from one note to another. Portamento Switch (PortametSw) Settings: off, on Height of bars indicates selected Portamento Switch setting for each Part. (A single bar indicates “off” setting, while full heignt indicates “on.”) This determines whether Portamento is on or off for the Part. (This parameter is not available for Drum Parts.) Multi Mode This determines the minimum number of sound elements that are reserved for the Part. This setting ensures that when the maximum simultaneous polyphony of 64 notes (or elements) is exceeded, the selected Part will still play up to the number of elements set here. For example, if the Element Reserve of a Part is set to 10, the sounds for that Part (up to 10 simultaneous notes) will not be cut off, even if the maximum polyphony is exceeded. The total number of Element Reserve values for all of the Parts cannot exceed 64. This parameter is useful when playing back dense song data, and it ensures that the most important Parts in the song data will play properly without being cut off. 109 Multi Edit Mode Note Limit Parameters Dry Level The Note Limit Low and High parameters allow you to set the range of notes for a Part’s Voice. Notes outside the range will not be played. Dry Level Range: HINT Note Limit can be used to set up keyboard splits. Set two Parts to the same MIDI channel (see page 96), but give them Note Limit settings so that one Part is played from the left side of the keyboard and the other is played from the right. This determines the level of the unprocessed sound of the Voice (sound with no effect processing). This parameter is only available when the Variation Connection parameter is set to SYS. (See page 145.) Note Limit Low (NoteLimitL) Range: C-2 — G8 000 — 127 Velocity Sensitivity Parameters Velocity Sensitivity Depth (VelSensDpt) Range: 000 — 127 This determines the lowest responding note for the Part. Notes below this value will not be played. This determines the degree to which velocity affects the Part’s Voice. Higher values make the Voice more sensitive to changes in velocity. Note Limit High (NoteLimitH) Range: C-2 — G8 This determines the highest responding note for the Part. Notes above this value will not be played. 110 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode Velocity Sensitivity Offset (VelSensOfs) Range: Velocity Limit Low (VelLimitLo) 000 — 127 Range: This determines the volume range over which velocity affects. For lower values, the velocity affects a volume range from minimum to medium-loud. For higher values, velocity affects a range from medium-soft to maximum. This determines the lowest velocity value at which the Part’s Voice will play. The higher the value, the harder the keyboard must be played for the Voice to sound. Velocity Limit High (VelLimitHi) Range: 127 Level at 000 — 127 7 12 at 64 at 0 000 — 127 0 Velocity This determines the highest velocity value at which the Part’s Voice will play. The lower the value, the less strength needed (in playing the keyboard) to get maximum volume. 127 NOTE Depending on the Voice used, if Velocity Sensitivity Offset is set to too low of a value, the Voice may not sound, no matter how strong the velocity. 1 Velocity Limit Parameters no sound VelLimitLo The Velocity Limit Low and High parameters allow you to set the effective velocity range for a Part’s Voice. Velocity values outside the range will not be played. (Velocity is generally the strength at which notes are played from a MIDI keyboard.) no 127 sound VelLimitHi Pitch Bend, Modulation Wheel, Assignable Controller Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl) HINT Velocity Limit can be used to set up velocity splits. A velocity split allows you to have one Part’s Voice sound when you play the connected keyboard strongly, and a different Voice sound when you play softly. Set two Parts to the same MIDI channel (see page 96), but give them different Velocity Limit settings so that one or the other sounds depending on how strongly you play the keyboard. Multi Mode Range: –24 — +24 semitones (+/– 2 octaves) This determines the Pitch Bend range for the Part’s Voice. (Pitch Bend is usually controlled by a pitch bend wheel on a MIDI keyboard.) 111 Multi Edit Mode Modulation Wheel — LFO Pitch Modulation Depth (MW LFOPMod) Range: MIDI instruments allow you to change the control change number for a particular controller: for example, setting the modulation wheel (normally 01) to control Volume (07). Refer to the owner’s manual of your particular instrument for more information. Also see page 62 in the VL Voice section for more details on controllers. 000 — 127 This determines how widely the pitch is modulated by the LFO (low frequency oscillator). This is generally controlled from a modulation wheel on a MIDI keyboard and produces a vibrato effect. The higher the value, the deeper the pitch modulation, and hence, the more pronounced the vibrato effect. Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (AC1 FilCtrl) Range: This determines the degree to which Assignable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the Cutoff Frequency of the Low Pass Filter for each Part. For maximum effect, this should be set to one of the extreme values, negative or positive. A setting of 00 results in no control over the Filter, even when AC1 is operated (or control change data is received). Negative settings affect the Filter negatively; in other words, when the controller is at the minimum position, control over the Filter is greatest (see illustration below). (The control number used for AC1 is set in the Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number parameter above.) Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number (AC1 CC No.) Range: 00 — 95 This determines the which MIDI control change number is assigned to the Assignable Controller (AC1) for the selected Part. AC1 can be used to affect the Filter (page 112), volume (Amplitude; page 113), LFO (page 133) or the Variation effect (page 145). Make sure that parameters you don’t want to be affected by AC1 are properly set to 00. HINT Though this parameter allows you to assign any control change number from 0 to 95, only a few of these are in common use. The controllers most likely to be encountered include: 01 — Modulation wheel or lever 02 — Breath controller 04 — Foot controller 07 — Volume controller Some or all of these may be available on your MIDI instrument, and can be used to control certain functions on the MU100R in real time. Some 112 –64 — +63 For positive values: Minimum effect Multi Mode Maximum effect For negative values: Maximum effect Minimum effect HINT Positive and negative values can be most effectively used by setting two different Parts to opposite settings. In this way, moving the controller (for example, a foot controller) one way will affect one Part and moving it the opposite way will affect the other Part. Multi Edit Mode Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude Control (AC1 AmpCtrl) Range: Output Assignment Output Select (OutPtSel) 64 — +63 Settings: This determines the degree to which Assignable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the volume (Amplitude) for each Part. For maximum effect, this should be set to one of the extreme values, negative or positive. A setting of 00 results in no volume control, even when AC1 is operated (or control change data is received). Negative settings affect the volume negatively; in other words, when the controller is at the minimum position, control over the volume is greatest. (The control number used for AC1 is set in the Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number parameter above.) NOTE For more information on using positive and negative values, see the illustration and hint in Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (page 112). Multi Mode stereo, ind1+2, ind1, ind2 This determines the output configuration for the selected Part. When set to “stereo,” the Part is output (with effects) through the main OUTPUT and PHONES jacks. When set to one of the “ind” (individual) settings, it is output through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. In this case, only Insertion effects can be applied; System effects cannot be applied to the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. When set to “ind1+2,” the Part is output in stereo (1: left, 2: right). Settings of “ind1” and “ind2” output the Part in mono to the corresponding jack. (Parts output through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks cannot be heard through the PHONES jack.) NOTE ● The Output Select Lock parameter (page 158) must be set to “off” in order to change this setting via MIDI. ● When the Part Mode parameter (page 108) is set to “drum” or “drum S1 — S4”, this setting is inactive. 113 Multi Edit Mode Drum Setup Controls The Drum Setup controls allow you to make a wide variety of settings for the drum sounds in a Drum Part. These settings include Pitch controls, Level, Pan, effect send, filter controls and EG (Envelope Generator), among others. Moreover, these parameters can be set to completely independent values for each of the drum sounds in a Part. The Drum Setup controls can only be called up by first selecting a Part to which a Drum Part is assigned. (For basic information on using the Drum setup controls, see page 39.) Parh: [EDIT] button → “DRUM” Drum Setup Controls ——————————————————— Pitch Parameters .................................................... 115 ● Pitch Coarse ● Pitch Fine ● Velocity Pitch Sensitivity (VelPchSens) Level...................................................................... 115 ● Level Pan ........................................................................ 115 ● Pan Effect Send Parameters ........................................... 115 ● Reverb Send (Rev Send) ● Chorus Send (Cho Send) ● Variation Send (Var Send) Filter Parameters .................................................... 116 ● LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff) ● LPF Resonance (LPF Reso) ● Velocity LPF Cutoff Sensitivity (VelLPFSens) ● HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff) EQ Parameters ....................................................... 117 ● EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq) ● EQ Low Gain ● EQ High Frequency (High Freq) ● EQ High Gain EG Parameters ....................................................... 117 ● EG Attack ● EG Decay 1 ● EG Decay 2 114 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode Assignment ............................................................ 117 ● Alternate Group Note On/Off .......................................................... 118 ● Receive Note On (RcvNoteOn) ● Receive Note Off Output Assignment ................................................ 118 ● Output Select (OutptSel) The Drum Setup parameters are only available when the Part Mode has been set to drumS1 — S4. (See page 108.) Pitch Parameters Pan Pitch Coarse Pan Range: –64 — +63 Settings: This determines the coarse pitch setting of the selected drum sound. This determines the stereo position of the selected drum sound. A setting of “Rnd” (Random) randomly assigns the drum to a pan position. This is useful when you want to have different drums sound from different random parts of the stereo image. Pitch Fine Range: –64 — +63 This determines the fine pitch setting of the selected drum sound. Effect Send Parameters Velocity Pitch Sensitivity (VelPchSens) Range: Reverb Send (Rev Send) –16 — +16 This determines the degree to which pitch changes of the selected drum sound respond to velocity. In other words, you can control how much the pitch of the sound changes by how hard or soft you play the keys of a connected keyboard. Positive values raise the pitch and negative values lower the pitch. A value of 00 results in no pitch change, whatever velocity is received. Level Level Range: Rnd (Random), L63 — C — R63 Range: 000 — 127 This determines the level of the selected drum sound that is sent to the Reverb effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” drum sound, no matter how much Reverb is applied to the Drum Part. NOTE Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 142.) Also, the parameters Reverb Send in Single Part control (page 97) and Reverb Return in All Part control (page 98) must be set to appropriate values. 000 — 127 This determines the volume of the selected drum sound. Multi Mode 115 Multi Edit Mode Chorus Send (Cho Send) Range: LPF Resonance (LPF Reso) 000 — 127 Range: This determines the level of the selected drum sound that is sent to the Chorus effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” drum sound, no matter how much Chorus is applied to the Drum Part. NOTE Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 143.) Also, the parameters Chorus Send in Single Part control (page 97) and Chorus Return in All Part control (page 98) must be set to appropriate values. This determines the amount of filter resonance or emphasis of the LPF Cutoff Frequency above for the selected drum sound. Higher values make the filter effect more pronounced and stronger, creating a resonant peak around the cutoff frequency. (For more information, see LPF Resonance on page 101.) Velocity LPF Cutoff Sensitivity (VelLPFSens) Range: Variation Send (Var Send) Settings: This determines the level of the selected drum sound that is sent to the Variation effect. A setting of off results in a completely “dry” drum sound, no matter how much Variation is applied to the Drum Part. HPF Cutoff Frequency (HPF Cutoff) Filter Parameters LPF Cutoff Frequency (LPF Cutoff) Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 — 127 (TG300B or C/M mode) This determines the cutoff frequency of the low pass filter (LPF) for the selected drum sound. The LPF filters out frequencies higher than the cutoff point and “passes” the lower frequencies. Lower cutoff values create a deeper, more rounded tone, while higher values create a brighter tone. (For more information, see LPF Cutoff Frequency on page 101.) 116 –16 — +16 This determines the degree to which the LPF Cutoff Frequency for the selected drum sound changes in response to velocity. In other words, you can shift the LPF Cutoff Frequency of the filter up or down (and thus change the timbre of the sound) depending on how hard or soft you play the keys of a connected keyboard. Positive values raise the LPF Cutoff Frequency and negative values lower it. A value of 00 results in no frequency change, whatever velocity is received. off, on (when Variation Connection is set to INS); 000 — 127 (when Variation Connection is set to SYS) NOTE Keep in mind that the Variation effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 144.) Also, the parameters Variation Send in Single Part control (page 97) and Variation Return in All Part control (page 99) must be set to appropriate values. –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 — 127 (TG300B or C/M mode) Multi Mode Range: –64 — +63 This determines the cutoff frequency of the high pass filter (HPF) for the selected drum sound. The HPF filters out frequencies lower than the cutoff point and “passes” the higher frequencies. Lower cutoff values preserve the fundamental and lower overtones of the sound, while higher values create a thinner, brighter tone. (For more information, see HPF Cutoff Frequency on page 101.) Multi Edit Mode EQ Parameters EG Decay 1 Range: EQ Low Frequency (Low Freq) Range: 32 Hz — 2.0 kHz This determines the Decay 1 time of the EG, or how rapidly the sound dies down to the Decay 2 level. (See illustration below.) Higher values result in a longer Decay time. This determines the frequency which is boosted or cut (in the Low Gain parameter below) for the selected drum sound. EQ Low Gain Range: –64 — +63 This determines the level of the selected frequency (in Low Freq above). Positive values boost the level of the selected frequency and negative values attenuate it for the selected drum sound. EG Decay 2 Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 — 127 (TG300B or C/M mode) This determines the Decay 2 time of the EG, or how rapidly the sound dies out completely. (See illustration below.) Higher values result in a longer Decay time. EQ High Frequency (High Freq) Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 — 127 (TG300B or C/M mode) 500 Hz — 16 kHz Level This determines the frequency which is boosted or cut (in the High Gain parameter below) for the selected drum sound. EG Attack EG Decay 1 EG Decay 2 Time EQ High Gain Range: Assignment –64 — +63 This determines the level of the selected frequency (in High Freq above) for the selected drum sound. Positive values boost the level of the selected frequency and negative values attenuate it. Alternate Group EG Parameters EG Attack Range: –64 — +63 (XG mode), 000 — 127 (TG300B or C/M mode) This determines the Attack Time of the EG (Envelope Generator), or how long it takes for the sound of the selected drum sound to reach full volume when a note is played. (See page 102 for more information about the EG function; also see illustration below.) Multi Mode Settings: off, 001 — 127 This determines the group assignment of the selected drum sound. Drums assigned to the same group cannot be sounded simultaneously. In other words, if one drum in a group is sounding while a second in the same group is played, the first drum sound will be cut off and the second will sound. HINT The main use for this parameter is in creating realistic hi-hat sounds. By assigning an open hi-hat and a closed hi-hat to the same group, you can “choke” or stop the open hi-hat sound by simply playing the closed hi-hat — just like pressing the pedal on an actual hihat set. 117 Multi Edit Mode Note On/Off Parameters Output Assignment Receive Note On (RcvNoteOn) Output Select (OutPtSel) Settings: on, off Settings: This determines how the selected drum sound responds to MIDI Note On messages. Normally, this should be set to on so that the corresponding drum sound plays when a MIDI Note On message is received. Set this to off when you want to keep the selected drum sound from playing. Receive Note Off Settings: on, off This determines how the selected drum sound responds to MIDI Note Off messages. When this is set to on, the selected sound will stop in response to the corresponding MIDI Note Off message. An on setting is good for some sustained sounds (like a whistle), whose duration you want to control or for key-controlled cymbal “chokes.” For most drum sounds, however, this should be set to off so that the drum sound plays back in its entirety (is not cut off). 118 Multi Mode stereo, ind1+2, ind1, ind2 This determines the output configuration for the selected drum sound. When set to “stereo,” the drum sound is output (with effects) through the main OUTPUT and PHONES jacks. When set to one of the “ind” (individual) settings, it is output (without effects) through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks. When set to “ind1+2,” the drum sound is output in stereo (1: left, 2: right). Settings of “ind1” and “ind2” output the drum sound in mono to the corresponding jack. (Drum sounds output through the INDIV. OUTPUT jacks cannot be heard through the PHONES jack.) NOTE The Output Select Lock parameter (page 158) must be set to “off” in order to change this setting. Multi Edit Mode VL Voice Part Parameters (Plugin) The VL Voice Part parameters give you comprehensive tools for changing the character and expressive control of the VL Voices. As with the other MU100R Voices, the edits that you make to these parameters affect the Part and not the actual Voice itself. In other words, any parameter changes made are applied to any other VL Voices you select. Make sure that the Part to be edited is appropriately enabled for VL Voices. For basic instructions on editing VL Voices, see page 62. Path: [EDIT] → “PLUGIN” Plugin ————————————————————————— Filter ...................................................................... 120 ● Filter Envelope Generator Depth Pressure ................................................................. 120 ● Pressure Control Change Number ● Pressure Control Depth Embouchure .......................................................... 120 ● Embouchure Control Change Number ● Embouchure Control Depth Tonguing................................................................ 121 ● Tonguing Control Change Number ● Tonguing Control Depth Scream .................................................................. 121 ● Scream Control Change Number ● Scream Control Depth Breath Noise .......................................................... 122 ● Breath Noise Control Change Number ● Breath Noise Control Depth Growl .................................................................... 122 ● Growl Control Change Number ● Growl Control Depth Throat Formant ...................................................... 123 ● Throat Formant Control Change Number ● Throat Formant Control Depth Harmonic Enhancer ............................................... 123 ● Harmonic Enhancer Control Change Number ● Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth Damping ............................................................... 124 ● Damping Control Change Number ● Damping Control Depth Absorption ............................................................. 124 ● Absorption Control Change Number ● Absorption Control Depth Multi Mode 119 Multi Edit Mode Filter Pressure Control Depth (PrsCtrlDpt) Settings: Filter Envelope Generator Depth (FilEG Dept) Settings: -64 — +63 Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to pressure. The higher the value the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in pressure in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in pressure in response to higher controller values. Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to dynamic filter. The higher the value the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in filter cutoff frequency in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in filter cutoff frequency in response to higher controller values. Pressure Pressure Control Change Number (Prs CC No.) Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB Details • Set this parameter to “+00” if you do not intend to control pressure via a controller. Embouchure Embouchure Control Change Number (Emb CC No.) Settings: “Pressure” corresponds to the amount of breath pressure applied to a reed or mouthpiece, or the speed of the bow applied to a string. Pressure variations affect both volume and timbre. The “Prs CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for pressure control. When set to “off” maximum pressure is applied at all times. Details • Note that pressure affects not only volume, but timbre and pitch as well. Accurate keyboard/controller pitch is produced only at maximum pressure. • The “PrsCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for pressure control to have any effect. 120 -64 — +63 Multi Mode off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Embouchure” corresponds to the tightness of the lips against the reed or against each other. In a string instrument Voice, embouchure corresponds to how strongly the bow is pressed against the string. This affects both pitch and timbre. The “Emb CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for embouchure control. When set to “off,” medium embouchure is applied at all times. Details • Note that with many Voices, accurate keyboard/controller pitch is produced only at medium embouchure. • The “EmbCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to appropriate values (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for embouchure control to have any effect. Multi Edit Mode Embouchure Control Depth (EmbCtrlDpt) Settings: Tonguing Control Depth (TngCtrlDpt) -64 — +63 Settings: Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to embouchure. The higher the value the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in embouchure in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause an decrease in embouchure in response to higher controller values. -64 — +63 Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to tonguing. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause an decrease in tonguing in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause an increase in tonguing in response to higher controller values. Tonguing Scream Tonguing Control Change Number (Tng CC No.) Scream Control Change Number (Scr CC No.) Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Tonguing” simulates the half-tonguing technique used by saxophone players by changing the “slit” of the reed. The slit is the space between the tip of the reed and the mouthpiece. The “Tng CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for tonguing control. When set to “off” no tonguing is applied. Details • Note that accurate keyboard pitch is produced only when maximum tonguing is applied or the tonguing controller is turned off. • The “TngCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for tonguing control to have any effect. Multi Mode Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Scream” drives the entire system into chaotic oscillation, creating effects that can only be achieved with physical modeling technology. The “Scr CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for scream control. When set to “off”, no scream variation can be produced via a controller, but a continuous scream value is determined by the “ScrCtrlDpt” parameter below. (Negative values increase the scream level.) Details • The “ScrCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for scream control to have any effect. 121 Multi Edit Mode Scream Control Depth (ScrCtrlDpt) Settings: Breath Noise Control Depth (BnzCtrlDpt) -64 — +63 Settings: Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to scream. The higher the value the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in scream effect in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in scream effect in response to higher controller values. -64 — +63 Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to breath noise. The higher the value the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in breath noise in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in breath noise in response to higher controller values. Breath Noise Growl Breath Noise Control Change Number (Bnz CC No.) Growl Control Change Number (Grl CC No.) Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Breath Noise” can be used to add the required amount of breath noise to a Voice. The “Bnz CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for breath noise control. When set to “off”, no breath noise variation can be produced via a controller, but a continuous breath noise value is determined by the “BnzCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative values increase the breath noise level). “Growl” produces a periodic pressure modulation which produces the “growl” effect often heard in wind instruments. The “Grl CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for growl control. When set to “off”, no growl variation can be produced via a controller, but a continuous growl value is determined by the “GrlCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative values increase the growl level). Details • The “BnzCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for breath noise control to have any effect. Details • The “GrlCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for growl control to have any effect. 122 Multi Mode Multi Edit Mode Growl Control Depth (GrlCtrlDpt) Settings: Throat Formant Control Depth (ThrCtrlDpt) -64 — +63 Settings: Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to growl. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in growl effect in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in growl effect in response to higher controller values. -64 — +63 Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to throat formant. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in throat formant effect in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in throat formant effect in response to higher controller values. Throat Formant Harmonic Enhancer Throat Formant Control Change Number (Thr CC No.) Harmonic Enhancer Control Change Number (Hrm CC No.) Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Throat Formant” controls the characteristics of the simulated player’s lungs, trachea, and oral cavity and Can add a realistic “roughness” to the sound. The “Thr CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for throat formant control. When set to “off”, no throat formant variation can be produced via a controller, but a continuous throat formant value is determined by the “ThrCtrlDpt” parameter, below (negative values increase the throat formant level). Details •The “ThrCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for throat formant control to have any effect. • Throat Formant only applies to some reedtype Voices. Multi Mode Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB The Harmonic Enhancer can vary the harmonic structure of the sound over a wide range. The “Hrm CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for harmonic enhancer depth (wet/dry balance) control. When set to “off,” no harmonic enhancer depth variation can be applied via a controller. Details • The “HrmCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for harmonic enhancer control to have any effect. • Since most VL Voices have sufficient natural harmonic content, the Harmonic Enhancer is actually only used on a few Voices. Therefore changing the controller destination with many Voices will produce either no change in the sound or a simple change in amplitude. 123 Multi Edit Mode Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth (HrmCtrlDpt) Settings: Damping Control Depth (DmpCtrlDpt) Settings: -64 — +63 Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to the harmonic enhancer. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause an increase in harmonic enhancer depth in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause a decrease in harmonic enhancer depth in response to higher controller values. Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to damping. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause a decrease in damping in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause an increase in damping in response to higher controller values. Absorption Apsorption Control Change Number (Abs CC No.) Damping Damping Control Change Number (Dmp CC No.) Settings: Settings: off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB off, 01 — 31, off, 33 — 95, AT, VEL, PB “Damping” simulates the effect of damping due to losses within the body of a wind instrument or in a string due to air friction. This affects both pitch and timbre. The “Dmp CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for damping control. When set to “off,” no damping variation can be applied via a controller. Details • Note that accurate keyboard pitch is produced only when damping is maximum. • The “DmpCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for damping control to have any effect. 124 -64 — +63 Multi Mode “Absorption” simulates the effect of highfrequency loss at the end of the air column or string. The “Abs CC No.” parameter specifies the controller to be used for absorption control. When set to “off,” no absorption variation can be applied via a controller. Details • Note that accurate keyboard pitch is produced only at when absorption is maximum. • The “AbsCtrlDpt” parameter (below) must be set to an appropriate value (higher than “+01” or lower than “-01”) for absorption control to have any effect. Multi Edit Mode Absorption Control Depth (AbsCtrlDpt) Settings: Controllers -64 — +63 Here’s a list of some of the physical controllers you might want to use with the VL tone generator section: Breath Controller Sets the amount of variation produced by the controller assigned to absorption. The higher the value, the greater the variation. Positive values cause a decrease in absorption in response to higher controller values (e.g., increased breath pressure or higher modulation wheel position), while negative values cause an increase in absorption in response to higher controller values. (MIDI control change no. 02) A natural candidate for controlling pressure, tonguing, throat formant, growl, and other parameters. Pitch Bend Wheel The pitch bend wheel on your keyboard or other MIDI device can be assigned to a range of parameters, but it’s “standard” function is pitch control. A controller parameter such as Embouchure can also be assigned to the pitch bend wheel for more realistic pitch variations. Modulation Wheel (MIDI control change no. 01) Since the modulation wheel on your keyboard or other MIDI device can be assigned to any controller parameter, it can be an important tool for musical expression. Use it in conjunction with a breath controller or a foot controller for broad expressive variation. Foot Controller (MIDI control change no. 04) Like the modulation wheel, a foot controller connected to your keyboard or other MIDI device can be assigned to any VL controller parameter. Aftertouch Keyboard aftertouch allows you to control any controller parameter by the pressure you apply to a key after it is initially pressed. This is perhaps the most “intimate” type of keyboard expression control. Multi Mode 125 Multi Edit Mode MIDI Control Change Number Assignments Velocity Although normally assigned to pressure (particularly in plucked string Voices), keyboard velocity can also be assigned to any other controller parameter. Others The MIDI protocol provides 119 control change numbers, some of which are preassigned to specific controllers — as noted above, “01” is “Modulation Wheel”, for example. 95 of these are available for assignments to the VL controller parameters, so any available MIDI control devices can be used to full advantage. A complete list of the available MIDI control change numbers is given below. 126 Control No. Controller off(00) off (used by Bank Select MSB) 01 Modulation Wheel 02 Breath Controller 03 Unassigned 04 Foot Controller 05 Portamento Time 06 Data Entry MSB 07 Volume Control 08~09 Unassigned 10 Panpot 11 Expression 12~31 Unassigned off(32) off (used by Bank Select LSB) 33~37 Unassigned 38 Data Entry LSB 39~63 Unassigned 64 Hold1 65 Portamento Switch 66 Unassigned 67 Soft Pedal 68~70 Unassigned 71 Harmonic Content 72 Release Time 73 Attack Time 74 Brightness 75~90 Unassigned 91 Effect Send Level (Reverb Effect) 92 Unassigned 93 Effect Send Level 3 (Chorus Effect) 94 Effect Send Level 4 (Variation Effect) 95 Unassigned AT After Touch VEL Velocity PB Pitch Bend Multi Mode Performance Mode In the Performance mode, the MU100R performs as a four-Part tone generator, with all Parts controlled over a single MIDI channel. The Performance mode is so named because it’s ideally suited to live performance situations. It allows you to play four different Voices at the same time from your MIDI keyboard — either in a layer, or in sophisticated keyboard and velocity splits. It also gives you comprehensive control over each of the four Parts for maximum performance flexibility. A total of 200 Performances are available: 100 Preset and 100 Internal. For basic information on using the Performance Mode, see page 23. NOTE Drum Parts are not available in the Performance mode. Performance Part Control ........................................................... 128 All Part ............................................................................... 128 Single Part .......................................................................... 129 Performance Edit Mode .............................................................. 131 Common ............................................................................ 131 Part ..................................................................................... 134 Copy and Store Operations ........................................................ 137 Copy .................................................................................. 137 Store ................................................................................... 138 Recall Function .................................................................. 140 Performance Mode 127 Performance Part Control Performance Part Control All Part For basic information on using the All Part controls in the Performance mode, see page 44. System MIDI Channel (Sys CH) Settings: Performance Volume (Pfm Vol) 01 — 16 Range: This determines the MIDI receive channel for all Parts of the Performance. Performance Bank Settings: 000 — 127 This determines the overall Volume of the Performance. Performance Pan (Pfm Pan) Pre (Preset), Int (Internal) This determines the bank of Performance programs: Preset or Internal. Preset Performances are those that have been created and loaded at the factory; the Internal bank is reserved for user-created Performances. Range: L63 — C — R63 This determines the overall Pan position of the Performance. Reverb Return (RevRtn) Range: 000 — 127 NOTE When changing Performance banks, there may be a slight delay before the sound changes. Performance Number Range: This determines the amount of Reverb return for the Performance in the overall mix. 001 — 100 This determines the Performance number. NOTE When changing Performance numbers, there may be a slight delay before the sound changes. 128 Performance Mode Performance Part Control Chorus Return (ChoRtn) Range: System Transpose (SysTran) 000 — 127 Range: This determines the amount of Chorus return for the Performance in the overall mix. –24 — +24 semitones This determines the overall Transpose setting of the Performance. Variation Return (VarRtn) Range: 000 — 127 This determines the amount of Variation return in the overall mix of the Performance. Variation Return is only available when the Variation Connection parameter is set to SYS. (See page 145.) Single Part For basic information on using the Single Part controls in the Performance mode, see page 46. Bank Number Program (Voice) Number Settings: A1 part: 000 — 003, 018, 019 A2 part: 000 — 003 1 — 4 part: XG Voice banks, MU100 Exclusive Voice banks, VL Voice banks Range: 001 — 100 This determines the Voice for the selected Part. (Refer to the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) This determines the bank number of the selected Part’s Voice. Each bank contains 128 Voices. (Refer to the SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) Performance Mode 129 Performance Part Control Volume Range: Chorus Send (ChoSend) 000 — 127 Range: This determines the Volume setting for the selected Part’s Voice. Pan Settings: Rnd (Random), L63 — C — R63 000 — 127 This determines the level of the selected Part’s Voice that is sent to the Chorus effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” Voice sound (no Chorus effect). NOTE Keep in mind that the Chorus effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 143.) Variation Send (VarSend) This determines the stereo position of the selected Part’s Voice. A setting of “Rnd” (Random) randomly assigns the Voice to a pan position. This is useful when you want to have different Voices sound from different random parts of the stereo image. Settings: off, on (when Variation Connection is set to INS); 000 — 127 (when Variation Connection is set to SYS) Reverb Send (RevSend) Range: 000 — 127 This determines whether the selected Part’s Voice is sent to the Variation effect or not. A setting of off or 000 results in no Variation effect being applied to the Voice. This determines the level of the selected Part’s Voice that is sent to the Reverb effect. A value of 000 results in a completely “dry” Voice sound. NOTE Keep in mind that the Reverb effect must be properly enabled and set for this parameter to work as intended. (See page 142.) 130 Note Shift (NoteSft) Range: –24 — +24 semitones This determines the key transposition setting for the Part’s Voice. Performance Mode Performance Edit Mode Performance Edit Mode The Performance Edit mode features various functions and parameters, grouped in the following sections: Common (related to the Performance as a whole), Part (related to each of the four Parts), and the Copy and Store operations. For basic information on using the Performance Edit mode, see page 43. Common Path: [EDIT] button → “ COM” Common ———————————————————————— Performance Name ................................................ 132 ● Performance Name (Perform Name) Portamento Parameters .......................................... 132 ● Portamento Switch (PortamnSw) ● Portamento Time (PortamnTm) Modulation Wheel Parameters .............................. 132 ● LFO Pitch Modulation Depth (MW LEOPMod) ● LFO Filter Modulation Depth (MW LFOFMod) Pitch Bend ............................................................. 133 ● Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl) A/D Part................................................................. 133 ● A/D Part Assignable Controller Parameters .......................... 133 ● Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number (AC1 CC No.) ● Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (AC1 FilCtrl) ● Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude Control (AC1 AmpCtrl) ● Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter Modulation Depth (AC 1 LFOFMod) The Common parameters allow you to name a Performance, enable the A/D Parts for a Performance, and set the control change number for realtime parameter control. Performance Mode 131 Performance Edit Mode Performance Name Performance Name (Perform Name) This allows you to give a name to your edited Performance. Operation 1 From the Performance Name display, press the ENTER button. Performance name 2 Use the SELECT </> buttons to select the character position (flashing character) in the name and use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to change the character at that position. 3 Press the EXIT button to return to the previous display (or press the PLAY button to return to the Play display). After creating and naming a Performance, you’ll probably want to save that Performance for future recall. For instructions on saving a Performance, refer to the Store operation on page 138. Portamento Parameters Portamento Switch (PortamnSw) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.) Use these to move among character positions. Portamento Time (PortamnTm) Flashes to indicate character position. Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.) Use these to change character at selected position. Up to 12 characters can be used for the Performance name. Available characters include all letters of the alphabet, in both upper and lower case, numbers from 0 to 9, and a variety of miscellaneous characters. 132 Modulation Wheel Parameters Modulation Wheel — LFO Pitch Modulation Depth (MW LFOPMod) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 112.) Performance Mode Performance Edit Mode Modulation Wheel — LFO Filter Modulation Depth (MW LFOFMod) Range: 000 — 127 HINT You can use the MU100R strictly as an effect processor for the A/D input (for example, your guitar or microphone) by Soloing the appropriate A/D Part (A1 or A2). Assignable Controller Parameters This determines how widely the Filter (page 135) is modulated by the LFO (low frequency oscillator). This is generally controlled from a modulation wheel on a MIDI keyboard, and depending on the Voice used, it creates a “swoosh” or “wah-wah” filter sweep effect. Higher values result in deeper filter modulation, creating a more pronounced filter sweep effect. Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode (page 112), with the exception that AC1 in the Performance mode can also control LFO filter modulation (see Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter Modulation Depth below). Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control (AC1 FilCtrl) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 112.) Pitch Bend Pitch Bend Control (PitBndCtrl) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.) A/D Part A/D Part Settings: Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number (AC1 CC No.) Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude Control (AC1 AmpCtrl) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 113.) Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter Modulation Depth (AC1LFOFMod) off, on Range: Height of bars indicates A/D Part setting. (A single bar indicates “off” setting, while full height indicates “on.”) This determines whether A/D Parts are enabled for the Performance or not. When set to “on,” Parts 3 and 4 are automatically set as A/D Parts (A1 and A2). 000 — 127 This determines the degree to which Assignable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the LFO modulation of the Filter. This creates a regular and continuous “wah-wah” or filter sweep effect. The higher the value, the greater the LFO filter modulation. (The control number used for AC1 is set in the Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number parameter above.) Performance Mode 133 Performance Edit Mode Part Path: [EDIT] button → “ PART” PART ————————————————————————— ■ FILTER ● LPF Cutoff Frequency ● LPF Resonance ● HPF Cutoff Frequency ■ EG (Envelope Generator) Level/Filter EG Parameters ● EG Attack Time ● EG Decay Time ● EG Release Time Pitch EG Parameters ● Pitch EG Initial Level ● Pitch EG Attack Time ● Pitch EG Release Level ● Pitch EG Release Time ■ EQ (Equalizer) ● EQ Low Frequency ● EQ Low Gain ● EQ High Frequency ● EQ High Gain ■ Vibrato ● Vivrato Rate ● Vivrato Depth ● Vivrato Delay ■ Others Detune .................................................................. 136 ● Detune Assignment ............................................................ 136 ● Mono/Poly Mode Note Limit Parameters ........................................... 136 ● Note Limit Low ● Note Limit High Dry Level ............................................................... 136 ● Dry Level (VarConnect=SYS) Velocity Parameters ............................................... 136 ● Velocity Sensitivity Depth ● Velocity Sensitivity Offset ● Velocity Limit Low ● Velocity Limit High ■ Plugin The Part menu contains the Filter, EG, Vibrato, Others and Plugin parameters for the Performance. 134 Performance Mode Performance Edit Mode ■ Filter Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “FILTER” (“FIL” when a VL Part is selected) The Filter section of Performance Edit parameters are the same as the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 100.) ■ EG Path:[EDIT] → “PART” → “EG” The EG section of Performance Edit parameters are the same as the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 102.) ■ EQ Path:[EDIT] → “PART” → “EQ” The EQ Performance Edit parameters are the same as the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode (See page 105). ■ Vibrato Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “VIBRATO” (“VIB” when VL Part is selected) The Vibrato Performance Edit parameters are the same as the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 106.) ■ Others Path:[EDIT] button → “PART” → “OTHERS” The Others Performance Edit parameters contains miscellaneous controls, including those related to tuning, velocity, note range, etc. With a few omitted parameters, these are the same as the parameters in the Multi Edit mode. NOTE The Part Edit parameter (available in Multi Edit) is not available in Performance Edit mode. No Drum Parts can be selected for a Performance. Performance Mode 135 Performance Edit Mode Detune Velocity Parameters Detune Velocity Sensitivity Depth (VelSensDpt) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 108.) Assignment Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.) Velocity Sensitivity Offset (VelSensOfs) Mono/Poly Mode Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 109.) Note Limit Parameters Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.) Velocity Limit Low (VelLimitLo) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.) Note Limit Low (NoteLimitL) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.) Note Limit High (NoteLimitH) Velocity Limit High (VelLimitHi) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 111.) Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.) Dry Level Dry Level Same as the corresponding parameter in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 110.) This parameter is only available when the Variation Connection parameter is set to SYS. (See page 145.) ■ Plugin Path: [EDIT] button → “PART” → “PLUGIN” The VL Voice section parameters of Performance Edit are the same as the corresponding parameters in the Multi Edit mode. (See page 119.) 136 Performance Mode Copy and Store Operations Copy and Store Operations The Copy and Store operations allow you to save and organize the Performances you’ve created. Copy The Copy operation allows you to copy the settings of one Performance program (Preset or Internal) to another Performance number (Internal only). Operation 1 From the Performance Edit menu, use the SELECT </> buttons to select “COPY.” Then, press the ENTER button to call up the Copy operation. 2 Use the SELECT </> buttons to select the desired parameter: memory location, source number or destination number. (The selected parameter flashes.) Then use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to change the value. Performance Mode 137 Copy and Store Operations Memory location (P = Preset, I = Internal) Source Performance number Use these to select desired parameter. Destination Performance number Use these to change value. 3 Press the ENTER button to actually execute the Copy operation. An “Executing…” message flashes in the display during the operation. When the data has been copied, the MU100R returns to the Performance Edit menu. To cancel the operation without copying, press the EXIT button (before pressing ENTER). Store Once you’ve edited or created a Performance, you can save that new Performance for future recall by using the Store operation. Performances can be saved to any one of the 100 Internal memory locations. With the exception of the Receive Channel and Transpose (Note Shift) settings made from the Play screen, all parameter settings in the Play screen and in the Edit, Effect and EQ modes are saved to the selected Performance number. Operation 1 From the Performance Edit menu, use the SELECT </> buttons to select “STORE.” Then, press the ENTER button to call up the Store operation. 138 Performance Mode Copy and Store Operations 2 Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to change the destination Performance number. Performance number Use these to change Performance number. 3 Press the ENTER button to actually execute the Store operation. An “Executing...” message flashes in the display during the operation. When the data has been stored, the MU100R returns to the Performance Edit menu. To cancel the operation without saving, press the EXIT button (before pressing ENTER). Performance Mode 139 Copy and Store Operations Recall Function Recall is a convenient function that allows you to recover an accidently deleted Performance. For example, if you are editing a Performance and inadvertently select a different Performance, the edited Performance would normally be lost. By using Recall before turning off the MU100R or editing another Performance, you can recover the previously edited Performance data. To use Recall: 1 Select RECALL in the Performance Edit Mode menu, then press the ENTER button. The following display briefly appears: 2 At the “Are you sure?” prompt above, press the ENTER button again to execute the function. If no previously edited Performance data exists, the following display briefly appears, indicating no Performance can be recalled. 140 Performance Mode Effect Edit Mode The MU100R features a built-in multi-effect processor with 6 independent digital effects: Reverb, Chorus, Variation, Insertion 1/2 and EQ. The first 5 of these are controlled in the Effect Edit mode. In this section, only the effect Types and the global parameters common to all Types are covered. For descriptions and details on the parameters for each effect Type, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. To enter the Effect Edit mode, press the EFFECT button. The following menu appears: Reverb (REV) .............................................................................. 142 Chorus (CHO) ............................................................................ 143 Variation (VAR) ........................................................................... 144 Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2) .............................................................. 146 Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters ........................................ 147 About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion ............... 152 Effect Edit Mode 141 Reverb (REV) Reverb (REV) Reverb recreates the sounds of various performance environments by adding an ambient wash of delays or reflections. Several different types of Reverb effects are available to simulate the ambience of different sized rooms. Explanations of the Reverb Type and Reverb Pan parameters are given below. For descriptions and explanations for all other Reverb parameters, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. Type Settings: Reverb Pan (RevPan) NO EFFECT, HALL 1 — 2, ROOM 1 — 3, STAGE 1 — 2, PLATE, WHITE ROOM, TUNNEL, CANYON, BASEMENT This determines the Reverb Type. Each Reverb Type has different values for the rest of the Reverb parameters; for example, Basement has a Reverb Time of 0.6 seconds, while Canyon has a Reverb Time of 12.0 seconds. Range: This determines the Pan position of the Reverb sound, or where it appears in the stereo image. For details on the parameters for each Reverb Type, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. NOTE When “NO EFFECT” is selected, Reverb is off and none of the other Reverb parameters are available (with the exception of the Reverb Pan parameter). HINT Generally when using Reverb, you can simply select the particular Type needed, and use it without bothering to adjust the other parameters. If fine tuning of the Reverb sound is necessary, delve into the other parameters as needed. 142 L63 — C — R63 Effect Edit Mode Chorus (CHO) Chorus (CHO) The Chorus section uses pitch modulation to create a variety of rich, spacious-sounding effects, including Chorus, Flanger, Symphonic and Phaser. Explanations of the Chorus Type and Chorus Pan parameters are given below. For descriptions and explanations for all other Chorus parameters, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. Type Settings: Chorus Pan (ChoPan) NO EFFECT; CHORUS 1 — 4; CELESTE 1 — 4; FLANGER 1 — 3; SYMPHONIC; ENSEMBLE DETUNE; PHASER 1 Range: L63 — C — R63 This determines the Pan position of the Chorus sound, or where it appears in the stereo image. This determines the Chorus Type. Depending on the Type selected, the specific parameters and values may differ. Send Chorus to Reverb (SendCho → Rev) Chorus 1 and 2 are used to subtly enhance the sound, and generally make it richer, fatter and warmer. Flanger uses modulation to create an animated, swirling motion effect, and produces a characteristic metallic sound. Symphonic also subtly enhances the sound by making a single instrument Voice sound like several. Phaser is similar to Flanger, but with a stronger and deeper modulation. This determines the level of the Chorus signal sent to and processed by the Reverb effect. A setting of 000 results in none of the Chorus-processed signal going to the Reverb. NOTE When NO EFFECT is selected, Chorus is off and none of the other Chorus parameters are available (with the exception of the Chorus Pan and Send Chorus to Reverb parameters). Range: 000 — 127 HINT Setting this to a relatively high level gives you a more natural sound, since the Chorus-processed sound is also being processed by the reverb. More unusual effects can be created by having a long Reverb and setting this to 0, so that the Chorus sound is dry (no Reverb) and the original sound is “drenched” in Reverb. For details on the parameters for each Chorus Type, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. Effect Edit Mode 143 Variation (VAR) Variation (VAR) The Variation section provides a wealth of additional effects for processing the Voices of the MU100R. It features some of the same effects found in the Reverb, Chorus and Insertion sections. This is not mere redundancy; it allows you to use two types of Reverb, Chorus or other effects on different Voices. For example, you may want to have the Flanger effect on one Voice and Phaser on another. Variation also gives you many special effects not found in the other sections, such as Delay, Gate Reverb, Wah and Pitch Change. The Variation section of effects can be applied either to a single selected Part or to all Parts, depending on the connection setting: Insertion or System. (See About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion on page 152 for more information.) Explanations of the Variation Type and other common parameters are given below. For specific descriptions of Variation Types and explanations for all other Variation parameters, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. Type Settings: 144 NO EFFECT; WHITE ROOM; TUNNEL; CANYON; BASEMENT; DELAY L,C,R; DELAY L,R; ECHO; CROSS DELAY; ER 1 — 2; GATE REVERB; REVERSE GATE; KARAOKE 1 — 3; CHORUS 1 — 4; CELESTE 1 — 4; FLANGER 1 — 3; SYMPHONIC; ENSEMBLE; DETUNE; AMBIENCE; ROTARY SPEAKER; 2WAY ROTARY SPEAKER; TREMOLO; AUTO PAN; PHASER 1 — 2, DISTORTION; COMP+ DISTORTION; OVER DRIVE; AMP SIMULATOR; 3BAND EQ (MONO); 2BAND EQ (STEREO); AUTO WAH (LFO); AUTO WAH+DIST; AUTO WAH+ODRV; TOUCH WAH 1; TOUCH WAH+DIST; TOUCH WAH+ ODRV; TOUCH WAH 2; PITCH CHANGE 1 — 2; AURAL EXCITER®; COMPRESSOR; NOISE GATE; VOICE CANCEL; TALK MOD; LO-FI; DIST+DELAY; ODRV+DELAY; CMP+DT+DLY; CMP+OD+DLY; WAH+DT+DLY; WAH+OD+DLY; THRU NOTE When NO EFFECT or THRU is selected for the Type, no Variation effect is applied, and only the common parameters shown below are available (with the exception of Dry/Wet). The NO EFFECT setting cancels the Variation effect. When the Variation Connection is set to SYS (System), the sound can be heard with no effect. When the Variation Connection is set to INS (Insertion), no sound is output for the Part. When set to THRU, the sound of the Part (or Parts) is output without any Variation effect. Generally, when Variation Connection is set to INS (Insertion), you should set the Type to Thru. When Variation Connection is set to SYS (System), you should set the Type to NO EFFECT. Effect Edit Mode Variation (VAR) Dry/Wet (Insertion connection) Range: Variation Connection (VarConnect) D63>W — (D=W) — D<W63 Adjusts the level balance of original sound (dry, or D) and processed sound (wet, or W). A setting of (D=W) results in an equal balance of dry and wet sound. Assignable Controller 1 Variation Control (AC1VarCtrl) (Insertion connection) Range: 000 — 127 Determines the amount of effect the Assignable Controller has on the Variation effect. Variation Pan (VarPan) (System connection) Range: Settings: INS (Insertion), SYS (System) Determines how the Variation effect is connected in the effect chain of the MU100R. When set to SYS (System), Variation is applied to all Parts, according to the amount of Variation Send set for each Part. When set to INS (Insertion), Variation is applied to only the selected Part, set in Send Variation parameters (see above). NOTE The common parameters above are common to nearly all the Variation effect types. (Exceptions are described in the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet.) L63 — C — R63 Determines the pan position of the Variation effect. Send Variation to Chorus (SendVar→Cho) (System connection) Range: 000 — 127 Determines the amount of Variation effect sound that is sent to the Chorus effect. Send Variation to Reverb (SendVar→Rev) (System connection) Range: 000 — 127 Determines the amount of Variation effect sound that is sent to the Reverb effect. Effect Edit Mode 145 Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2) Insertion 1, 2 (INS 1, 2) The Insertion 1 and 2 effects provide additional effects for processing individual Parts. Explanations of the Type, Dry/Wet Balance and Part parameters are given below. For descriptions and explanations for all other parameters, refer to the separate SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA booklet. The Insertion effects are set up for Insertion routing and can be applied only to a single selected Part. Refer to About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion on page 152 for more information. Type Settings: THRU; HALL 1 — 2; ROOM 1 — 3; STAGE 1 — 2; PLATE; DELAY L,C,R; DELAY L,R; ECHO; CROSS DELAY; KARAOKE 1 — 3; CHORUS 1 — 4; CELESTE 1 — 4; FLANGER 1 — 3; SYMPHONIC; ENSEMBLE DETUNE; ROTARY SPEAKER; TREMOLO; AUTO PAN; PHASER 1; DISTORTION; OVER DRIVE; AMP SIMULATOR; 3BAND EQ (MONO); 2BAND EQ (STEREO); AUTO WAH (LFO); TOUCH WAH 1 — 2, AURAL EXCITER®, COMPRESSOR; NOISE GATE Assignable Controller 1 Insertion 1/2 Control (AC1INS1/2Ctrl) Range: –64 — +63 This determines the degree to which Assignable Controller 1 (AC1) affects the MIDI-controllable parametes of the Insertion effects. Each of the Insertion effect types have one parameter which can be controlled by the AC1. (For details, see the “Effect Parameter List” of the “SOUND LIST & MIDI DATA” booklet.) This parameter is not available in the performance mode. Insertion 1, 2 Part (INS 1, 2 Part) Range: Part 1 — 32, AD 1, AD 2, off NOTE When Thru is selected, no effect is applied, and none of the parameters are available (with the exception of the Part parameter). Dry/Wet Balance Range: D63>W — (D=W) — D<W63 This determines the balance between the direct, unprocessed signal (dry) and the processed sound (wet). Use this parameter together with the Output Level parameter above to obtain the desired overall sound. 146 This determines the Part to which the Insertion effect is applied. Insertion can be applied to only one Part at a time. Effect Edit Mode Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters Path: [EFFECT] button → “PLG” → “PLG100-VH” These parameters control the Harmony effect. Other Harmony parameters not included in this section are the MIDI channel settings for the harmony and melody, which are set in the Utility mode (see page 171). For general information on the Harmony effect and how to use it, refer to the Guided Tour section, page 77. Type Settings: THRU, VOCODER HM, CHORDAL HM, DETUNE HM, CHROMAT.HM (Chromatic) NOTE When more than three MIDI notes are received (or two notes, when the Lead Gender Type parameter is set to any setting but “off”), priority is given first to the most recently played notes. (In other words, the harmonies of earlier notes are cut off.) This determines the Type of the Harmony effect (as explained below). For information on how each of these Types can be set, refer to the Mode parameter (page 148), which features different settings depending on the Type. Other Harmony parameters may or may not be available, depending on the Type selected here. Hint The Vocoder Type is best suited when: • You want to determine the precise harmony notes yourself, including their octave register and whether they are above or below the original melody note. • You want to use harmony notes and voicings that fall outside the standard chords available in the Chordal type (below). • You can play the harmony part on the keyboard, or have it played on a sequencer. • You want to precisely control how the harmony note or notes change pitch around a fixed melody pitch. Thru Chordal No Harmony effect is applied. This produces up to three harmony notes that correspond to the chords you play on a connected MIDI keyboard (or chords recorded to a sequencer). For example, if you play a C major triad on the keyboard and sing C note (and Chordal Mode is set to “trio”), the resulting harmonies will be C, E, and G. Thirty-four different chord types are recognized in this mode (see list below), giving you an amazingly full and flexible palette of harmonies, suitable for nearly any music style. The number of harmonies produced and their position above or below the melody is set in the Mode parameter (page 148). NOTE When Thru is selected, the only other available parameter is Insert Part (page 151). Vocoder This produces up to three harmony notes whose pitches correspond to the notes you play on a connected MIDI keyboard. In other words, you can sing the melody and “play” the harmony or harmonies from the keyboard (or from a sequencer). The Harmony sound can also be transposed (see the Mode parameter below). Effect Edit Mode 147 Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters In general, the Chordal Type is best suited when you want to simply play the chords and have the Harmony effect automatically sort out the suitable notes. For Vocoder Type: no trans No transposition. The harmony notes correspond exactly to the pitch of the incoming MIDI notes. Chords Recognized in Chordal Type Detune auto trans This produces a slightly “detuned” pitch and mixes it with the input signal for a rich chorusing effect. The amount of the detuning is set in the Mode parameter. MIDI note data from a keyboard or sequencer has no effect in this type. Automatic transposition of the harmony notes. This keeps the harmony notes close (±600 cents) to the input signal, no matter which octave the MIDI notes are played. For example, if your vocal is at a pitch of C3, playing an E note anywhere on the connected MIDI keyboard results in a harmony note of E3. NOTE When Detune is selected, the Harmony Gender Type and Lead Pitch Correction parameters are not available. Chromatic (CHROMAT.HM) This produces a harmony at a fixed pitch interval from the original sound (such as an octave, or a third). The amount of the pitch shift is set in the Mode parameter. MIDI note data from a keyboard or sequencer has no effect in this type. This fixes the octave transposition of the harmony notes, selectable from 3 octaves below (-) to 3 octaves above (+). For Chordal Type: duet above (Duet Above) Produces one harmony note, in a pitch above the lead note. duet below (Duet Below) Mode Settings: -3oct trns — +3oct trns (Available settings differ depending on selected Type; see below.) Produces one harmony note, in a pitch below the lead note. duet abv+b (Duet Above + Bass) Produces two harmony notes — one in a pitch above the lead note, and one an octave below the chord root harmony. (The “+b” in the type name stands for “added bass note.”) trio above (Trio Above) Produces two harmony notes, in pitches above the lead note. trio a&b (Trio Above & Below) Produces two harmony notes — one in a pitch above the lead note, and one below. 148 Effect Edit Mode Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters trio below (Trio Below) 3rd below Produces two harmony notes, in pitches below the lead note. Produces a major third harmony note in the octave below the input note. (Harmony is transposed eight semitones down.) trio a&b+b (Trio Above & Below+Bass) Produces three harmony notes — one in a pitch above the lead note, and two below — one of them an octave below the chord root harmony. (The “+b” in the type name stands for “added bass note.”) 5th below Produces a perfect fifth harmony note in the octave below the input note. (Harmony is transposed five semitones down.) quar above (Quartet Above) unison Produces three harmony notes, in pitches above the lead note. Produces a “harmony” note at the same pitch as the input note. (This can be clearly distinguished from the original signal by changing the Harmony Gender; see below.) quar a&b (Quartet Above & Below) Produces three harmony notes — two in pitches above the lead note, and one below. quar below (Quartet Below) Produces three harmony notes, in pitches below the lead note. 3rd above Produces a major third harmony note in the same octave as the input note. (Harmony is transposed four semitones up.) 5th above For Detune Type: low Detunes the pitch by ±7 cents (least amount of detuning). Produces a perfect fifth harmony note in the same octave as the input note. (Harmony is transposed seven semitones up.) oct above Produces a harmony note an octave above the input note. mid-low Detunes the pitch by ±11 cents. Harmony Gender Type (H.GendrTyp) mid-high Detunes the pitch by ±15 cents. Settings: off, Auto high Detunes the pitch by ±20 cents (most amount of detuning). For Chromatic Type: oct below Produces a harmony note an octave below the input note. This determines the gender of the harmony notes. When set to “off,” the gender of the harmony notes does not change (relative to the actual gender of the singer). When set to “Auto,” keep in mind that the gender change effect may vary according to the quality, character and pitch of the actual voice. Effect Edit Mode 149 Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters NOTE The Harmony Gender Type parameter is not available when Harmony Type is set to Detune (page 147). Lead Gender Type (L.GendrTyp) Settings: off, unis (unison), male, fem. (female) These settings determine whether the gender of the “lead” voice can be changed or not. It also lets you set the gender. When this is set to “off,” the gender of the lead voice cannot be changed. When this is set to “unis” (unison), the lead voice is reproduced at the same pitch as the voice; however, the gender can be changed by using the Lead Gender Depth parameter below. The “male” and “fem.” (female) settings reproduce the voice with the respective male or female vocal qualities. (To finely adjust the quality of the lead voice, use the Lead Gender Depth parameter below.) You can control the pitch of the lead voice separately from the harmonies. One useful application would be to have melody and harmony data on different tracks/ MIDI channels of sequencer song data — the melody track would control the pitch of the lead voice, while the harmony track would control the harmonies. This would ensure that all vocal parts stay in tune with each other and with the song — even if your actual singing is slightly off pitch! To control the pitch of the lead voice from a connected MIDI keyboard or sequencer (separate from the harmonies), make the following settings: Lead Gender Type — “unis”, “male”, or “fem.” Pitch Correction — “on” Melody Channel (page 171) — Set to same channel as the MIDI device. (Match this to the melody track of the song data.) Harmony Channel (page 171) — Set to different value from Melody Channel. (Match this to the harmony track of the song data.) NOTE When this is set to “unis”, “male” or “fem.”, up to two-part harmonies are provided. Using the Lead Voice To properly use the lead voice, make sure to set the following parameters: Lead Gender Type — “unis,” “male,” or “fem.” Lead Gender Depth — Set to desired/appropriate value. Lead/Harmony Balance — Set to appropriate value. (For values at or near the maximum of “L<H63,” lead may not sound.) 150 Effect Edit Mode Plugin (PLG) — Harmony Parameters Lead Gender Depth (L.GendrDpt) Range: Lead/Harmony Balance (Lead/Harm) Range: -64 — +63 This determines the quality or character of the lead voice, and depends on the setting made in Lead Gender Type above. (This parameter has no effect when Lead Gender Type is set to “off.”) Extreme negative or positive values result in pronounced distortion of the voice quality. Also, the effect may vary according to the quality, character and pitch of the actual voice. Experiment with this to find values that sound most natural (or unnatural, if you prefer). L63>H (maximum lead, minimum harmony) — L=H (equal level) — L<H63 (maximum harmony, minimum lead) This determines the relative balance of the lead and harmony voices. For most pop song applications, this should be set to “L=H” or a slightly higher lead level (such as “L10>H” or more). Insert Part (Ins Part) Settings: 01 — 32, AD01, AD02, off Lead Pitch Correction (PchCorrect) Settings: off, on This determines whether the pitch of the lead voice is controlled by MIDI note data or not. When this parameter and Lead Gender are set to “on,” the pitch of the lead voice is “corrected” to the pitch of the received MIDI note on Melody Channel (page 171). This determines the Part to which the Harmony effect is applied. For example, to apply Harmony to a microphone input through A/D INPUT 1, set this to “AD01.” When set to “off,” the Harmony effect is cancelled. NOTE The Pitch Correction parameter is not available when Harmony Type is set to Detune (page 147). Also, this parameter has no effect when Lead Gender Type is set to “off.” Effect Edit Mode 151 About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion The multi-effects of the MU100R provide not only a wide range of sound processing controls, but also a flexible system for connecting them. Unlike simple effect routing schemes on conventional sound modules that process all voices with the same effects, the MU100R allows you to put independent, special effects on one or two Parts, as well as use overall effects for processing all 34 Parts together. For example, you can have a Distortion effect on a guitar Part and a rotary speaker effect for an organ Part, yet still use ambient effects such as Reverb and Chorus for processing the overall mix. All the effect sections are connected or routed in one of two ways: System or Insertion. System applies the selected effect to all 34 Parts, while Insertion applies the selected effect to one specific Part. Reverb, Chorus, and EQ are all System effects, and Insertion 1 and 2, and Harmony are Insertion effects. The Variation effect section, on the other hand, can be configured for either System or Insertion routing. (This is done from the Variation Connection parameter; see page 145.) Since System and Insertion are part of the XG MIDI (Extended General MIDI) format, you can create and play back song data using the same flexible effect routings on any tone generator or sound module having the XG mark. NOTE The Variation Connection default setting is Insertion. The illustrations and explanations below cover the System and Insertion connections in greater detail. 152 Effect Edit Mode Effect Edit Mode insertion 1 on/off INS1 insertion 1 on/off INS1 insertion 1 on/off INS1 insertion 1 on/off insertion 2 on/off INS2 insertion 2 on/off INS2 insertion 2 on/off INS2 insertion 2 on/off Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony part Harmony can be applied to only one Part at a time. var send cho send rev send dry level var send cho send rev send dry level var send cho send rev send dry level var send cho send rev send dry level DRY LINE VARIATION send variation to reverb send variation to chorus CHORUS send chorus to reverb REVERB PAN chorus pan reverb pan PAN PAN variation return variation pan chorus return reverb return Thick line indicates stereo signal. EQ OUT NOTES • The Parts to which Insertion 1, 2 are applied is determined by the Part parameter in the Insertion section (page 146). • The Part to which Harmony is applied is determined by the Insert Part parameter in the Harmony Edit section (page 151). • Even though the System routing applies the selected effect to all Parts, you can control how much the Reverb, Chorus and Variation effects are applied to any individual Part (with the Reverb Send, Chorus Send and Variation Send parameters in the Single Part controls; see page 97). For the effects to be properly heard, the Reverb Return, Chorus Return and Variation Return parameters in the All Parts controls must also be set to appropriate values (see pages 98 — 99). • The stereo position of the effects is controlled by the Reverb Pan, Chorus Pan and Variation Pan parameters; see pages 142, 143, 145. • You can set Reverb, Chorus and Variation to be routed in parallel or in serial, and you can determine the amount of Variation effect that is sent to Chorus and Reverb, as well as the amount of Chorus that is sent to Reverb. This is done with the Send Variation to Chorus (page 145), Send Variation to Reverb (page 145), and Send Chorus to Reverb (page 133) parameters. When these are all set to 0, all three effects are in parallel routing. Higher values for each provide varying degrees of serial routing. part 32 part 1 part A2 part A1 INS2 insertion 2 part insertion 1 part INS1 Insertion 2 can be applied to only one Part at a time. Insertion 1 can be applied to only one Part at a time. VARIATION CONNECTION = SYSTEM About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion When Variation is set to System: 153 154 Effect Edit Mode insertion1on/off INS1 insertion1on/off INS1 insertion1on/off INS1 insertion1on/off INS2 insertion2 on/off INS2 insertion2 on/off INS2 insertion2 on/off INS2 insertion2 on/off insertion2 part insertion2 can be applied to only one Part at a time PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off PLG Harmony on/off Harmony part Harmony can be applied to only one Part at a time variation on/off VAR variation on/off VAR variation on/off VAR variation on/off VAR variation part Varationcan be applied to only one Part at a time dry cho send rev send dry cho send rev send dry cho send rev send dry cho send rev send DRY LINE CHORUS send chorus to reverb REVERB chorus pan PAN PAN reverb pan chorus return reverb return Thick line indicates stereo signal. EQ OUT NOTES • As with System above, the Parts to which Insertion 1, 2 are applied is determined by the Part parameter in the Insertion section (page 146). The Part to which Harmony is applied is determined by the Insert Part parameter in the Harmony Edit section (page 151). Also, the Part to which Variation is applied is determined by the Variation Send control in the Single Part controls (page 97). • As with System above, the effects cannot be properly heard unless the Reverb Send, Chorus Send and Variation Send parameters in the Single Part controls (page 97) and the Reverb Return and Chorus Return parameters in the All Parts controls are set to appropriate values. • The stereo position of the effects is controlled by the Reverb Pan and Chorus Pan parameters. (See pages 142, 143.) • You can set Reverb and Chorus to be routed in parallel or in serial, and you can determine the amount of Chorus that is sent to Reverb. This is done with the Send Chorus to Reverb parameter (see page 133). When this is set to 0, Reverb and Chorus are in parallel routing. Higher values for each provide varying degrees of serial routing. part32 part1 part A2 part A1 INS1 insertion1 part insertion1 can be applied to only one Part at a time About the Effect Connections — System and Insertion When Variation is set to Insertion: Equalizer (EQ) Edit The Equalizer (EQ) Edit parameters allow you to adjust the overall tone of the MU100R sound in five separate frequency bands. EQ presets are also provided for instantly calling up tone settings specially suited for different types of music. Low Lo Mid Mid Hi Mid High 0 dB Frequency To enter the Equalizer Edit mode, press the EQ button. EQ Type Settings: Concert: Flat, Jazz, Pops, Rock, Concert EQ Type provides five different preset EQ settings, specially programmed for specific types of music. The Flat setting is a “flat” EQ preset with no change in equalization. Jazz, Pops, Rock and Concert each have different EQ settings and frequency bands, specially suited for those types of music. EQ Frequency Parameters Thru: Jazz: Pops: Rock: 80 Hz, 500 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 4.0 kHz, 8.0 kHz 50 Hz, 125 Hz, 900 Hz, 3.2 kHz, 6.3 kHz 125 Hz, 315 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 2.0 kHz, 5.0 kHz 125 Hz, 200 Hz, 1.2 kHz, 2.2 kHz, 6.3 kHz Range: 80 Hz, 315 Hz, 1.0 kHz, 6.3 kHz, 8.0 kHz –12 — +12 dB The remaining EQ parameters let you set the level of each of the five frequency ranges: low, low-mid, mid, high-mid and high. The bars in the display show the EQ settings as a frequency “curve,” with peaks indicating level boosts in the frequency range and valleys indicating level cuts. A setting of 00 dB corresponds to no level change. NOTE Changing the EQ Type automatically restores the default Frequency Parameter settings and cancels any Frequency Parameter settings you have made. Equalizer (EQ) Edit 155 Utility Mode The Utility mode lets you set functions related to the overall operation of the MU100R, such as Master Tune, display contrast and playing of the Demo Song. Included also are utility operations, such as various kinds of data transfer with an external data storage device, and initializing of the MU100R settings. To enter the Utility mode, press the UTIL button. The following menu appears: System Functions (SYS) ............................................................... 157 Dump Out Functions (DUMP) .................................................... 161 Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI ................................... 161 Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST ............................ 161 Initialize Functions (INIT) ........................................................... 165 Demo Song Play (DEMO) ........................................................... 168 VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) ............... 169 VL Voice System Parameters ............................................... 169 Harmony System Parameters .............................................. 171 156 Utility Mode System Functions (SYS) System Functions (SYS) The System functions provide various controls of the overall operation of the MU100R, such as Master Tune, Mute and A/D Part Lock, some MIDI receive filters and a display Contrast control. Master Tune (M.Tune) Range: A/D Part Lock –102.4 — +102.3 cents (approx. +/– 1 semitone) Settings: This determines whether or not the current parameter values and Variation effect settings of the A/D Parts are reset when receiving a GM System On or XG System On message. If you want to keep the current parameter values and Variation settings of the A/D Parts, set Mute Lock to on. (This parameter has no effect in the Performance mode.) This determines the overall fine tuning of the MU100R’s Voices. It also affects the pitch of the individual drum/percussion sounds of the drum kits. Master Tune is especially useful for adjusting the pitch of the MU100R when playing with other instruments. The actual pitch of each Voice depends also on the other pitch related parameters: Key (in Play mode) and Detune (in Edit mode). NOTE At around 440 Hz, 1 Hz is approximately equal to 4 cents. off, on Multi Mode Equalizer Lock (Mlt EQ Lock) Settings: off, on Mute Lock Settings: off, on This determines whether or not the Part Mute status of the MU100R is reset when receiving a GM System On or XG System On message. Generally, this message is automatically transmitted to the MU100R as part of General MIDI song data. When Mute Lock is set to off, this resets the Mute status of the Parts on the MU100R. If you want to keep the current Mute settings and disable this reset, set Mute Lock to on. (For more information on the Mute function, see page 85.) Utility Mode This determines whether the Equalizer settings (page 155) are initialized or change in response to incoming MIDI messages. When this is set to “on,” the current Equalizer settings are maintained, ignoring any EQ-related messages that are received with XG System On or GM System On messages, allowing you to protect your original Equalizer settings. When set to “off,” the Equalizer changes according to incoming XG/GM System On messages. This setting affects the Multi mode only, and not the Performance mode. 157 System Functions (SYS) Output Select Lock (OutSel Lock) Settings: Receive System Exclusive (RcvSysExcl) on, off Settings: This determines whether or not the Output Select settings (pages 113, 118) are reset when receiving a GM System On or XG System On message. It also determines whether the Output Select setting for a Part can be edited via MIDI or not. If you want to “lock” the Output Select settings and keep them from being changed, set this to “on.” off, on This determines whether System Exclusive messages are received or not. System Exclusive messages are data specifically (or “exclusively”) related to the MU100R. The On setting allows these messages to be received. This should be to On when receiving bulk data from a MIDI data storage device. (See page 18.) Receive Bank Select (RcvBankSel) Receive General MIDI Exclusive (RcvGMExcl) Settings: off, on off, on This determines whether GM System On or XG System On messages are received or not. The on setting allows these messages to be received. 158 Settings: Utility Mode This determines whether Bank Select messages are received or not. Bank Select messages can be sent from another MIDI device to change the banks of Voices on the MU100R. (See page 31.) The On setting allows Bank Select messages to be received. System Functions (SYS) Thru Port Contrast Range: Range: 1—8 This determines the contrast of the display. Adjust this as necessary for optimum visibility. (At extreme settings, the display may not be readable.) Dump Interval (DumpIntrval) Settings: 50, 100, 150, 200, 300 This determines the length of time the MU100R pauses when sending blocks of data in the Dump Out functions. If the receiving device fails to process the data or displays a “buffer full” type message, try setting this parameter to a higher value and send the data again. 1—8 Some MIDI devices and sequencers are capable of transmitting data over several MIDI “ports,” effectively breaking the 16channel barrier. When this data is received via the TO HOST terminal on the MU100R, this parameter determines which MIDI port’s data will be routed through the MIDI OUT terminal. This allows you to connect another multitimbral tone generator to the MU100R and play back data over 48 independent MIDI channels — 32 on the MU100R and another 16 on the connected tone generator. NOTE The MU100R can receive Cable messages (F5) when the TO HOST terminal is connected to the serial terminal of a computer. On the MU100R, MIDI receive channels A1 — A16 are controlled from Port 1, and channels B1 — B16 are controlled from Port 2. If the software you are using can address separate MIDI ports, data can be received over 32 channels simultaneously, allowing 32 parts to be played with only one serial cable. By connecting another multitimbral tone generator to the MIDI OUT terminal of the MU100R and setting the Thru Port function to a value other than 1 or 2, you can play back data over a total of 48 MIDI channels — 32 on the MU100R and another 16 on the connected tone generator. Thru Port setting: 3—8 MIDI OUT POWER ON/ OFF MIDI IN Port 1: Channels A1 — A16 Port 2: Channels B1 — B16 Computer and Software with multiple-port capability Tone Generator Utility Mode 159 System Functions (SYS) Display Bank Select (DispBankSel) Settings: Voice Map (Map) 1 (displays only banks with unique Voices), 2 (displays all banks) This determines whether the MU100R displays all Voice banks or not when changing banks. (For information on changing banks, see page 28.) When this is set to “1,” the MU100R conveniently skips over banks that have the same Voice. In other words, when you step through the available banks, the display stops only on banks for which the Voice is unique or different (for the selected program number). If “2” is selected, all banks are displayed in succession, regardless of whether the Voices are the same or not. The Display Bank Select setting itself cannot be changed by incoming MIDI messages. 160 Utility Mode Settings: MU basic, MU100Native This determines the Voice configuration or assignment of the XG Voice set of the MU100R. This parameter should be set to match particular types of song data. For playback of data recorded on or intended for the MU90R, MU80, and MU50, set this to “MU basic.” For playback of other GM- and XG-compatible data, as well as the most recent song data (especially that intended for the MU100R), this should be set to “MU100Native.” NOTES • Only the Voice map of the basic Voice bank (MSB = 0, LSB = 0) is affected by this parameter. The other extended Voice banks are not affected. • This setting is not affected by incoming XG System On or GM System On MIDI messages. Dump Out Functions (DUMP) Dump Out Functions (DUMP) The Dump Out functions allow you to save the various settings of the MU100R (such as settings for Parts, Performances, system, etc.) to a MIDI sequencer, computer or a MIDI data recorder (such as the Yamaha MDF2 MIDI Data Filer). The following illustrations show example connections for the Dump Out functions. Saving and Restoring Data via MIDI MU100R MIDI OUT POWER ON/ MIDI IN MIDI Data Recorder OFF MIDI IN MIDI OUT Bulk Dump data can be sent and received using the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT connections. Saving and Restoring Data via TO HOST MU100R POWER TO HOST ON/ OFF Computer SERIAL PORT (with sequencer or MIDI librarian software) Bulk Dump data can be sent and received using the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT connections. Operation 1 Make sure that the MU100R is properly connected to the device and that the HOST SELECT switch is properly set. When using the MIDI terminals, connect the MIDI OUT of the MU100R to the MIDI IN of the data recorder. (See the illustrations above.) Also, set the HOST SELECT switch to MIDI. When using the TO HOST terminal, make sure that the HOST SELECT switch is set corresponding to the device to be used. (Refer to page 19 for more on host computer connections.) Utility Mode 161 Dump Out Functions (DUMP) 2 Press the UTIL button and select “DUMP,” then press the ENTER button. 3 From the Dump Out menu, select the type of data to be sent: All, Multi or Performance. Then, press the ENTER button to call up the selected data dump. All This transmits all MU100R data (including Part, Performance, system, and all parameter values) to the connected device. 162 Utility Mode Dump Out Functions (DUMP) Multi Settings: 32 Parts, 16 Parts, 32 Parts + A/D, 16 Parts + A/D This transmits the selected MU100R Multi Part data (including System, Effect and EQ data) to the connected device. (Use the VALUE -/+ buttons to select the type/amount of data to be transmitted.) Performance (PERFORM) Settings: ALL, I 001 — I 100 (Internal Performance numbers) This transmits the selected MU100R Performance data to the connected device. (Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to select the type/amount of data to be transmitted.) 4 From the “Are you sure?” prompt, press the ENTER button to execute the operation, or press the EXIT button to cancel it and return to the Dump Out menu. A “Transmitting…” message appears in the display during the operation. When the transmission is completed, the MU100R returns to the Dump Out menu. NOTE If you have more than one MU100R connected in your MIDI system and wish to send different sets of data to each, you can specify a different Device Number for each. (See page 98.) You should set the Device Number on each MU100R you use, before dumping the data to a data storage device. Then, when you reload the data to the connected MU100Rs, each unit will automatically receive only the data that has the corresponding Device Number. Utility Mode 163 Dump Out Functions (DUMP) To reload the data from the data recorder back to the MU100R: Make sure that the devices are properly connected (see the Restoring Data illustrations on page 18), and execute the appropriate data transfer operation from the data recorder. (Refer to the owner’s manual of that device for instructions.) The MU100R automatically receives incoming bulk data. 164 Utility Mode Initialize Functions (INIT) Initialize Functions (INIT) The Initialize functions allow you to restore the factory settings of the MU100R. NOTE Since the Initialize functions replace existing data, you should save any and all important settings to a MIDI data storage device before using these functions. (See page 18.) Operation 1 Press the UTIL button and select “INIT,” then press the ENTER button. 2 From the Initialize menu, select the type of data to be initialized: Factory Settings (FactSet), selected Sound Module mode (XGInit, GM Init, C/MInit, PFMInit) or Drum (DrumInit) Then, press the ENTER button to call up the selected data dump. Utility Mode 165 Initialize Functions (INIT) Factory Settings (FactSet) This restores the original factory settings of the MU100R. NOTE This function replaces internal performance data to the “Internal Performance 2.” To restore the “Internal Performance 1” (loaded at first), load the data from included floppy disk. (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) Selected Sound Module Mode: Extended General MIDI (XGInit) General MIDI (GM Init) Computer Music (C/MInit) 166 Utility Mode Initialize Functions (INIT) Performance (PFMInit) One of the four parameters above will be available, depending on the currently selected Sound Module mode: XG, TG300B, C/M or PFM. Initializing this parameter restores the original settings for the selected mode. NOTES • For the PFMInit setting, only the currently selected Performance will be initialized. • For XGInit and GM Init, the initialized settings are the same as when the MU100R is reset upon receiving an XG System On or GM System On message. Drum (DrumInit) Range: DrumS1 — DrumS4 This restores the original drum settings for the selected Drum Setup S1 — S4. (Use the VALUE -/+ buttons or data dial to select the desired Drum Setup.) NOTE This parameter is not available when the MU100R is set to Performance mode. 3 From the “Are you sure?” prompt, press the ENTER button to execute the operation, or press the EXIT button to cancel it and return to the previous display. An “Executing…” message appears in the display during the operation. When the operation is completed, the MU100R returns to the Initialize menu. Utility Mode 167 Demo Song Play (DEMO) Demo Song Play (DEMO) The Demo Song function in the Utility menu allows you to play the built-in Demo Song. Operation 1 Press the UTIL button and select “DEMO,” then press the ENTER button. 2 Press the ENTER button to start the Demo Song. The Demo Song starts playing immediately and repeats indefinitely until stopped (in step 4 below). Playback of the individual Parts of the song is shown graphically by the “level meter” bars in the display. NOTE During Demo Song playback, no panel controls (with the exception of the EXIT button and the VOLUME control) can be used. 3 To stop playback of the song, press the EXIT button. 4 To exit from the Demo Song function, press the EXIT button again. 168 Utility Mode VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) VL Voice and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) VL Voice System Parameters Path: [UTIL] button → “PLUGIN” → “PLG100-VL” These parameters include assignment of the Part for the VL Voice, as well as other controls that affect overall operation. For more information on the VL Voices and how to use them, refer to page 62. Part Assign Details • The “Expd” setting is recommended when using a WX controller in the “tight lip” mode. The “Norm” setting is recommended when using the WX controller “loose lip” mode. • The settings made here are effective only for the internal VL tone generator. Settings: In XG Mode: 01 - 16, off In Performance Mode: 01 - 04, off Breath Mode This determines the Part to which the VL Voice is assigned. If a Part is not properly assigned here, none of the VL Voice banks can be selected for the Part. NOTE The VL voices cannot be assinged to several Parts at one time since the VL tone generator section is monophonic. WX Lip Mode Settings: Norm, Expd WX-series Wind MIDI Controllers produce pitch bend data ranging from “-16” to “+32” in response to lip (reed) pressure. The WX Lip parameter determines whether these values are used as is (“Norm”), or expanded to a full “-64” through “+63” range (“Expd”). This is also effective for pitch bend data transmitted from devices other than those of the WX-series. Utility Mode Settings: BC/WX, Vel, TchEG Sets the control source to be used for “breath” control. This parameter should be set to “BC/WX” when a breath controller or Yamaha WX-series Wind MIDI Controller is being used. When “Velocity” is selected, breath variation is controlled by keyboard initial touch response. When “Touch EG” is selected, breath variation is controlled by a combination of initial keyboard touch response and aftertouch pressure. Initial key velocity sets the initial breath level, and aftertouch pressure determines the shape of the subsequent breath envelope. 169 VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) Breath Control Settings: BC, Exp This determines the MIDI control change number to be used for breath control of the VL Voice, when breath controller data (number 02) is received via MIDI. When “BC” is selected, control number 02 (breath control) is used. When “Exp” is selected, control number 11 (expression) is used. Breath Curve Range: -16 — +16 Determines the relationship between breath controller data (number 02) received via MIDI, and the actual amount of breath variation applied. Negative settings result in a large breath variation with a relatively small amount of breath pressure applied to the controller, while positive settings require a greater range of input breath control values to produce the same degree of breath variation. Details • This is also effective for breath controller data transmitted from devices other than those of the WX-series. • The settings made here are effective only when “BC/WX” is selected for the Breath Mode. 170 Utility Mode VL Voices and Harmony System Parameters (PLUGIN) Harmony System Parameters Path: [UTIL] button → “PLUGIN” → “PLG100-VH” These parameters include the MIDI channel settings for the harmony and melody. For general information on the Harmony effect and how to use it, refer to the Guided Tour section, page 77. Harmony Channel (Harmony Ch) Settings: off, 1 - 16 This determines the MIDI channel over which the Harmony effect is controlled. For example, when this is set to the same value as the MIDI transmit channel of a connected MIDI keyboard and the Vocoder or Chordal Harmony Type is selected (page 147), you can use the keyboard to “play” harmonies. (See page 77.) Melody Channel (Melody Ch) Settings: off, 1 - 16 This determines the MIDI channel over which the lead sound of the Harmony effect is controlled. For example, when this is set to the same value as the MIDI transmit channel of a connected MIDI keyboard, you can use the keyboard to control the pitch of the lead sound. Utility Mode 171 Sound Module Mode (MODE) This lets you select the operating mode of the MU100R. Press the MODE button, then use the SELECT </> buttons to select the desired Sound Module mode: XG (Extended General MIDI), TG300B (General MIDI), C/M (Computer Music) or PFM (Performance). If XG, TG300B or C/M are selected, the MU100R automatically sets itself to the Multi mode. When PFM is selected, the MU100R is in the Performance mode. (See page 6.) The bottom right of the display indicates the currently selected Sound Module mode. XG TG300B C/M PERFORM Arrow indicates selected Sound Module mode. Press the EXIT button (or any one of the other mode select buttons: PLAY, EDIT, UTIL, EFFECT or EQ) to use the MU100R in the current mode. NOTES • When the MU100R is not set to the XG mode and an XG System On message is received, the MU100R changes to the XG mode after a slight pause of 0.5 seconds. • When the TG300B or C/M mode is selected, the VL Voices and Harmony effect cannot be used. • In the C/M mode, the Voices available in Parts 11 - 16 are different from those available in Parts 1 - 9. (Refer to the “Sound List & MIDI Data” booklet.) • The TG300B mode also has multiple banks. In the C/M mode, there is only one bank (“Fix” appears at the Bank Number parameter), and for the drum Part only one drum kit can be selected. 172 Sound Module Mode (MODE) Show Control Change Miscellaneous Functions Show Control Change This function allows you to view the currently used control change number, its type and its value (in decimal format). It also lets you transmit the displayed value with a single button press. Operation 1 From the Multi Play mode or Performance Play mode, doubleclick the ENTER button (press it twice quickly). (The Show Control Change display appears.) Type of controller Number of controller Current value 2 To transmit the currently displayed message, press the ENTER button again. The message is transmitted via the MIDI or TO HOST terminals. 3 Press the EXIT button to return to the Play display. Miscellaneous Functions 173 Show Control Change This is convenient for quickly entering desired settings to a sequencer. Displaying/Sending Voice Bank Settings The Show Control Change function also allows you to view and send Voice bank MSB and LSB settings within the XG mode. To do this: 1) From the Multi Play mode (XG mode), select the desired bank number. (For information on selecting banks, see page 28.) 2) With the bank number parameter highlighted, double-click the [ENTER] button. 3) Press the [EXIT] button to return to the Play display. NOTE MSB/LSB values are used in conjunction with each other to provide a greater number of banks than would be possible with the 128-number limit of MIDI's hexadecimal system. For example, the XG Voices are contained on banks 000 - 127; these banks are selected over MIDI with the MSB value of 000. MU100 Exclusive Voice banks are at MSB 048. For more information on MSB and LSB values, see page 30. 174 Miscellaneous Functions Show Exclusive Show Exclusive This function allows you to view the current system exclusive message (in hexadecimal format). It also lets you transmit the displayed value with a single button press. Operation 1 Double-click the ENTER button (press it twice quickly). (The Show Exclusive display appears.) System Exclusive message (in hexadecimal format) 2 To transmit the currently displayed message, press the ENTER button again. The message is transmitted via the MIDI or TO HOST terminals. 3 Press the EXIT button to return to the previous display. Miscellaneous Functions 175 176 Miscellaneous Functions A PPENDIX Troubleshooting Troubleshooting Even though the MU100R is exceptionally easy to use, it may occasionally not function as you expect it to. If that happens, check the possible problems and solutions below before assuming that the instrument is faulty. Problem Possible Cause and Solution No power. If you are using an AC adaptor, check that the adaptor is properly plugged into both the AC outlet and the MU100R (See page 3.) No sound. Check that: ● The panel volume control is set to an appropriate level. ● Other volume-related parameters are set to appropriate levels. (See Volume and Expression in the Single Part controls, page 96, and Master Volume and Master Attenuator in the All Part controls, page 98.) ● Mute or Solo are not active. (See page 85.) If a Part is being muted, or an empty Part is being soloed, you may not get any sound. ● The Variation effect settings are appropriate. No sound will be output at all if Variation Connection is set to INS (page 145), Variation Send is turned on for the Part (page 97), and NO EFFECT is selected for the Variation Type (page 144). The easiest solution in such a case is to turn off Variation Send for the Part. ● The EG Attack Time (page 103) is appropriately short, for short percussive sounds. ● The Velocity Sensitivity Offset (page 111) is appropriate. ● The Note Limit Low and Note Limit High (pages 110, 136) settings are appropriate. If the former is set higher than the latter, no sound will be output. ● The Velocity Limit Low and Velocity Limit High (pages 111, 136) settings are appropriate. If the former is set too high and the latter too low, no sound may be output. No sound when playing the MU100R from a computer, sequencer or external keyboard. Check all MIDI connections, making sure that the MIDI OUT of the external device is connected to the MIDI IN of the MU100R, and that the MIDI IN of the external device is connected to the MIDI OUT of the MU100R. (See pages 17 – 19.) Or, if you are using the TO HOST terminal with a computer, make sure that the terminal is properly connected to the computer and that the HOST SELECT switch is properly set for your particular computer. (See pages 19 – 22.) Also, make sure that you have turned on the connected MIDI instrument or computer before turning on the MU100R. If you haven’t, simply turning the MU100R off and back on again may solve the problem. Notes are cut off or omitted. The maximum polyphony of the MU100R may be exceeded. The MU100R can play no more than 64 notes at once. (Though 64 notes may seem to be more than enough, you may run short when playing a connected keyboard along with some densely arranged song data.) Reverb, Chorus and/or Variation effects cannot be heard. Check all Reverb-, Chorus- and Variation-related controls: Reverb Send, Chorus Send and Variation Send in Single Part controls (page 97); Reverb Return, Chorus Return and Variation Return (when Variation Connection is set to SYS) in All Part controls (pages 98 — 99). Also check the individual effect settings; if no Type has been selected, or if the parameter settings are too low, there may be no effect sound. The A/D input sound (mic, guitar, etc.) cannot be heard. Make sure that the appropriate A/D Part (A1 or A2) has been turned on and that the A/D INPUT control is set to an appropriate level. Also for best results, make sure that the A/D input type (Mic, Guitar, Keyboard, Audio) is set to match the input you are using. VL Voice Section/ Harmony Effect The VL Voices and/ or Harmony effect cannot be used. Check the following points: ● The VL Voices and Harmony effect can only be used in the XG or Performance modes. ● The VL Voice must be assigned to a Part in the Part Assign parameter (page 169), and the Harmony effect must be assigned to a Part in the Insert Part parameter (page 151). ● The VL Voices can only be used with Parts 1 – 16. ● When using MIDI, the VL Voices and Harmony effect can only be controlled via the MIDI-A terminal. When using TO HOST, they can only be controlled via MIDI port 1. Other notes on VL Voices and Harmony effect: ● ● ● ● 178 The VL Voices and Harmony effect can be used in the Performance mode; however, the Store operation saves only edits made from the panel controls, and not any of the “hidden” parameters accessible via MIDI. When controlling certain VL Voice and Harmony effect parameters via MIDI, the value or setting displayed in the LCD may not change, even though the actual value does. Any edits made to the “hidden” VL Voices/Harmony effect parameters (accessible only via MIDI) are not saved; turning off the power automatically cancels these settings. When backing up VL Voice and Harmony effect data via MIDI, the time it takes for the data transfer may be quite long. Be careful not to turn off the power or disconnect the AC adaptor until the operation is completed. Appendix Troubleshooting Problem About VL Section Possible Cause and Solution Some voices sound as if they are in the original octave even when shifted down an octave. This is because Virtual Acoustic synthesis accurately simulates the acoustic behaviour of a pipe or string. Simply stated, the harmonic balance of the voice when played in the normal octave is retained even when the voice is shifted down an octave. The change in timbre can be greater or less, depending on the selected voice. Portamento produces more of a glissando effect on some voices. Trumpets and some other brass instruments tend to exhibit this phenomenon more than others. In a VA tone generator portamento is produced by lengthening or shortening the instrument's pipe or string and changing the Embouchure. A trumpet is designed to emphasize the “modes” of the pipe(s) to produce notes over a wide range using only three valves. When portameto is applied to a trumpet voice, the pitch tends to jump from mode to mode, thus producing the observed glissando effect. The same effect occurs with some flute voices. Saxophone modes are not nearly as strong as trumpet modes, but some sax voices do have two definite modes which, when spanned by a portamento slide, can produce irregularities. The filter, EG, and other parameters have more effect on some voices than others. Most voices use the low-pass filter type, but some use the bandpass, high-pass, or band eliminate types. Some voices use very little filter processing at all. Changing the filter settings may not produce a particularly noticeable effect. Also the internal Breath Noise, Throat Formant, Growl, Harmonic Enhancer and Pitch EG parameter settings can have a significant effect on how much the parameters accessible via the VL section controls actually affect the sound. Some bowed string instrument voices tend to “squeek”. As anyone who has played (or tried to play) a real violin knows, these instruments naturally tend to squeek if not properly controlled. The same occurs with VA synthesis. As with a real bowed string instrument, bow speed and pressure must be properly controlled in the VL section to produce the desired sound. Bow speed is usually controlled either via breath control or an expression pedal. Bow pressure is controlled via control number 13: “64” is medium pressure, lower values produced reduced bow pressure, and higher values produce increased bow pressure. Pitch bends produced by a pitch bend wheel are not always accurate. Natural acoustic musical instruments have no “pitch parameter”. Pitch is determined by the properties of the instrument’s resonant body as well as the condition of the instrument’s driver. The same applies to Virtual Acoustic Synthesis: in the VL section’s pitch bend is simulated by manipulating the appropriate pipe/string length and driver characteristics. As a result, the pitch bend range may not always be “mathematically” accurate. With reed instruments such as saxophone or clarinet, highly realistic pitch bends are produced by controlling both pitch and embouchure at the same time. Since the embouchure component of the pitch bend behaves with characteristics acoustic unpredictability, precise pitch bends are not always produced. Some voices don’t respond as expected to EG edits. The effect of editing envelope generator parameters may not always be as expected — particularly with plucked string instrument voices such as guitar or bass. This is because the VL section actually simulates the plucking, free oscillation, and muting of the strings rather than simply using an EG to approximate these events. If the sound of a string voice decays naturally, for example, setting a long release time will have little or no effect on the actual sound of the voice. Since the attack and decay portions of the voice also have natural timbre variations, these can be unnaturally altered by inappropriate EG settings — which is OK if you’re trying to produce an unnatural effect. Trial and experimentation and the only sure ways to determine how the EG parameters are going to affect a particular voice. The VL section is a monophonic tone generator. Why is the “poly” mode initialy selected when the VL-XG sound module mode is engaged? This is to provide compatibility between the currrent XG format and future polyphonic VL-series tone generators. It also provides a certain degree of compatibility to allow playback of VL-XG song data on existing tone generators which do not feature the VLXG extension. Specifically, to switch the VL section to the mono mode a “mono mode” command (control change no.126, value 0-16) is embedded in the song data which, when received by a 32-note or 64-note polyphonic XG tone generator, switches the appropriate parts to the mono mode. The same will apply to future polyphonic VL-series tone generators, so no changes will be required. The VL section therefore has a “poly” which is automatically selected when a MIDI “XG on” system exclusive message is received. Appendix 179 Error Messages Error Messages Battery Low! The battery voltage (for internal memory backup) may be too low. Bring the unit to your local Yamaha dealer or any other authorized Yamaha service personnel. Illegal Data! A data error resulted during reception of MIDI messages. Try transmitting the data again, or turn the MU100R off and back on again. MIDI Buffer Full! Too much MIDI data is being received by the MU100R at one time. Reduce the amount of data being sent to the MU100R. HOST is OffLine! This message appears when the host computer is not turned on, the connecting cable is not properly connected, or the sequencing software is not active. SysEx Adrs ERROR! The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the address of the message and try transmitting again. SysEx Data ERROR! The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the data of the message (as to whether it requires an MSB or LSB header) and try transmitting again. SysEx Size ERROR! The data of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the size of the message and try transmitting again. Check Sum ERROR! The checksum of the received System Exclusive message is incorrect. Check the checksum of the message and try transmitting again. This Parameter isn’t Excl Data The selected parameter has no System Exclusive value and cannot be displayed with the Show Exclusive function. No Parameter The selected parameter for use with the Show Exclusive function does not exist as a valid parameter. Rcv CH is OFF! The selected parameter for use with the Show Exclusive function cannot be converted to a MIDI message value since the Receive Channel for the Part is off. Set the Receive Channel to an appropriate value. 180 Appendix Specifications Specifications Tone Generation Method AWM2 (Advanced Wave Memory 2), Virtual Acoustic Synthesis System (VL) Maximum Simultaneous Polyphony 64-note + 1-note (VL) Sound Module Modes XG (Extended General MIDI), TG300B, C/M, and Performance Multi-timbral Capacity 32-Part (on 32 MIDI channels; with element reserve priority for later notes and dynamic Voice allocation) Internal Voice/Program Structure Normal Programs Total Voices ......................... 1267 + 256 (VL) XG mode ............................. 1074 + 256 (VL) TG300B mode .................... 614 C/M mode ........................... 128 (Parts 1 — 9), 64 (Parts 11 — 16) Drum Programs Total Programs .................... 46 XG mode ............................. 36 TG300B mode .................... 10 C/M mode ........................... 1 Performance Programs Up to four Voices plus all effect settings can be memorized to a Performance. Preset Programs .................. 100 User Programs .................... 100 Effects Six sections of multi-effects: Reverb (12 Types), Chorus (14 Types), Variation (70 Types), Insertion 1, 2 (43 Types), Harmony (4 Types), Effect and EQ (4 Types) Display Custom back-lit LCD Appendix 181 Specifications Controls VOLUME control; A/D INPUT level control; Mode select buttons: PLAY, UTIL (UTILITY), MODE, EDIT, EFFECT, EQ; other buttons: MUTE/SOLO, ENTER, EXIT, PART -/+, SELECT </>, VALUE -/+; data dial; POWER button Jacks and Terminals Front panel: PHONES jack (1/4"), A/D INPUT 1, 2 jacks (1/4"), Rear panel: INDIVIDUAL OUTPUT 1, 2 jacks; OUTPUT R, L/MONO jacks (Right, Left/Mono); DC IN jack; TO HOST terminal; HOST SELECT switch; MIDI IN A/B, MIDI OUT, and MIDI THRU terminals Computer/MIDI Interface Direct connection to host computer port (RS-232C, RS-422) with optional cables (CCJ-PC1, CCJ-PC1, CCJ-MAC); MIDI terminals allow connection to MIDI sequencer or MIDI controller Data Transfer (Baud) Rate MIDI Mac PC-1 PC-2 — — — — 31,250 bps (bits per second) 31,250 bps 31,250 bps 38,400 bps Power Supply Yamaha PA-5B AC Adaptor (included) Dimensions (W × D × H) 483 × 229 × 44 mm (19" × 9" × 1-3/4") Weight 2.4 kg (5 lbs., 5 oz.) Included Accessories Owner’s Manual, Yamaha PA-5B AC Adaptor Floppy Disk * Specifications subject to change without notice. 182 Appendix Glossary Glossary A/D input Abbreviation for analog-to-digital. The A/ D inputs of the MU100R allow you to process analog inputs (such as a microphone, electric guitar, CD player, or another electronic instrument) with the digital effects of the MU100R and mix them with the internal Voices. host computer The controlling computer in a computer music system. The host computer is connected to the MU100R (via the TO HOST or MIDI terminals) and runs the software necessary for recording and playing back song data, which is reproduced by the internal sound sources and effects of the MU100R. Assignable Controller 1 Certain functions on the MU100R (such as the Filter, Volume or Variation effect) can be changed in real time by controllers on a connected MIDI instrument. Assignable Controller 1 lets you determine which controller (for example: modulation wheel, breath controller, foot controller, etc.) is used for that purpose. LFO Abbreviation for low frequency oscillator, which generates a low frequency signal that is used to modulate certain aspects of the sound, such as pitch or level. Chorus, Flanger, Tremolo, Vibrato and other modulation effects use LFOs. AWM2 Abbreviation for Advanced Wave Memory 2, an enhanced version of Yamaha’s original tone generation system, featuring digital filters for superior sound. MIDI Acronym for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, a worldwide standard that allows MIDI-compatible instruments and devices to communicate with each other. For the instruments to communicate, they normally must be set to the same MIDI channel. bank A set of Voices or programs. The MIDI standard supports up to 128 banks, each of which can contain up to 128 Voices or programs. edit Editing is the process of changing or adjusting the settings of the MU100R. EG Abbreviation for Envelope Generator, a common control on electronic instruments that affects the “shape” (or envelope) of the sound in time. The MU100R provides two types of EGs: one for level and the other for pitch. Filter A control for affecting the frequency content of a sound. Filters are used to selectively cut or boost certain frequency ranges in the sound — subtly enhancing the sound, or dramatically changing its character. On the MU100R, the Filter can be controlled in real time with the Assignable Controller 1. General MIDI (GM) An addition to the MIDI standard which effectively ensures that any General MIDI-compatible song data can be properly played back on any General MIDI-compatible tone generator. The standard specifies that a GM-compatible tone generator must have at least 24-note polyphony, 16-part multi-timbral capacity and 128 standard voices. The MU100R exceeds this with 64note polyphony, 32-part multi-timbral capacity and 1523 Voices. modulation wheel A controller found on most MIDI keyboards which is normally used to control pitch and other types of modulation. It can be used to control various aspects of the MU100R sound by proper setting of the Assignable Controller 1. (See page 53.) multi-timbral This refers to the capacity of a tone generator to produce several different sounds at once. The MU100R is a 32-Part multi-timbral tone generator, capable of playing 32 different instrument Voices at once, each over an independent MIDI channel. Mute The Mute function of the MU100R allows you to silence one Part to hear how all of the other Parts sound without it. parameter The word “parameter” refers to any adjustable setting of an electronic musical instrument. For example, the Vibrato function of the MU100R has three parameters: Rate, Depth, and Delay. Part The Voices of the MU100R are assigned to separate Parts, and up to 32 of these Parts can sound simultaneously. Parts are analogous to the various instrumental parts in music: e.g., piano part, guitar part, etc. Appendix 183 Glossary Performance In the MU100R, “Performance” refers to an operation mode and the programs that are used in that mode. A Performance can contain up to four different Parts, all controllable over the same MIDI channel. The preset Performances of the MU100R are special multi-Part sound programs designed particularly for live performance and studio recording purposes. Pitch Bend A function found on virtually all MIDI keyboards (usually controlled with a pitch bend wheel) that allows the pitch to be raised or lowered continously. The Pitch Bend Control parameter on the MU100R allows you to set the range over which the pitch can be changed. polyphony The number of notes that can be sounded simultaneously by an electronic instrument. The MU100R has 64-note polyphony, ensuring that even the most complex song data will play back completely and accurately, with no “note robbing.” port To answer the need for more MIDI channels (the limit is 16), many MIDI interfaces offer two or more MIDI ports, each of which can address 16 MIDI channels. The MU100R is equipped with two independent MIDI ports (A and B), providing 32-channel operation. The two ports are also addressable via the TO HOST computer interface. Portamento A function found on early synthesizers that creates a continuous pitch glide between successively played notes. On the MU100R, the time of the pitch glide can be adjusted. return Related to effect operation, “return” refers to the effect-processed signal that is returned to the overall sound mix. For example, the parameter Reverb Return determines the amount of Reverb-processed signal that is blended with the overall sound mix of the MU100R. (“Return” is the companion function of “send” below.) send Related to effect operation, “send” refers to the signal that is sent to an effect for processing. For example, the parameter Reverb Send determines the degree to which an individual Part is processed with the Reverb effect. (“Send” is the companion function of “return” above.) Solo The Solo function of the MU100R allows you to isolate a single Part, to hear how that Part sounds by itself. Sound Module mode The MU100R has four Sound Module modes, and these determine the basic operation of the unit as a tone generator. Three Multi modes (XG, TG300B and C/M) and one Performance mode (PFM) are available. tone generator An electronic instrument that functions as a MIDI-controllable sound source. For the most part, the term “tone generator” refers to those devices that have no keyboard or other controller, but are meant to be connected to and played from a separate keyboard or computer. Variation In the MU100R, “Variation” refers to the special section of various effects, including Reverb, Delay, Chorus, and many others. The Variation effects total 70, and can be used simultaneously with the other effect sections of the MU100R: Reverb, Chorus, Insertion 1, 2 Harmony Effect and EQ. velocity The speed at which a note is played (for example, on a keyboard). Normally, the faster (or harder) a key is struck, the higher the corresponding note’s velocity — and, hence, the louder the sound produced. The MU100R features a variety of velocity-related parameters that provide extensive control over the velocity response of the Voices, and even allow you to set up sophisticated velocity splits, in which the Voices change in response to playing velocity. Vibrato Vibrato is a quavering, vibrating sound, and is produced in the MU100R by regularly modulating the pitch of a Voice. The speed and depth of the Vibrato can be adjusted, as well as the time it takes before the Vibrato effect is applied. Voice The basic sound unit (or sound program) of the MU100R. There are a total of 1523 Voices available on the MU100R. XG-MIDI An abbreviation for Extended General MIDI, a new standard created by Yamaha which significantly improves on the General MIDI standard by providing a greater variety of high-quality Voices and enhanced effect operation. sequencer A device used for recording, editing and playing back of MIDI data. Sequencers are generally of two types: “dedicated” sequencer units, and computer-based sequencing software. The MU100R can be used with either type. 184 Appendix Index Index A A/D input ................................................................ 87 A/D Part .......................................................... 87, 133 A/D Part Lock ....................................................... 157 Absorption Control Change Number .................... 124 Absorption Control Depth .................................... 125 All Part control ......................................... 35, 98, 128 Alternate Group (Drum Setup) ............................. 117 Assignable Controller 1 .......................... 53, 112, 133 Assignable Controller 1 Amplitude Control .................................................... 113, 133 Assignable Controller 1 Control Change Number ................................................... 112, 133 Assignable Controller 1 Filter Control ......... 112, 133 Assignable Controller 1 Insertion 1/2 Control ..... 146 Assignable Controller 1 LFO Filter Modulation Depth .......................................... 133 Assignable Controller 1 Variation Control ........... 145 B Bank (Performance mode) ...................... 24, 128–129 Bank Number (Multi mode) ............................. 27, 96 Breath Control ...................................................... 170 Breath Curve ......................................................... 170 Breath Mode ......................................................... 169 Breath Noise Control Change Number ................ 122 Breath Noise Control Depth ................................. 122 C C/M mode ................................................................. 6 Chordal Type ........................................................ 147 Chorus .................................................................. 143 Chorus Pan ............................................................ 143 Chorus Return (Multi mode) .................................. 98 Chorus Return (Performance mode) ..................... 128 Chorus Send (Drum Setup) .................................. 116 Chorus Send (Multi mode) ..................................... 97 Chorus Send (Performance mode) ........................ 130 Chorus Type .......................................................... 143 Chromatic Type .................................................... 148 Common parameters ............................................. 131 computer, connecting cables ................................... 19 computer, connecting MU100R with ..................... 19 computer, IBM PC and clones ................................ 21 computer, Macintosh .............................................. 19 connections, audio .................................................. 12 connections, MIDI .................................................. 17 Contrast ................................................................ 159 Copy ..................................................................... 137 Detune Type .......................................................... 148 Device number ........................................................ 98 Display Bank Select ............................................. 160 Drum Setup controls ............................................. 114 Dry Level ..................................................... 110, 136 Dry/Wet (Variation) .............................................. 145 Dry/Wet Balance (Insertion) ................................. 146 Dump Interval ....................................................... 159 Dump Out functions ............................................. 161 E Effect Edit mode ................................................... 141 effect connections (System and Insertion) ............ 152 EG (Envelope Generator) ............................. 102, 135 EG Attack (Drum Setup) ...................................... 117 EG Attack Time .................................................... 103 EG Decay 1 (Drum Setup) ................................... 117 EG Decay 2 (Drum Setup) ................................... 117 EG Decay Time .................................................... 103 EG Release Time .................................................. 104 Element Reserve ................................................... 109 Embouchure Control Change Number ................. 120 Embouchure Control Depth .................................. 121 EQ Frequency parameters .................................... 155 EQ High Frequency ...................................... 105, 117 EQ High Gain ............................................... 105, 117 EQ Low Frequency ....................................... 105, 117 EQ Low Gain ................................................ 105, 117 EQ Type ................................................................ 155 Equalizer (EQ) ................................ 80, 105, 135, 155 Expression .............................................................. 97 F Filter ............................................................. 100, 135 Filter EG Depth .................................................... 120 G Growl Control Change Number .......................... 122 Growl Control Depth ............................................ 123 H Harmonic Enhancer Control Change Number ..... 123 Harmonic Enhancer Control Depth ...................... 124 Harmony Channel ................................................. 171 Harmony Parameters ............................................ 147 Harmony Gender Type ......................................... 149 Harmony Type ...................................................... 147 HPF Cutoff Frequency (Drum Setup) .................. 116 HPF Cutoff Frequency (Multi mode) ................... 101 D Damping Control Change Number ....................... 124 Damping Control Depth ....................................... 124 Demo song ...................................................... 15, 168 Detune .......................................................... 108, 136 I Individual outputs ............................................... 3, 83 Initialize functions ................................................ 165 Insert Part .............................................................. 151 Appendix 185 Index Insertion connection ..................................... 145, 152 Insertion 1, 2 effects ............................................. 146 Insertion Part ........................................................ 146 Insertion Type ....................................................... 146 L Lead Gender Depth ............................................... 150 Lead Gender Type ................................................ 150 Lead Pitch Correction ........................................... 151 Lead/Harmony Balance ........................................ 151 Level (Drum Setup) .............................................. 115 LPF Cutoff Frequency (Drum Setup) ................... 116 LPF Cutoff Frequency (Multi mode) .................... 101 LPF Resonance (Drum Setup) .............................. 116 LPF Resonance (Multi mode) ............................. 101 M Master Attenuator ................................................... 98 Master Tune .......................................................... 157 Master Volume ........................................................ 98 Melody Channel ................................................... 171 MIDI channel .................................................. 96, 128 MIDI data flow (diagram) ...................................... 91 MIDI data storage device ....................................... 18 MIDI devices, connecting to .................................. 17 MIDI keyboard, playing the MU100R with ........... 17 MIDI keyboard, selecting Voices with ................... 31 MIDI, Receive Channel .................................. 96, 128 MIDI, Receive Port ................................................. 96 Modulation Wheel — LFO Filter Modulation Depth ........................ 133 Modulation Wheel — LFO Pitch Modulation Depth ................. 112, 132 Mono/Poly Mode .......................................... 109, 136 MU100 Exclusive Voice ......................................... 30 Multi Edit mode .................................................... 100 Multi mode ............................................................. 85 Multi Mode Equalizer Lock ................................. 157 Mute ........................................................................ 85 Mute Lock ............................................................ 157 N Note Limit High ........................................... 110, 136 Note Limit Low ............................................ 110, 136 Note Shift (Multi mode) ......................................... 97 Note Shift (Performance mode) ............................ 130 O Others parameters ......................................... 107, 135 Output Select (Drum Setup) ................................. 118 Output Select (Multi mode) .................................. 113 Output Select Lock ............................................... 158 P Pan (Drum Setup) ................................................. 115 Pan (Multi mode) .................................................... 97 Pan (Performance mode) ...................................... 130 Part Assign ............................................................ 169 186 Part Mode ............................................................. 108 Parts, selecting ........................................................ 27 Performance Bank ................................................ 128 Performance Edit mode ........................................ 131 Performance mode .......................................... 43, 127 Performance Name ............................................... 132 Performance Number ............................................ 128 Performance Pan ................................................... 128 Performance Part control ...................................... 128 Performance Volume ............................................ 128 Performances, selecting Preset or Internal ............. 24 Pitch Bend Control ....................................... 111, 133 Pitch Coarse (Drum Setup) ................................... 115 Pitch EG ............................................................... 104 Pitch EG Attack Time ........................................... 104 Pitch EG Initial Level ........................................... 104 Pitch EG Release Level ........................................ 104 Pitch EG Release Time ......................................... 104 Pitch Fine (Drum Setup) ....................................... 115 Plugin ............................................ 119, 136, 147, 169 Portamento Switch ....................................... 109, 132 Portamento Time .......................................... 109, 132 Pressure Control Change Number ........................ 120 Pressure Control Depth ......................................... 120 Program (Voice) Number (Multi mode) ................. 96 Program (Voice) Number (Performance mode) ... 129 R Recall Function ..................................................... 140 Receive Bank Select ............................................. 158 Receive General MIDI Exclusive ......................... 158 Receive Note Off (Drum Setup) ........................... 118 Receive Note On (Drum Setup) ............................ 118 Receive System Exclusive .................................... 158 Resonance (LPF; Drum Setup) ............................. 116 Resonance (LPF; Multi mode) ............................. 101 Reverb ................................................................... 142 Reverb Pan ............................................................ 142 Reverb Return (Multi mode) .................................. 98 Reverb Return (Performance mode) ..................... 128 Reverb Send (Drum Setup) ................................... 115 Reverb Send (Multi mode) ..................................... 97 Reverb Send (Performance mode) ........................ 130 Reverb Type .......................................................... 142 S Scream Control Change Number ......................... 121 Scream Control Depth .......................................... 122 Send Chorus to Reverb ......................................... 133 Send Variation to Chorus ...................................... 145 Send Variation to Reverb ...................................... 145 Show Control Change ........................................... 173 Show Exclusive .................................................... 174 Single Part control (Multi mode) ............................ 33 Single Part control (Performance mode) .............. 129 Solo ......................................................................... 85 Sound Module mode ........................................ 6, 172 Store ...................................................................... 138 System connection ................................................ 153 System functions .................................................. 157 Appendix Index System MIDI Channel .......................................... 128 System Transpose ................................................. 129 T TG300B mode .......................................................... 6 Throat Formant Control Change Number ............ 123 Throat Formant Control Depth ............................. 123 Thru Port ............................................................... 159 Tonguing Control Change Number ...................... 121 Tonguing Control Depth ....................................... 121 Transpose ................................................................ 99 U Utility mode .......................................................... 156 V Variation ............................................................... 144 Variation Connection ............................................ 145 Variation Pan ........................................................ 145 Variation Return (Multi mode) ............................... 99 Variation Return (Performance mode) .................. 129 Variation Send (Drum Setup) ............................... 116 Variation Send (Multi mode) .................................. 97 Variation Send (Performance mode) .................... 130 Variation Type ....................................................... 144 Velocity LPF Cutoff Frequency ............................ 116 Velocity Limit High ...................................... 111, 136 Velocity Limit Low ....................................... 111, 136 Velocity Pitch Sensitivity ..................................... 115 Velocity Sensitivity Depth ............................ 110, 136 Velocity Sensitivity Offset ............................ 111, 136 Vibrato .......................................................... 106, 135 Vibrato Delay ........................................................ 106 Vibrato Depth ....................................................... 106 Vibrato Rate .......................................................... 106 Virtual Acoustic Synthesis ...................................... 62 VL Voice ................................................................. 62 VL Voice Part Parameters ..................................... 119 Vocoder Type ........................................................ 147 Voice Map ............................................................. 160 Voices, selecting ..................................................... 26 Volume (Multi mode) ............................................. 96 Volume (Performance mode) ........................ 128, 130 W WX Lip Mode ...................................................... 169 X XG mode ............................................................ 6, 26 Appendix 187 For details of products, please contact your nearest Yamaha or the authorized distributor listed below. Pour plus de détails sur les produits, veuillez-vous adresser à Yamaha ou au distributeur le plus proche de vous figurant dans la liste suivante. NORTH AMERICA CANADA Yamaha Canada Music Ltd. 135 Milner Avenue, Scarborough, Ontario, M1S 3R1, Canada Tel: 416-298-1311 U.S.A. Yamaha Corporation of America 6600 Orangethorpe Ave., Buena Park, Calif. 90620, U.S.A. Tel: 714-522-9011 MIDDLE & SOUTH AMERICA Die Einzelheiten zu Produkten sind bei Ihrer unten aufgeführten Niederlassung und bei Yamaha Vertragshändlern in den jeweiligen Bestimmungsländern erhältlich. Para detalles sobre productos, contacte su tienda Yamaha más cercana o el distribuidor autorizado que se lista debajo. ITALY Yamaha Musica Italia S.P.A., Combo Division Viale Italia 88, 20020 Lainate (Milano), Italy Tel: 02-935-771 SPAIN Yamaha-Hazen Electronica Musical, S.A. Jorge Juan 30, 28001, Madrid, Spain Tel: 91-577-7270 PORTUGAL Valentim de Carvalho CI SA Estrada de Porto Salvo, Paço de Arcos 2780 Oeiras, Portugal Tel: 01-443-3398/4030/1823 GREECE MEXICO Yamaha De Mexico S.A. De C.V., Departamento de ventas Javier Rojo Gomez No.1149, Col. Gpe Del Moral, Deleg. Iztapalapa, 09300 Mexico, D.F. Tel: 686-00-33 BRASIL Yamaha Musical Do Brasil LTDA. Ave. Reboucas 2636, São Paulo, Brasil Tel: 011-853-1377 Philippe Nakas S.A. Navarinou Street 13, P.Code 10680, Athens, Greece Tel: 01-364-7111 Yamaha De Panama S.A. Edificio Interseco, Calle Elvira Mendez no.10, Piso 3, Oficina #105, Ciudad de Panama, Panama Tel: 507-69-5311 OTHER LATIN AMERICAN COUNTRIES AND CARIBBEAN COUNTRIES Yamaha Music Latin America Corp. 6101 Blue Lagoon Drive, Miami, Florida 33126, U.S.A. Tel: 305-261-4111 EUROPE THE UNITED KINGDOM Yamaha-Kemble Music (U.K.) Ltd. Sherbourne Drive, Tilbrook, Milton Keynes, MK7 8BL, England Tel: 01908-366700 IRELAND Danfay Ltd. 61D, Sallynoggin Road, Dun Laoghaire, Co. Dublin Tel: 01-2859177 GERMANY/SWITZERLAND Yamaha Europa GmbH. Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen, F.R. of Germany Tel: 04101-3030 AUSTRIA Yamaha Music Austria Schleiergasse 20, A-1100 Wien Austria Tel: 01-60203900 Yamaha Scandinavia AB J. A. Wettergrens Gata 1 Box 30053 S-400 43 Göteborg, Sweden Tel: 031 89 34 00 YS Copenhagen Liaison Office Generatorvej 8B DK-2730 Herlev, Denmark Tel: 44 92 49 00 FINLAND Warner Music Finland OY/Fazer Music Aleksanterinkatu 11, P.O. Box 260 SF-00101 Helsinki, Finland Tel: 0435 011 BELGIUM Yamaha Music Belgium Keiberg Imperiastraat 8, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium Tel: 02-7258220 FRANCE Yamaha Musique France, Division Professionnelle BP 70-77312 Marne-la-Vallée Cedex 2, France Tel: 01-64-61-4000 Narud Yamaha AS Grini Næringspark 17 N-1345 Østerås, Norway Tel: 67 14 47 90 PT. Yamaha Music Indonesia (Distributor) PT. Nusantik Gedung Yamaha Music Center, Jalan Jend. Gatot Subroto Kav. 4, Jakarta 12930, Indonesia Tel: 21-520-2577 KOREA Cosmos Corporation #131-31, Neung-Dong, Sungdong-Ku, Seoul Korea Tel: 02-466-0021~5 Yamaha Music Malaysia, Sdn., Bhd. 16-28, Jalan SS 2/72, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia Tel: 3-717-8977 PHILIPPINES Yupangco Music Corporation 339 Gil J. Puyat Avenue, P.O. Box 885 MCPO, Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines Tel: 819-7551 SINGAPORE Yamaha Music Asia Pte., Ltd. Blk 17A Toa Payoh #01-190 Lorong 7 Singapore 1231 Tel: 354-0133 TAIWAN THAILAND Siam Music Yamaha Co., Ltd. 865 Phornprapha Building, Rama I Road, Patumwan, Bangkok 10330, Thailand Tel: 2-215-3443 ICELAND Skifan HF Skeifan 17 P.O. Box 8120 IS-128 Reykjavik, Iceland Tel: 525 5000 OTHER EUROPEAN COUNTRIES Yamaha Europa GmbH. Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen, F.R. of Germany Tel: 04101-3030 AFRICA Yamaha Corporation, International Marketing Division Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430 Tel: 053-460-2312 THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA AND OTHER ASIAN COUNTRIES Yamaha Corporation, International Marketing Division Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430 Tel: 053-460-2317 OCEANIA AUSTRALIA Yamaha Music Australia Pty. Ltd. 17-33 Market Street, South Melbourne, Vic. 3205, Australia Tel: 3-699-2388 NEW ZEALAND MIDDLE EAST TURKEY/CYPRUS Yamaha Europa GmbH. Siemensstraße 22-34, 25462 Rellingen, F.R. of Germany Tel: 04101-3030 OTHER COUNTRIES Yamaha Corporation, International Marketing Division Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430 Tel: 053-460-2312 HEAD OFFICE SY12 INDONESIA Kung Hsue She Trading Co., Ltd. No. 322, Section 1, Fu Hsing S. Road, Taipei 106, Taiwan. R.O.C. Tel: 02-709-1266 NORWAY THE NETHERLANDS Yamaha Music Nederland Kanaalweg 18G, 3526KL, Utrecht, The Netherlands Tel: 030-2828411 Tom Lee Music Co., Ltd. 11/F., Silvercord Tower 1, 30 Canton Road, Tsimshatsui, Kowloon, Hong Kong Tel: 730-1098 MALAYSIA SWEDEN DENMARK PANAMA ASIA HONG KONG Music Houses of N.Z. Ltd. 146/148 Captain Springs Road, Te Papapa, Auckland, New Zealand Tel: 9-634-0099 COUNTRIES AND TRUST TERRITORIES IN PACIFIC OCEAN Yamaha Corporation, International Marketing Division Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430 Tel: 053-460-2317 Yamaha Corporation, Electronic Musical Instrument Division Nakazawa-cho 10-1, Hamamatsu, Japan 430 Tel: 053-460-2445 VZ03920 708CMIT23.2-01AO M.D.G., EMI Division Yamaha Corporation 1997, Printed in Japan-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
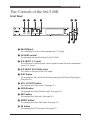 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
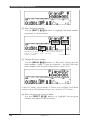 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
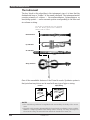 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
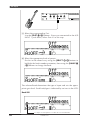 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
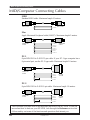 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
-
 161
161
-
 162
162
-
 163
163
-
 164
164
-
 165
165
-
 166
166
-
 167
167
-
 168
168
-
 169
169
-
 170
170
-
 171
171
-
 172
172
-
 173
173
-
 174
174
-
 175
175
-
 176
176
-
 177
177
-
 178
178
-
 179
179
-
 180
180
-
 181
181
-
 182
182
-
 183
183
-
 184
184
-
 185
185
-
 186
186
-
 187
187
-
 188
188
-
 189
189
-
 190
190
-
 191
191
-
 192
192
-
 193
193
-
 194
194
-
 195
195
-
 196
196
-
 197
197
-
 198
198
-
 199
199
-
 200
200
Yamaha MU100R El manual del propietario
- Categoría
- Sintetizador
- Tipo
- El manual del propietario
en otros idiomas
- français: Yamaha MU100R Le manuel du propriétaire
- italiano: Yamaha MU100R Manuale del proprietario
- English: Yamaha MU100R Owner's manual
- Deutsch: Yamaha MU100R Bedienungsanleitung
- русский: Yamaha MU100R Инструкция по применению
- Nederlands: Yamaha MU100R de handleiding
- português: Yamaha MU100R Manual do proprietário
- dansk: Yamaha MU100R Brugervejledning
- polski: Yamaha MU100R Instrukcja obsługi
- čeština: Yamaha MU100R Návod k obsluze
- svenska: Yamaha MU100R Bruksanvisning
- Türkçe: Yamaha MU100R El kitabı
- suomi: Yamaha MU100R Omistajan opas
- română: Yamaha MU100R Manualul proprietarului
Artículos relacionados
-
Yamaha MU5 Manual de usuario
-
Yamaha PLG100-VH El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha CBX-K1 El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha CBX-K3 El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha MU50 Manual de usuario
-
Yamaha TG300 El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha MU90R El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha VL70-m Manual de usuario
-
Yamaha CBX-T3 El manual del propietario
-
Yamaha TG300 El manual del propietario



















































































































































































































